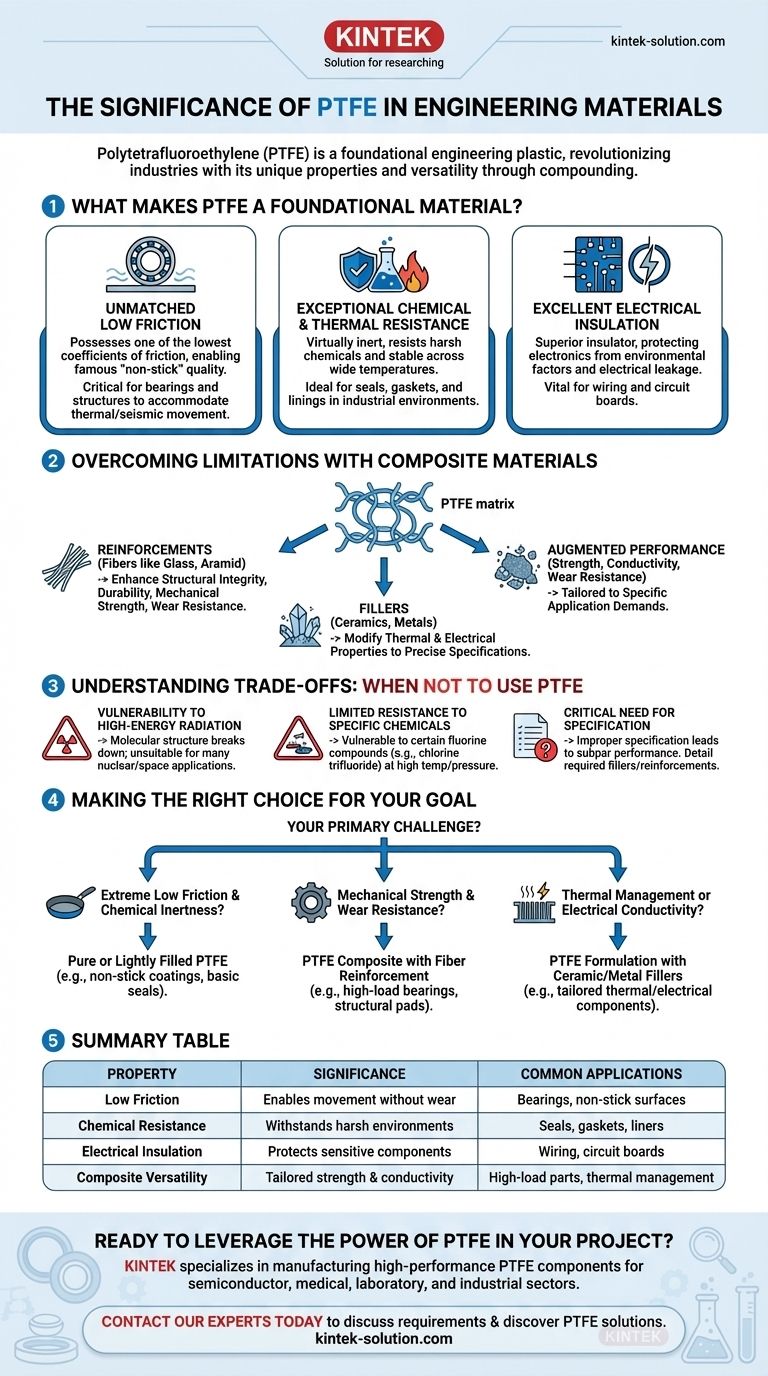
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most significant and indispensable engineering plastics in modern industry. Its unique combination of extremely low friction, broad chemical and thermal resistance, and excellent electrical insulation has made it a foundational material that has revolutionized countless applications, from aerospace and electronics to large-scale civil engineering projects.
At its core, the significance of PTFE lies in its unparalleled versatility. While its base properties are remarkable, its true power is unlocked when it is compounded with fillers and reinforcements, allowing engineers to tailor its performance to overcome its natural limitations for highly specific, demanding applications.

What Makes PTFE a Foundational Engineering Material?
The value of PTFE stems from a distinct set of properties that are difficult to find in a single material. These characteristics make it a default choice for solving many complex engineering challenges.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material, giving it its famous "non-stick" quality.
This property is critical in applications like bearing pads for bridges and buildings, allowing massive structures to accommodate thermal expansion and seismic movement without generating destructive stress.
Exceptional Chemical and Thermal Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and non-corrosive, capable of resisting attack from a vast range of aggressive chemicals.
Combined with its stability across a wide temperature range, this makes it ideal for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing and other harsh industrial environments.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a superior electrical insulator, PTFE is vital in electronics and electrical engineering.
It protects sensitive components from environmental factors and prevents electrical leakage, ensuring the reliability and longevity of everything from wiring to complex circuit boards.
Overcoming Limitations with Composite Materials
While pure PTFE is powerful, its true engineering potential is realized when it is used as a base matrix for composite materials. This approach enhances its properties to meet specific performance demands.
The Role of the PTFE Matrix
In a composite, PTFE serves as the matrix that holds everything together. Its inherent non-stick and resistant properties form the foundation of the final material's performance.
Introducing Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers are additives blended into the PTFE matrix to augment its natural characteristics. They can dramatically improve mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal or electrical conductivity.
Common reinforcements include fibers like glass or aramid, which add structural integrity and durability. Fillers such as ceramics or metals are used to modify the thermal and electrical properties to precise specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Not to Use PTFE
Despite its versatility, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its inherent limitations is crucial for successful application and avoiding material failure.
Vulnerability to High-Energy Radiation
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, which can cause its molecular structure to break down. This makes it unsuitable for many nuclear and space applications without proper shielding.
Limited Resistance to Specific Chemicals
While broadly inert, PTFE is vulnerable to a handful of highly reactive chemicals. These include certain fluorine compounds like chlorine trifluoride and xenon difluoride, especially under high pressure and temperature.
The Critical Need for Specification
A common point of failure is improper material specification. Simply requesting "PTFE" without detailing the required fillers or reinforcements can lead to subpar performance.
If specifications are not provided, a fabrication house may use its standard stock material, which may not meet the mechanical, thermal, or electrical demands of your specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE formulation is about matching the material's properties to the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme low friction and chemical inertness: A pure or lightly filled PTFE is often the most effective and economical choice for applications like non-stick coatings or basic seals.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: A PTFE composite with glass or aramid fiber reinforcement is necessary for components like high-load bearings, piston rings, and structural pads.
- If your primary focus is thermal management or electrical conductivity: Specify a PTFE formulation with ceramic or metal fillers designed to achieve the precise thermal or electrical properties your application requires.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's core strengths and how to augment them is key to leveraging this remarkable material effectively.
Summary Table:
| Property | Significance | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Friction | Enables movement without wear | Bearings, non-stick surfaces |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands harsh environments | Seals, gaskets, liners |
| Electrical Insulation | Protects sensitive components | Wiring, circuit boards |
| Composite Versatility | Tailored strength & conductivity | High-load parts, thermal management |
Ready to leverage the power of PTFE in your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a standard solution or a custom-fabricated part from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures you get the precise material formulation and performance your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our PTFE solutions can solve your toughest engineering challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















