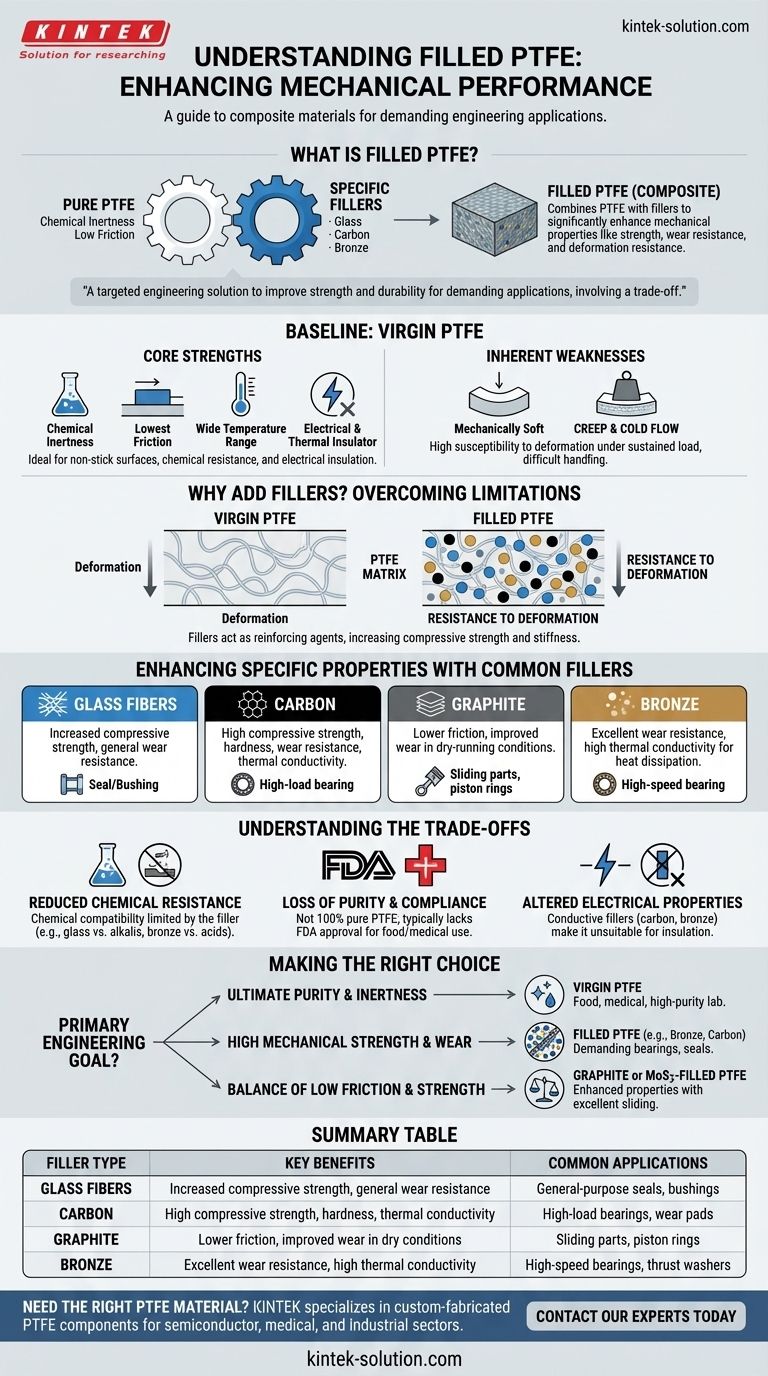
In essence, filled PTFE is a composite material created by adding specific fillers—like glass, carbon, or bronze—to pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This is done to significantly enhance mechanical properties such as strength, wear resistance, and resistance to deformation under load, which are inherent weaknesses of PTFE in its pure, or "virgin," form.
While virgin PTFE is prized for its extreme chemical inertness and low friction, it is mechanically soft. Adding fillers is a targeted engineering solution to improve its strength and durability for demanding applications, but this enhancement always involves a trade-off, typically in purity, chemical compatibility, or electrical properties.

First, Understand the Baseline: Virgin PTFE
The Core Strengths
Pure PTFE is a remarkable polymer with the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid, making it an ideal choice for non-stick surfaces and sliding applications.
It is virtually impervious to chemical attack and offers excellent performance across a wide range of temperatures. It is also a superb electrical and thermal insulator.
The Inherent Weaknesses
Despite its strengths, virgin PTFE is mechanically soft and pliable, which can make it difficult to handle during production and machining.
Its most significant drawback is a high susceptibility to creep and cold flow. This is the tendency for the material to deform permanently when subjected to a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures.
Why Add Fillers to PTFE?
To Overcome Mechanical Limitations
The primary purpose of adding fillers is to solve the problem of creep and cold flow.
Fillers act as a reinforcing agent within the soft PTFE matrix. This dramatically increases the material's compressive strength, stiffness, and ability to resist deformation under load.
To Enhance Specific Properties
Different fillers are chosen to impart specific characteristics tailored to the end-use application.
Glass fibers are a common, all-around choice for increasing compressive strength and general wear resistance.
Carbon significantly enhances compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance. It also improves thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-speed applications.
Graphite is often added to lower the coefficient of friction even further and improve wear properties, particularly in dry-running conditions.
Bronze provides excellent wear resistance and high thermal conductivity, making it a superior choice for applications that generate significant frictional heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Filled PTFE
Reduced Chemical Resistance
While pure PTFE is nearly inert, the fillers themselves are not. A filler like glass can be attacked by strong alkalis, and bronze can be attacked by various acids.
The overall chemical compatibility of the composite material is limited by the chemical resistance of its weakest component—the filler.
Loss of Purity and Compliance
The addition of any filler means the material is no longer 100% pure PTFE.
This is a critical factor for applications in food processing, medical devices, or pharmaceutical manufacturing. Virgin PTFE often carries FDA approval for these uses, whereas most filled grades do not.
Altered Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators available.
Adding conductive fillers like carbon or bronze fundamentally changes this property. The resulting composite becomes more electrically conductive, making it completely unsuitable for insulation applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and chemical inertness: Virgin PTFE is the only choice, essential for food, medical, and high-purity laboratory applications.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength and wear resistance: A filled PTFE is necessary. Choose bronze or carbon-filled grades for demanding bearing, seal, or bushing applications.
- If your primary focus is a balance of low friction and improved strength: Graphite-filled or MoS2-filled PTFE provides enhanced mechanical properties while maintaining excellent sliding characteristics.
By understanding the fundamental trade-off between PTFE's inherent properties and the targeted enhancements offered by fillers, you can make a precise and effective material decision for your project.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fibers | Increased compressive strength, general wear resistance | General-purpose seals, bushings |
| Carbon | High compressive strength, hardness, thermal conductivity | High-load bearings, wear pads |
| Graphite | Lower friction, improved wear in dry conditions | Sliding parts, piston rings |
| Bronze | Excellent wear resistance, high thermal conductivity | High-speed bearings, thrust washers |
Need the right PTFE material for your application? KINTEK specializes in custom-fabricated PTFE components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the ultimate purity of virgin PTFE or the enhanced mechanical properties of filled grades, our precision manufacturing ensures optimal performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















