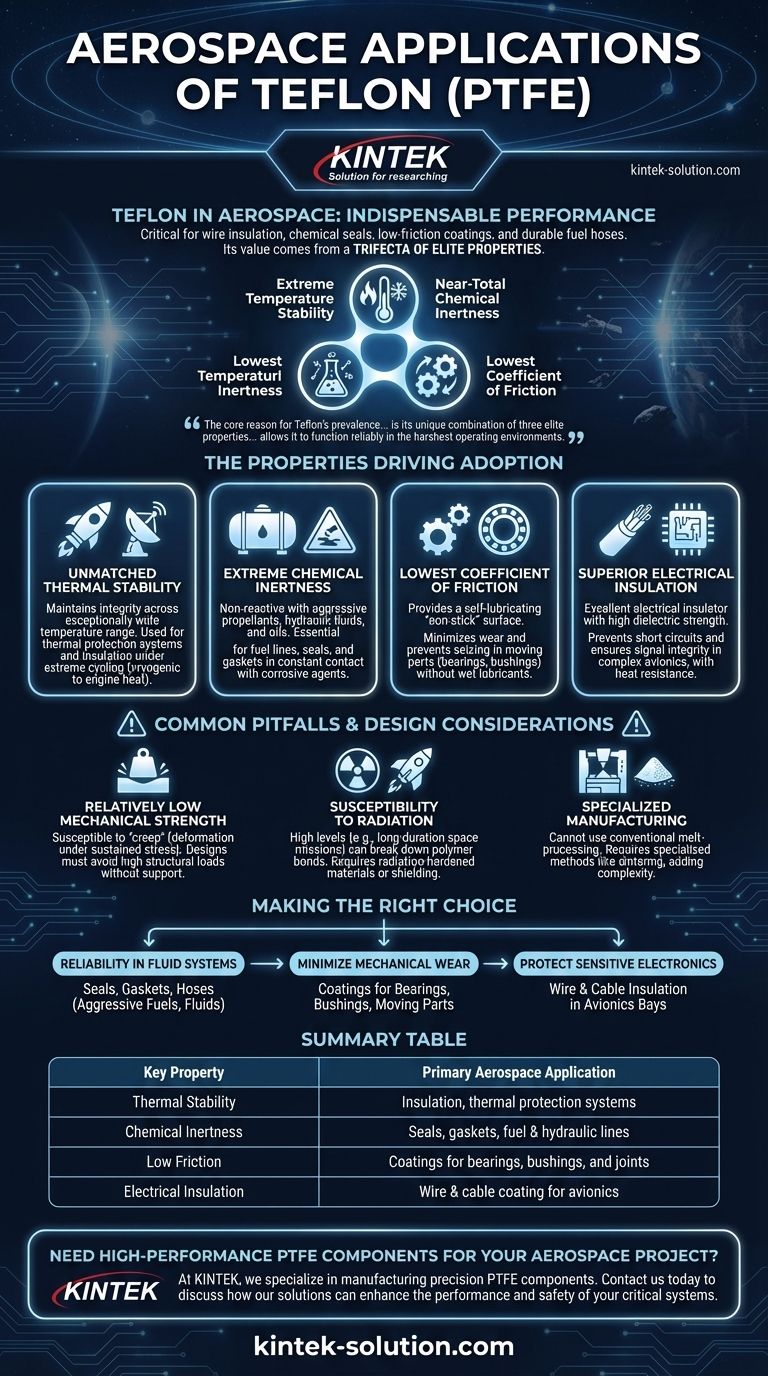
In the aerospace industry, Teflon is indispensable for a range of critical applications where performance and reliability are non-negotiable. It is most commonly used for high-performance wire and cable insulation, chemically resistant seals and gaskets, low-friction coatings for bearings and mechanical parts, and durable fuel hoses.
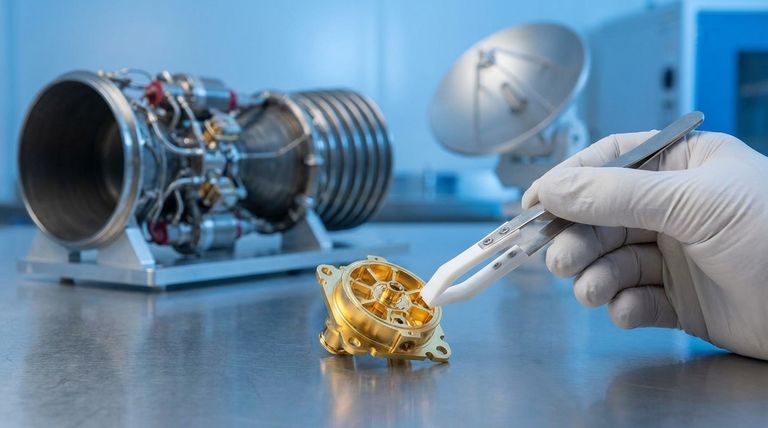
The core reason for Teflon's prevalence in aerospace is not a single feature, but its unique combination of three elite properties: extreme temperature stability, near-total chemical inertness, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This trifecta allows it to function reliably in the harshest operating environments imaginable.

The Properties Driving Aerospace Adoption
To understand where Teflon (PTFE) is used, you must first understand why it is selected over other materials. Its value is rooted in a few fundamental characteristics that make it uniquely suited for the demands of flight and space exploration.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Teflon maintains its structural integrity and performance across an exceptionally wide temperature range. It can withstand the cryogenic cold of deep space and the high temperatures generated within engine compartments or during atmospheric reentry.
This property makes it essential for components in thermal protection systems and as insulation that will not degrade under extreme thermal cycling.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
Teflon is non-reactive with nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This is a critical safety and reliability feature in aerospace.
It means Teflon can be used for fuel lines, seals, and gaskets that are in constant contact with aggressive rocket propellants, hydraulic fluids, and oils without degrading or failing.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
Known for its "non-stick" quality, Teflon provides a self-lubricating surface that minimizes friction between moving parts. This significantly reduces wear and tear and prevents components from seizing up.
This property is leveraged by applying Teflon coatings to bearings, bushings, and other mechanical joints, especially in situations where traditional wet lubricants are impractical or could fail.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Teflon is an excellent electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength. It does not conduct electricity, making it an ideal material for protecting wiring.
This is why it is the material of choice for coating wires and cables in complex avionics systems, where it prevents short circuits and ensures signal integrity while also providing heat resistance.
Common Pitfalls and Design Considerations
While its properties are exceptional, Teflon is not a universal solution. Engineers must account for its specific limitations to ensure system integrity.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or other engineering plastics, Teflon is relatively soft and can be susceptible to "creep"—the tendency to deform slowly under sustained mechanical stress.
Designs must account for this by ensuring components are not subjected to high structural loads without proper support.
Susceptibility to Radiation
In long-duration space missions outside of Earth's protective magnetosphere, high levels of radiation can cause the bonds in the Teflon polymer to break down over time.
For missions with high radiation exposure, engineers may need to select radiation-hardened materials or provide adequate shielding for critical Teflon components.
Specialized Manufacturing Processes
Teflon cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like many other thermoplastics. It requires specialized methods like sintering, which can add complexity and cost to manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material is paramount in aerospace engineering. Teflon's use cases are distinct and are driven by its core strengths.
- If your primary focus is reliability in fluid systems: Teflon's chemical inertness makes it the definitive choice for seals, gaskets, and hoses exposed to aggressive fuels and hydraulic fluids.
- If your primary focus is minimizing mechanical wear without wet lubricants: Its exceptionally low coefficient of friction is ideal for coating bearings, bushings, and other moving parts that must operate smoothly in a vacuum or at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive electronics: Its high-performance dielectric properties and thermal stability are critical for insulating wires and cables in dense, high-temperature avionics bays.
Ultimately, Teflon's unique combination of properties ensures operational integrity in environments where failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Aerospace Application |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Insulation, thermal protection systems |
| Chemical Inertness | Seals, gaskets, fuel & hydraulic lines |
| Low Friction | Coatings for bearings, bushings, and joints |
| Electrical Insulation | Wire & cable coating for avionics |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Aerospace Project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the demanding semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get parts that meet the rigorous standards of aerospace reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the performance and safety of your critical systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















