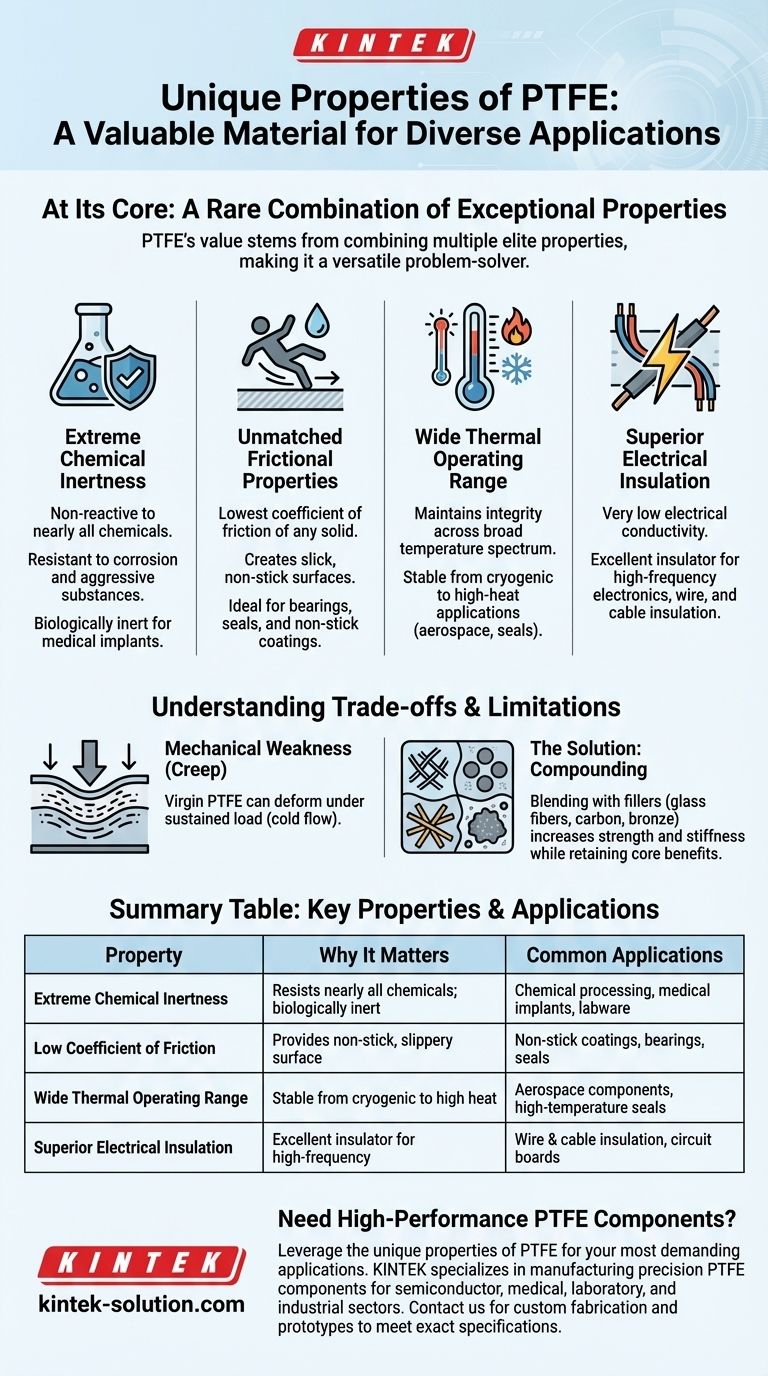
At its core, the value of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) stems from a rare combination of exceptional properties that few other materials can offer simultaneously. Its most unique characteristics are extreme chemical inertness, a very wide operating temperature range, an incredibly low coefficient of friction creating a non-stick surface, and excellent performance as an electrical insulator.
PTFE is not valuable for a single standout feature, but for its unique ability to combine multiple elite properties. This versatility makes it a go-to problem-solver in applications ranging from aerospace and chemical processing to medical implants and consumer cookware.

The Pillars of PTFE's Performance
To understand why PTFE is so widely used, we must look at how its core properties function in tandem. Each one addresses a specific and often critical engineering challenge.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The molecular structure of PTFE makes it non-reactive to nearly all chemicals. It is exceptionally resistant to corrosion and aggressive substances.
This property is fundamental to its use in harsh environments. It is used to create containers, gaskets, and pipework for handling chemicals that would degrade most other materials.
In a medical context, this translates to biological inertia. PTFE does not react with bodily fluids and elicits minimal tissue reaction, making it a trusted material for implants and medical devices.
Unmatched Frictional Properties
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid. This gives it an extremely slick, slippery, and non-stick surface.
This is the property behind its most famous application: non-stick coatings on cookware. It prevents materials from adhering to its surface.
Industrially, this low-friction quality is critical for components like bearings, seals, and conveyor systems, where reducing resistance and wear is paramount.
Wide Thermal Operating Range
PTFE maintains its structural integrity and core properties across an impressively broad spectrum of temperatures.
It has a very high melting point and thermal stability, allowing it to perform reliably in high-heat applications where other plastics would fail.
Simultaneously, it remains stable and functional at very low temperatures, making it suitable for cryogenic and aerospace applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE has very low electrical conductivity, which makes it an excellent electrical insulator.
This property is leveraged extensively in the electronics industry for insulating wires, cables, and other high-frequency components where signal integrity is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and objectivity requires acknowledging PTFE's limitations. Its primary weakness is mechanical, not chemical or thermal.
Mechanical Weakness (Creep)
Virgin PTFE is a relatively soft material that is subject to a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow.
This means that under a sustained load or constant pressure, the material can slowly deform or change shape over time, which can be an issue for certain structural applications.
The Solution: Compounding
To counteract this weakness, PTFE is often blended with other materials, creating what is known as a compound.
Adding fillers like glass fibers, carbon, or bronze can dramatically increase its strength, stiffness, and resistance to creep, all while retaining its primary benefits like chemical resistance and low friction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine which of PTFE's properties is most critical.
- If your primary focus is purity or handling aggressive chemicals: Rely on PTFE's extreme chemical and biological inertness.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction or creating a non-stick surface: Leverage its exceptionally low coefficient of friction.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme heat or cold: Its wide thermal operating range is its most valuable asset.
- If your primary focus is preventing electrical current flow: Its properties as a superior electrical insulator are key.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of properties ensures its role as a premier material for solving difficult engineering problems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all chemicals; biologically inert. | Chemical processing equipment, medical implants, labware. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Provides a non-stick, slippery surface. | Non-stick coatings, bearings, seals. |
| Wide Thermal Operating Range | Stable from cryogenic temperatures to high heat. | Aerospace components, high-temperature seals. |
| Superior Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator for high-frequency applications. | Wire & cable insulation, circuit boards. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Leverage the unique properties of PTFE for your most demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your project and discover how our PTFE solutions can solve your engineering challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















