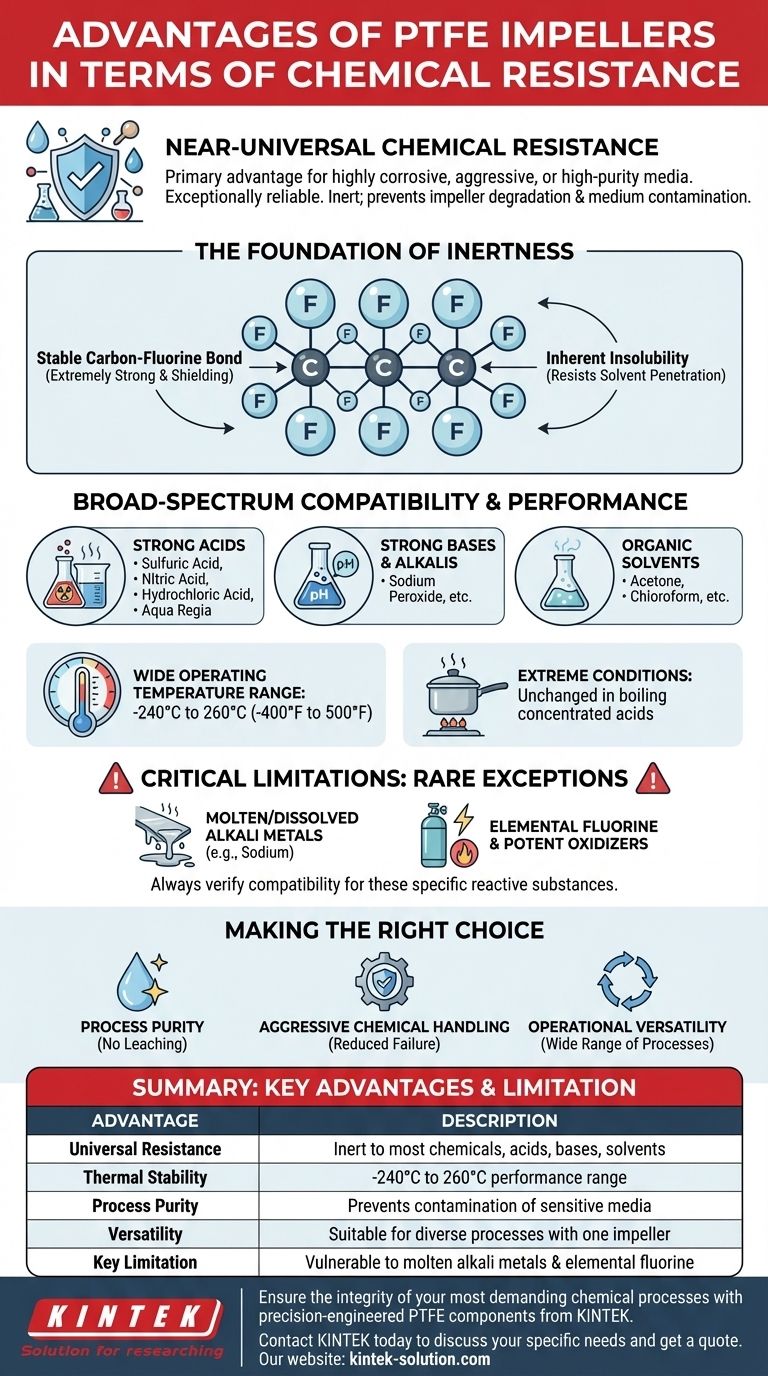
The primary advantage of PTFE impellers is their near-universal chemical resistance. This makes them exceptionally reliable for applications involving highly corrosive, aggressive, or high-purity media. PTFE is almost completely chemically inert, meaning it will not react with or degrade in the presence of nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and organic solvents.
The core value of PTFE's chemical resistance is not just its compatibility with a long list of substances, but its fundamental inertness. This ensures process integrity by preventing both impeller degradation and contamination of the medium being mixed.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with unique properties that make it one of the most chemically resistant materials known. Its performance stems directly from its molecular structure.
An Exceptionally Stable Molecular Structure
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms in PTFE is extremely strong and stable. This molecular backbone effectively shields the carbon chain from chemical attack, rendering the material non-reactive to most substances.
Inherent Insolubility
PTFE is highly insoluble in almost all solvents, especially at temperatures below 300°C (572°F). This prevents chemicals from penetrating and weakening the material, a common failure mode for less resistant plastics.
A Practical Guide to PTFE's Compatibility
In real-world applications, PTFE's chemical resistance provides a significant operational advantage, outperforming many other high-performance plastics like PEEK and Nylon.
Broad-Spectrum Resistance
PTFE impellers are virtually impervious to a vast range of chemicals. This includes common and aggressive substances such as:
- Strong Acids: Sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and even aqua regia.
- Strong Bases & Alkalis: Sodium peroxide and others.
- Organic Solvents: Acetone, chloroform, and nearly all others.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
The material's stability is maintained even under harsh operating conditions. PTFE remains unchanged when exposed to boiling concentrated acids, demonstrating its robustness for demanding chemical processes.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
PTFE's chemical resistance is complemented by its excellent thermal stability. It maintains its properties across a wide temperature range, typically from -240°C to 260°C (-400°F to 500°F), allowing it to be used in both cryogenic and high-temperature chemical applications.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
While its resistance is exceptional, no material is universally immune. Understanding PTFE's specific vulnerabilities is critical for safe and effective application.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
PTFE is known to react with a very small and specific group of highly reactive substances. These include:
- Molten or dissolved alkali metals (e.g., sodium).
- Elemental fluorine and related highly potent oxidizing agents.
Exposure to these specific chemicals can cause degradation and system failure. Always verify compatibility if your process involves these rare but potent substances.
Physical vs. Chemical Properties
It is important to distinguish between chemical resistance and mechanical properties. While chemically inert, PTFE is a relatively soft material. For applications involving high abrasion or significant physical stress, a different material or a lined-metal impeller might be a more suitable choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE impeller is a decision rooted in the chemical demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is process purity: PTFE is an excellent choice as its inertness ensures it will not leach contaminants into your medium.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE provides unmatched resistance to nearly all acids, bases, and solvents, reducing the risk of equipment failure and leaks.
- If your primary focus is operational versatility: A PTFE impeller allows you to use the same equipment for a wide variety of chemical processes without concerns about material compatibility.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE impeller provides a powerful guarantee of chemical compatibility for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Universal Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and organic solvents. |
| Exceptional Thermal Stability | Maintains performance from -240°C to 260°C (-400°F to 500°F). |
| Process Purity | Prevents contamination of sensitive or high-purity media. |
| Operational Versatility | Suitable for a wide range of chemical processes with one impeller. |
| Key Limitation | Vulnerable to a small group of highly reactive substances (e.g., molten alkali metals, elemental fluorine). |
Ensure the integrity of your most demanding chemical processes with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Our PTFE impellers, seals, liners, and labware are manufactured to the highest standards, providing the unmatched chemical resistance and process purity your applications require. Whether you need a custom prototype or a high-volume order for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, we deliver reliable solutions.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















