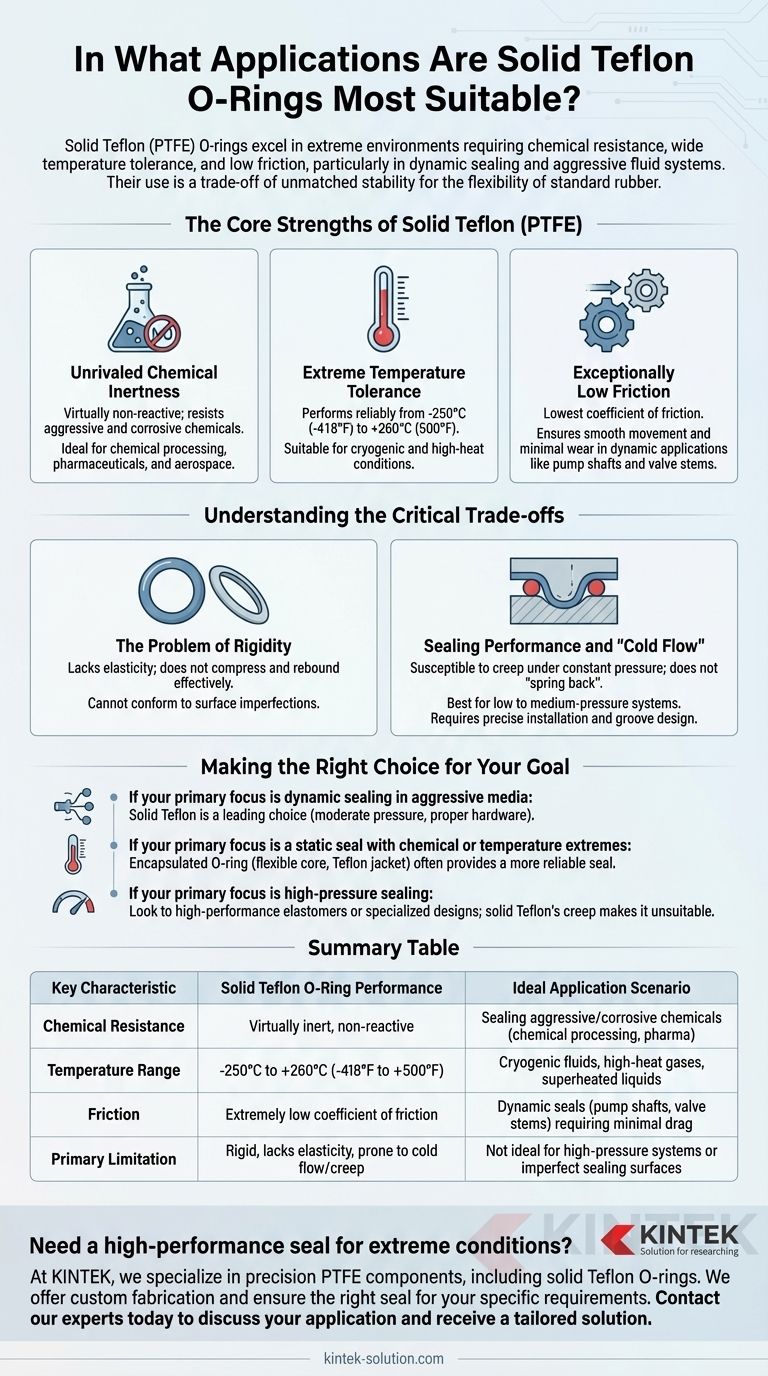
At their best, solid Teflon (PTFE) O-rings are used in applications that demand extreme chemical resistance, a wide temperature tolerance, and very low friction. They excel in dynamic sealing scenarios where parts slide against each other, as well as in systems handling aggressive fluids or operating at cryogenic or high-heat levels where traditional elastomers would fail.
The core decision to use a solid Teflon O-ring is a trade-off. You are choosing its unmatched chemical and thermal stability at the direct expense of the flexibility and resilient sealing power found in standard rubber O-rings.

The Core Strengths of Solid Teflon (PTFE)
Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
Solid Teflon is virtually non-reactive, making it the ideal choice for sealing systems that process aggressive or corrosive chemicals. Its material integrity is not compromised by exposure to a vast range of industrial fluids.
This property makes it indispensable in industries like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace, where seal failure due to chemical attack is not an option.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
PTFE O-rings perform reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows of -250°C (-418°F) up to high-heat conditions of +260°C (500°F).
This makes them suitable for sealing systems involving heated gases, superheated liquids, or cryogenic fluids where conventional elastomers would become brittle or degrade.
Exceptionally Low Friction
Teflon possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. Its non-stick surface ensures smooth movement and minimal wear in dynamic applications.
This is critical for components like pump shafts, valve stems, and pistons that require a durable seal with minimal drag to operate efficiently and reliably over time.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The Problem of Rigidity
The primary drawback of solid Teflon is its lack of elasticity. Unlike rubber, it is a rigid material that does not compress and rebound effectively.
This inherent stiffness means it cannot easily conform to surface imperfections in a gland or groove, potentially compromising the seal.
Sealing Performance and "Cold Flow"
Because it lacks memory, a solid Teflon O-ring does not "spring back" after being compressed. It is susceptible to a phenomenon called creep or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms under constant pressure.
This limits its effectiveness in applications requiring significant compression for a tight seal, especially under low or fluctuating pressure. It is best suited for low to medium-pressure systems.
Installation and Groove Design
The rigidity of solid Teflon O-rings can make installation challenging, as they cannot be easily stretched over components.
Effective sealing often requires a precisely machined groove and careful installation to ensure the O-ring is properly seated and energized without being damaged.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a solid Teflon O-ring is correct for your purpose, you must weigh its distinct advantages against its significant limitations.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing in aggressive media: Solid Teflon is a leading choice, provided pressures are moderate and the hardware is designed to accommodate a rigid seal.
- If your primary focus is a static seal with chemical or temperature extremes: An encapsulated O-ring, which combines a flexible core with a Teflon jacket, often provides a more reliable seal.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing: You should look to high-performance elastomers or specialized seal designs, as solid Teflon's tendency to creep makes it unsuitable.
Ultimately, choosing a solid Teflon O-ring is a deliberate engineering decision that prioritizes its exceptional resistance and low friction over the flexibility of traditional elastomers.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Solid Teflon O-Ring Performance | Ideal Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Virtually inert, non-reactive | Sealing aggressive/corrosive chemicals (chemical processing, pharma) |
| Temperature Range | -250°C to +260°C (-418°F to +500°F) | Cryogenic fluids, high-heat gases, superheated liquids |
| Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction | Dynamic seals (pump shafts, valve stems) requiring minimal drag |
| Primary Limitation | Rigid, lacks elasticity, prone to cold flow/creep | Not ideal for high-pressure systems or imperfect sealing surfaces |
Need a high-performance seal for extreme conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including solid Teflon O-rings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the right seal for your specific chemical, temperature, and friction requirements.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing a perfect fit and reliable performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















