In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is commonly used in a wide range of medical devices, particularly for components that require extreme chemical resistance, low friction, and high purity. You will find it in critical parts of heart-lung machines, as seals in fluid pumping systems, and as plungers in syringes.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use in medicine is its unique combination of properties: it is nearly frictionless, chemically inert to almost all substances, and maintains its integrity across a wide range of temperatures, making it a highly reliable and safe material for critical applications.

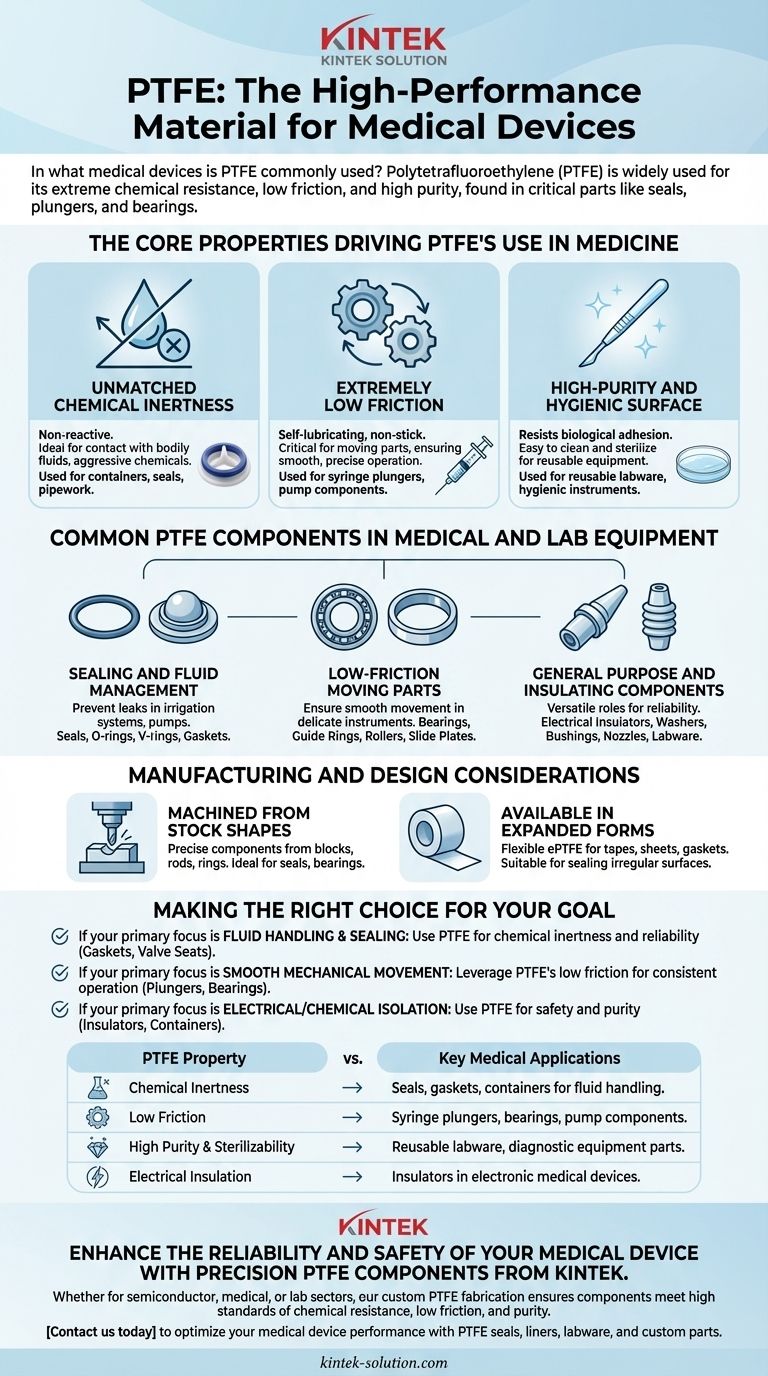
The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Use in Medicine
To understand where PTFE is used, it's essential to understand why it is chosen. Its selection is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of its fundamental material characteristics.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is renowned for its non-reactive nature. This makes it an ideal material for any component that comes into contact with bodily fluids, aggressive cleaning agents, or reactive chemicals used in laboratory settings.
It is frequently used for containers, seals, and pipework that transport these sensitive or corrosive materials, ensuring no contamination or material degradation occurs.
Extremely Low Friction
The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, giving it a trademark "non-stick" or self-lubricating quality.
This property is critical for devices with moving parts, such as syringe plungers, pump components, and sample transport mechanisms, where smooth, consistent, and frictionless movement is necessary for precise operation.
High-Purity and Hygienic Surface
Because PTFE is so non-reactive and non-stick, it creates a surface that is difficult for biological materials to adhere to.
This makes components easy to clean and sterilize, a non-negotiable requirement for hygienic instruments and reusable medical equipment.
Common PTFE Components in Medical and Lab Equipment
PTFE is rarely the primary structural material of a large device. Instead, it is machined into specific, high-performance components that enable the function of the larger assembly.
Sealing and Fluid Management
A majority of PTFE's medical applications involve controlling the flow of liquids and gases. Its ability to create a durable, chemically resistant seal is invaluable.
Common components include seals, O-rings, V-rings, gaskets, and ball valve seats. These are found in irrigation systems, diagnostic equipment, and chemical transport pumps where preventing leaks is critical.
Low-Friction Moving Parts
For mechanical reliability in delicate instruments, PTFE is the material of choice for parts that slide or rotate against each other.
You will find it used as bearings, guide rings, rollers, and slide plates in rotary tools and other precision equipment.
General Purpose and Insulating Components
Beyond its primary roles, PTFE's versatility allows it to be used for a variety of other essential parts.
Its excellent dielectric properties make it a superior electrical insulator for complex electronic medical devices. It is also machined into washers, bushings, nozzles, and various custom labware.
Manufacturing and Design Considerations
While incredibly versatile, PTFE presents certain practical considerations that are important to understand. It is not a material that is easily injection molded like many common plastics.
Machined from Stock Shapes
Most PTFE medical components are machined or compression molded from standard stock shapes like blocks, rods, and rings.
This manufacturing process is ideal for producing high-precision parts like seals and bearings but can influence the complexity and cost of the final component design.
Available in Expanded Forms
In addition to solid components, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is formed into flexible materials like tapes, sheets, and joint sealants.
These forms offer the same chemical and thermal benefits but with added flexibility, making them suitable for creating custom gaskets and sealing irregular surfaces in medical equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use PTFE should be driven by the specific performance requirements of your medical device component.
- If your primary focus is fluid handling and sealing: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for gaskets, O-rings, and valve seats due to its chemical inertness and reliability.
- If your primary focus is smooth mechanical movement: Leverage PTFE's extremely low friction for components like syringe plungers, bearings, and guide rings to ensure consistent, effortless operation.
- If your primary focus is electrical or chemical isolation: Use PTFE for insulators or containers where its dielectric properties and non-reactive nature are critical for safety and purity.
By understanding these applications, you can leverage PTFE's unique properties to enhance the reliability and safety of your medical device design.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Property | Key Medical Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Seals, gaskets, containers for fluid handling |
| Low Friction | Syringe plungers, bearings, pump components |
| High Purity & Sterilizability | Reusable labware, diagnostic equipment parts |
| Electrical Insulation | Insulators in electronic medical devices |
Enhance the reliability and safety of your medical device with precision PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether you're designing for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom PTFE fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your components meet the highest standards of chemical resistance, low friction, and purity.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom parts can optimize your medical device performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















