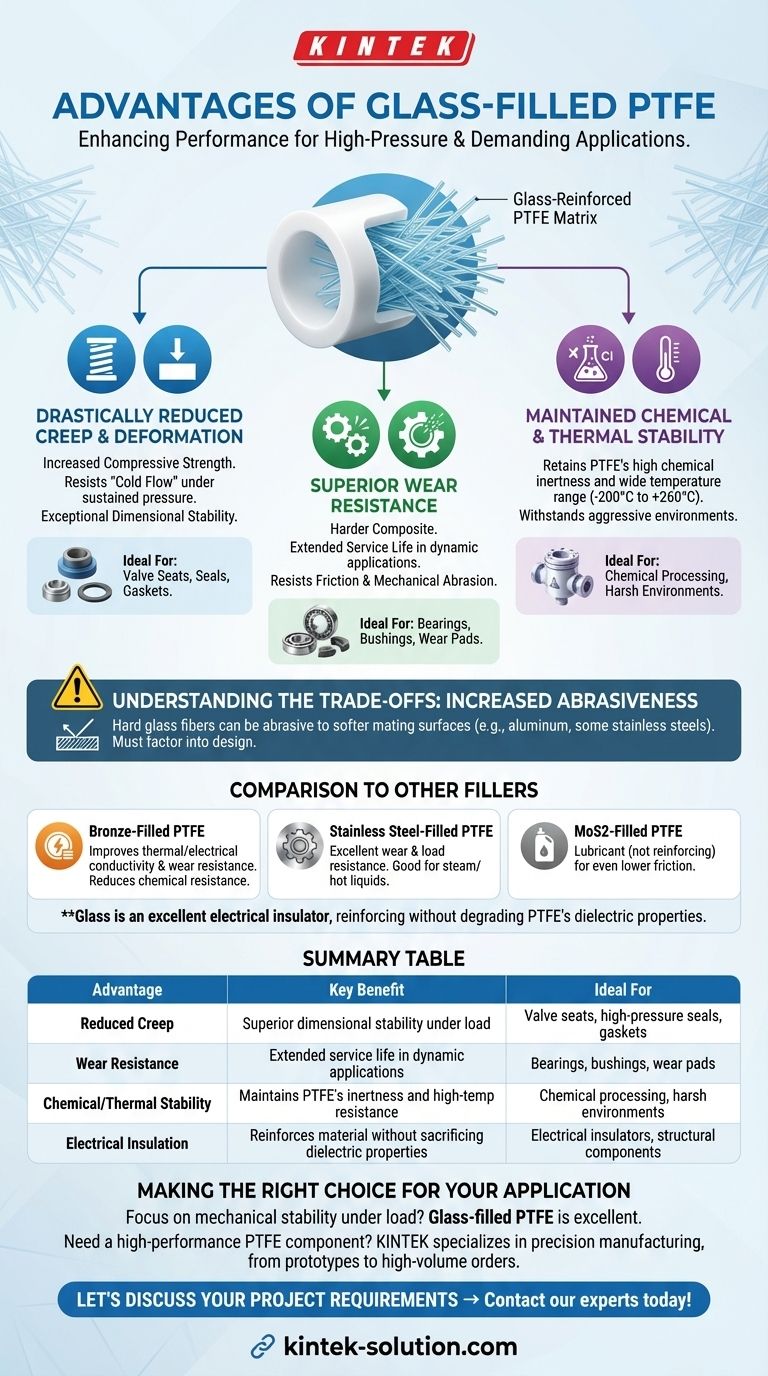
The primary advantages of using glass as a filler in Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are a significant increase in compressive strength and a marked improvement in resistance to wear and creep. This enhancement transforms the material, allowing it to perform reliably under higher pressures and in more demanding mechanical applications compared to its unfilled counterpart.
Adding glass fibers fundamentally transforms PTFE from a soft, low-friction polymer into a harder, more durable composite. While this greatly improves its mechanical properties for structural and high-pressure use, it comes at the cost of increased abrasiveness against mating surfaces.

Why Modify PTFE in the First Place?
The Strengths of Pure PTFE
Unfilled, or "virgin," PTFE is renowned for its exceptional properties. It possesses near-universal chemical resistance, an extremely wide operating temperature range (-200°C to +260°C), and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
The Limitations of Pure PTFE
The primary drawback of pure PTFE is that it is mechanically soft. Under sustained pressure or load, it is prone to creep, also known as "cold flow," where the material slowly and permanently deforms. This limits its use in applications requiring dimensional stability.
The Core Benefits of Glass-Filled PTFE
Drastically Reduced Creep and Deformation
Glass fibers act as a reinforcing skeleton within the PTFE matrix. This structure provides exceptional rigidity and dimensional stability, drastically reducing the tendency of the material to creep under mechanical load.
This makes glass-filled PTFE highly suitable for higher pressure applications such as valve seats, seals, and gaskets where maintaining shape is critical for performance.
Superior Wear Resistance
The hardness of the glass fibers provides a significant improvement in wear resistance compared to soft, unfilled PTFE. Components made from glass-filled PTFE will last longer in dynamic applications where they are subject to friction and mechanical abrasion.
Maintained Chemical and Thermal Stability
While reinforcing the material, glass filler does not compromise PTFE's inherent chemical inertness or its high-temperature resistance. This creates a composite material that can withstand both aggressive chemical environments and significant mechanical stress simultaneously.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Increased Abrasiveness
This is the most critical consideration when selecting glass-filled PTFE. The hard glass fibers can be abrasive to softer mating surfaces, such as aluminum or even some stainless steels. This must be factored into the design of the entire system to prevent premature wear on other components.
Comparison to Other Common Fillers
The choice of filler is entirely dependent on the application's demands.
- Bronze fillers also increase wear resistance but excel at improving thermal and electrical conductivity. However, they reduce PTFE's chemical resistance.
- Stainless steel fillers offer excellent wear and load resistance and perform well with steam or hot liquids.
- MoS2 (Molybdenum Disulfide) is not a reinforcing filler but a lubricant, added specifically to lower the coefficient of friction even further.
Maintained Electrical Insulation
Unlike metallic fillers such as bronze or stainless steel, glass is an excellent electrical insulator. Therefore, adding glass fibers reinforces the material without significantly degrading PTFE's excellent dielectric properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE formulation requires a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is mechanical stability under load: Glass-filled PTFE is an excellent choice for components like bearings, valve seats, and structural insulators that must resist deformation.
- If your primary focus is low friction against a soft mating surface: Unfilled PTFE or a MoS2-filled variant is a better option to prevent damaging the other component.
- If your primary focus is thermal or electrical conductivity: Bronze-filled PTFE should be your first consideration, but you must account for its reduced chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness with zero abrasion: Pure, unfilled PTFE remains the superior choice, provided the mechanical loads are low.
By understanding these material trade-offs, you can select the precise PTFE formulation that delivers optimal performance and longevity for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Creep | Superior dimensional stability under load | Valve seats, high-pressure seals, gaskets |
| Wear Resistance | Extended service life in dynamic applications | Bearings, bushings, wear pads |
| Chemical/Thermal Stability | Maintains PTFE's inertness and high-temp resistance | Chemical processing, harsh environments |
| Electrical Insulation | Reinforces material without sacrificing dielectric properties | Electrical insulators, structural components |
Need a high-performance PTFE component for a demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including glass-filled formulations, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a part that delivers optimal mechanical stability, wear resistance, and longevity for your specific challenge.
Let's discuss your project requirements → Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Conductive Glass Substrate Cleaning Rack
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















