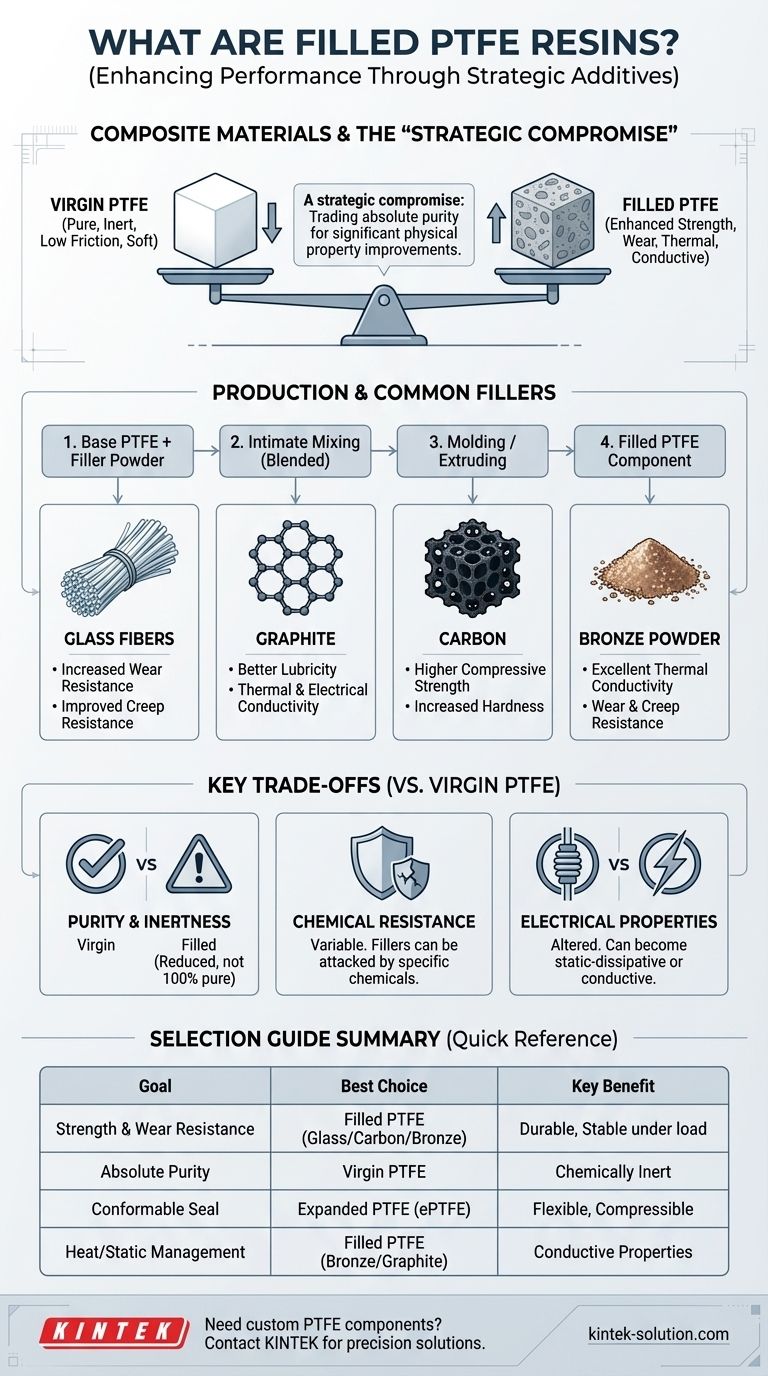
In short, filled PTFE resins are composite materials. They are created by mixing a base Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymer with specific additives, or "fillers," to enhance its physical properties. This process overcomes some of the inherent limitations of pure PTFE, such as its softness and tendency to deform under load.
The core concept to understand is that filled PTFE is a strategic compromise. By adding materials like glass, carbon, or metal powders, you trade the absolute purity and chemical inertness of virgin PTFE to gain significant improvements in wear resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal conductivity.

Why Fillers Are Added: Enhancing PTFE's Core Properties
To understand filled PTFE, you must first appreciate the characteristics of its pure, or "virgin," form and the specific problems fillers are meant to solve.
The Starting Point: Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is renowned for its extremely low friction, excellent chemical resistance, and high-purity insulating properties. However, it is also a relatively soft material that can suffer from creep, also known as "cold flow," where it slowly deforms under sustained pressure.
The Role of Common Fillers
Fillers are precisely chosen to counteract these weaknesses and add new capabilities. The base PTFE resin and the filler powder are blended together in a process called intimate mixing before being molded or extruded.
- Glass Fibers: These are the most common fillers. They dramatically increase wear resistance and creep resistance, making the material more durable and dimensionally stable under load.
- Graphite: Often combined with other fillers, graphite improves lubricity (reducing friction even further) and enhances wear properties. It also increases thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Carbon: Carbon, in fiber or powder form, significantly increases compressive strength and hardness. It provides good wear resistance and is chemically resistant.
- Powdered Metals (e.g., Bronze): Adding bronze powder drastically improves thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate quickly. It also offers excellent wear and creep resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not a universal upgrade. It involves a series of critical trade-offs that dictate where the material can be used.
Purity vs. Performance
The most significant trade-off is purity. The addition of any filler means the material is no longer 100% PTFE. This makes filled grades unsuitable for applications with stringent purity requirements, such as in the food, pharmaceutical, or high-purity semiconductor industries.
Chemical Resistance
While PTFE itself is nearly chemically inert, the fillers may not be. For example, glass fibers can be attacked by strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid. This means the overall chemical compatibility of the composite must be carefully evaluated for the specific application.
Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. Introducing conductive fillers like carbon or bronze powder fundamentally changes this property, transforming the material into one that is static-dissipative or even conductive.
How Filled PTFE Compares to Other Variants
The term "modified PTFE" can be confusing. Filled PTFE is just one of several common variations.
Filled vs. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Filled PTFE is a composite material where another substance is added. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE), however, is created by physically stretching virgin PTFE. This creates a microporous structure that is highly compressible and flexible, making it ideal for gaskets and seals.
Filled Resins vs. Fluoroadditives
Filled PTFE resins are bulk materials used to manufacture solid components like bearings, seals, or rings. Fluoroadditives, or PTFE micro powders, are low-molecular-weight PTFE used as an additive in other materials like inks, lubricants, and coatings to impart low-friction characteristics.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
Choosing the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: A filled PTFE with glass, carbon, or bronze is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity and broad chemical inertness: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the only option.
- If your primary focus is creating a conformable seal on an uneven surface: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) provides the necessary flexibility and compressibility.
- If your primary focus is managing heat or static electricity: A PTFE filled with bronze or graphite will provide the required thermal or electrical conductivity.
Ultimately, understanding that "PTFE" is a family of materials allows you to select the precise formulation engineered to solve your specific problem.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Primary Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fibers | Increases wear & creep resistance | Bearings, seals, bushings |
| Graphite | Improves lubricity & thermal conductivity | Self-lubricating parts, heat exchangers |
| Carbon | Enhances compressive strength & hardness | Pumps, valves, mechanical components |
| Bronze Powder | Boosts thermal conductivity & wear resistance | High-load, high-temperature applications |
Need a custom PTFE component engineered for your specific performance requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication capabilities—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get the exact filled or virgin PTFE material solution your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our tailored PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















