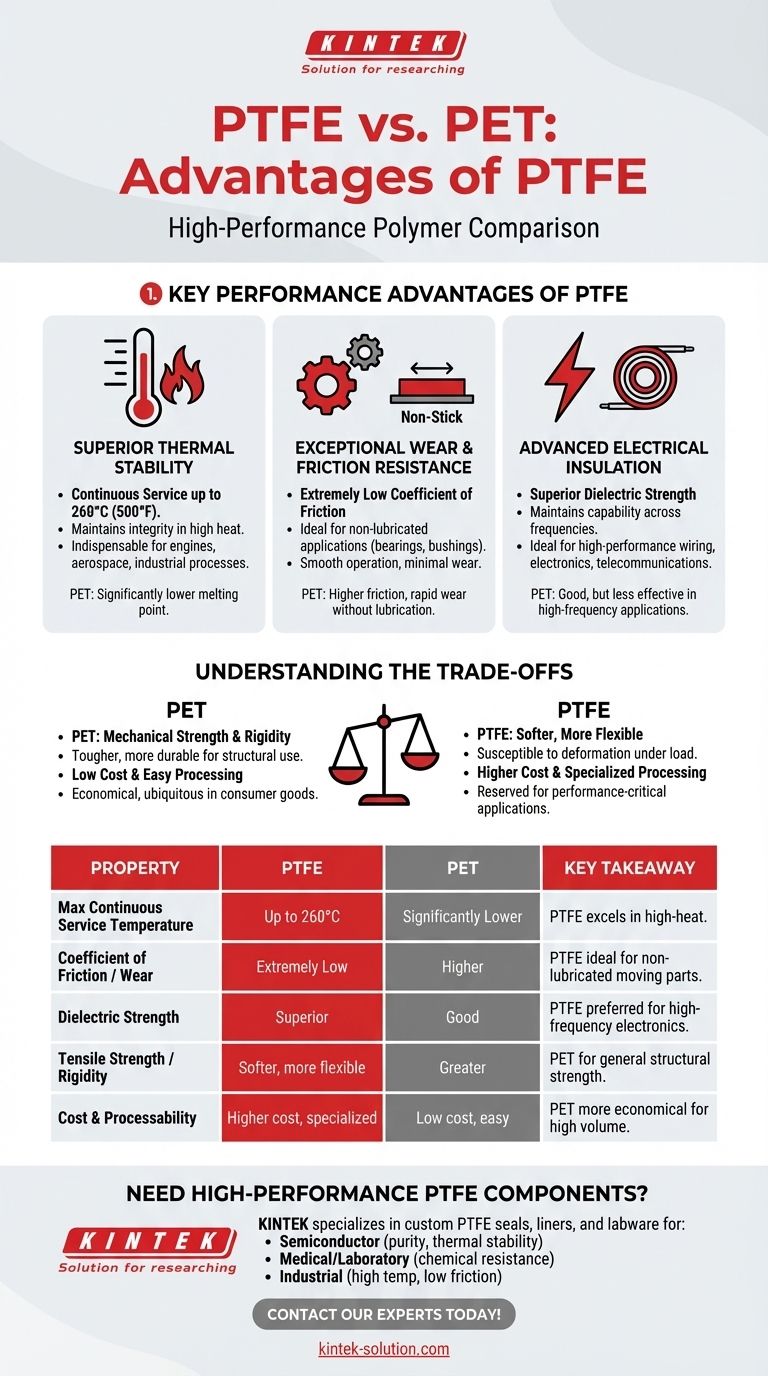
In a direct comparison, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers significant performance advantages over Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) in three critical areas: thermal stability, wear resistance, and electrical insulation. These characteristics make PTFE the superior choice for demanding engineering applications where PET would quickly fail.
The choice between PTFE and PET comes down to specialization versus versatility. While PET is a common, cost-effective material, PTFE is a high-performance polymer engineered for extreme conditions where heat, friction, and electrical integrity are the primary concerns.
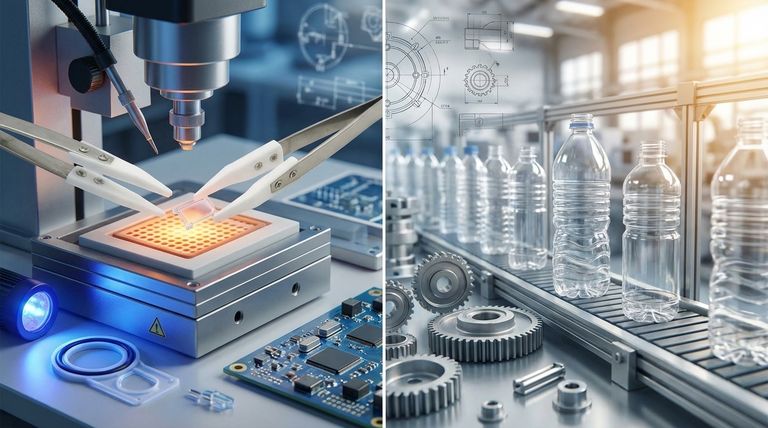

Key Performance Advantages of PTFE
PTFE's unique chemical structure gives it properties that PET cannot match. For engineers and designers, these differences are critical in selecting the right material for a specific, demanding context.
Superior Thermal Stability
PTFE demonstrates exceptional performance at high temperatures. It maintains its structural integrity and properties in continuous service up to 260°C (500°F).
This makes it indispensable for applications involving high heat, such as seals and gaskets in engines, high-temperature industrial processes, and components in aerospace systems. PET, by contrast, has a much lower melting point and would deform or degrade under similar conditions.
Exceptional Wear and Friction Resistance
One of PTFE's most famous attributes is its extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it a "non-stick" quality. This directly translates to superior wear resistance, especially in non-lubricated applications.
Components like bearings, bushings, and sliding plates made from PTFE can operate smoothly with minimal wear and no external lubrication. PET parts in the same scenario would generate more friction, heat, and wear out rapidly.
Advanced Electrical Insulation
PTFE possesses superior electrical insulating properties, also known as high dielectric strength. It maintains this capability across a wide range of frequencies.
This makes it an ideal material for high-performance wiring, cable insulation, and connectors in the electronics and telecommunications industries, where preventing signal loss and electrical interference is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE excels in these specialized areas, it is not a universal replacement for PET. Acknowledging the trade-offs is essential for making a sound engineering decision.
Mechanical Strength and Rigidity
PET generally offers greater tensile strength and rigidity compared to PTFE. It is a tougher, more durable material for structural components that do not face extreme temperatures or friction.
PTFE is a softer, more flexible material and can be susceptible to "creep" or deformation under sustained load.
Cost and Processability
There is a significant difference in cost and manufacturing complexity. PET is a commodity polymer that is inexpensive and very easy to process using standard methods like injection molding.
PTFE is a more expensive specialty polymer that requires specialized techniques for processing, which adds to the final component cost. This is why PET is ubiquitous in consumer goods and packaging, while PTFE is reserved for performance-critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be driven by the most critical performance requirement of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature environments or non-lubricated moving parts: PTFE is the definitive choice due to its thermal stability and inherently low-friction nature.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation for high-frequency electronics: PTFE's superior dielectric properties make it the clear and reliable winner.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness, mechanical strength, and ease of manufacturing for general use: PET provides an excellent balance of properties and is the more practical solution.
Understanding these core differences empowers you to select the polymer that precisely matches your application's unique performance demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | PET | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Continuous Service Temperature | Up to 260°C (500°F) | Significantly Lower | PTFE excels in high-heat environments. |
| Coefficient of Friction / Wear | Extremely Low | Higher | PTFE is ideal for non-lubricated moving parts. |
| Dielectric Strength (Electrical Insulation) | Superior | Good | PTFE is preferred for high-frequency electronics. |
| Tensile Strength / Rigidity | Softer, more flexible | Greater | PET offers better structural strength for general use. |
| Cost & Processability | Higher cost, specialized processing | Low cost, easy to process | PET is more economical for high-volume consumer goods. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for industries where performance under extreme conditions is non-negotiable.
- For the Semiconductor Industry: Our PTFE parts provide the ultimate purity and thermal stability required for sensitive processes.
- For Medical and Laboratory Applications: We deliver components that meet stringent standards for chemical resistance and reliability.
- For Industrial and Specialized Uses: We create solutions that withstand high temperatures, reduce friction, and ensure superior electrical insulation.
We partner with you from prototype to high-volume production, ensuring your components are engineered to excel. Let's discuss your specific requirements → Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















