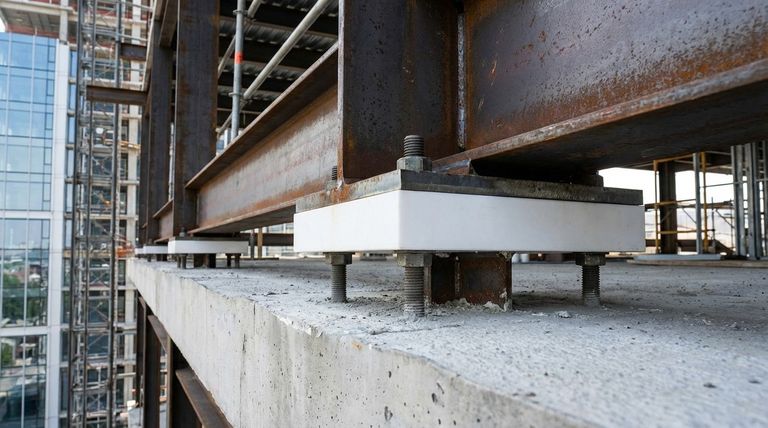
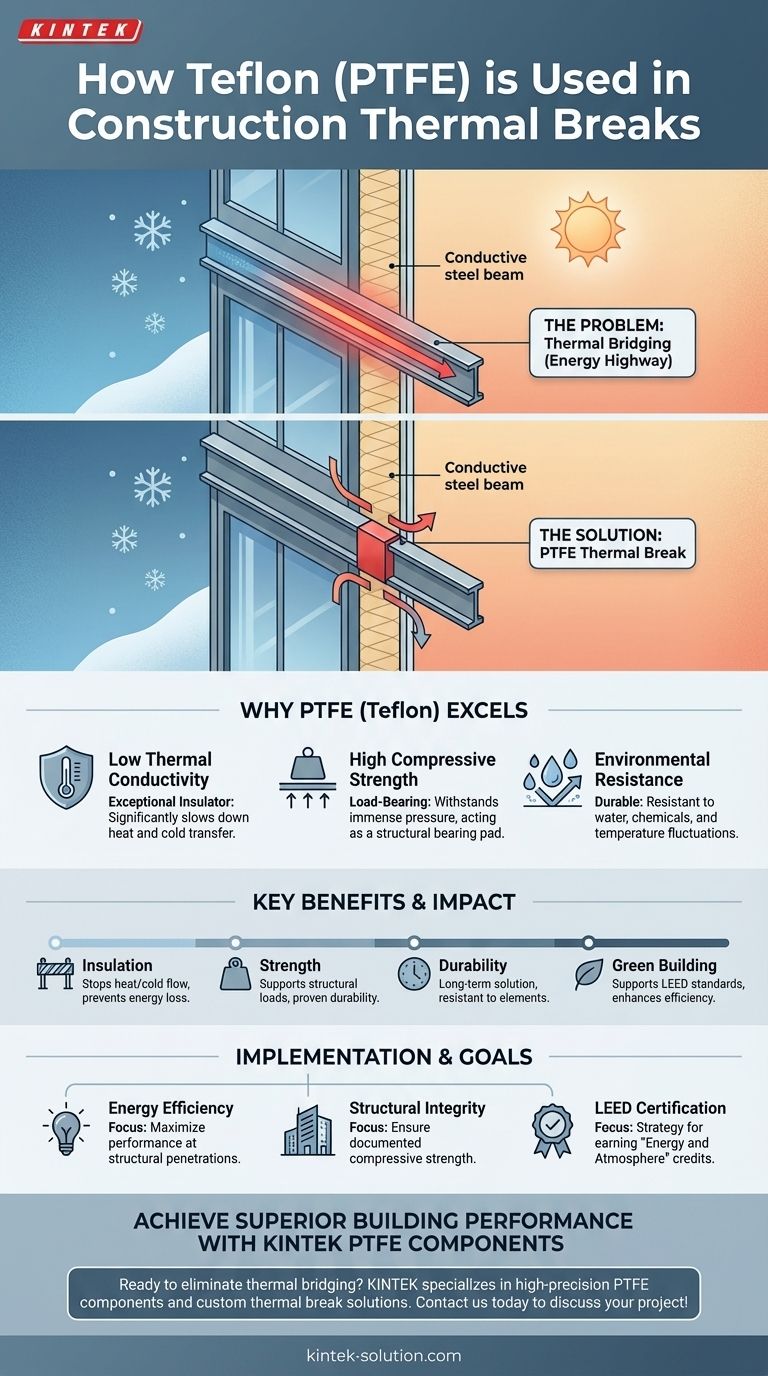
In modern construction, Teflon is used as a high-performance insulating material within structural thermal breaks. Specifically, materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) are fabricated into pads or sheets that are placed between conductive structural elements, such as steel beams, to stop the unwanted transfer of heat and cold. This application is crucial for creating energy-efficient buildings that meet modern environmental standards like LEED.
The core function of Teflon in a thermal break is to provide a durable, load-bearing insulating barrier between structural components. This prevents conductive materials from creating an energy-draining "highway" for heat or cold, severing the path of thermal bridging.

The Problem: Understanding Thermal Bridging
What is a Thermal Bridge?
A thermal bridge is a pathway of high thermal conductivity that allows heat to flow across a thermal barrier. Think of a metal spoon left in a mug of hot coffee—the handle quickly becomes hot because the metal efficiently conducts heat from the liquid.
In a building, structural steel beams, concrete slabs, or metal window frames can act just like that spoon, creating a bridge that bypasses the building's insulation.
The Impact on Building Performance
These bridges compromise a building's energy efficiency, leading to higher heating and cooling costs. They can also create cold spots on interior surfaces, which may lead to moisture condensation, occupant discomfort, and potential mold growth over time.
Why Teflon (PTFE) Excels as a Thermal Break
Exceptional Insulating Properties
The primary reason for using Teflon, most often in the form of PTFE, is its low thermal conductivity. It is a highly effective insulator that significantly slows down the transfer of thermal energy.
By placing a PTFE pad between two steel beams, you effectively sever the thermal bridge, forcing heat to travel through the insulating material instead of the highly conductive steel.
High Compressive Strength and Durability
Unlike many common insulators, PTFE can withstand immense pressure without being crushed. This high compressive strength allows it to be used in load-bearing structural connections.
It serves not just as an insulator but also as a structural bearing pad, safely transferring loads between elements while preventing direct metal-to-metal contact.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
As noted in construction applications, PTFE is highly resistant to water, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. This ensures the thermal break will not degrade over the lifetime of the building, providing a reliable, long-term solution.
Key Considerations for Implementation
Choosing the Right Material
While "Teflon" is a common brand name, the specific materials used are typically PTFE or FEP. PTFE is the most common choice for structural thermal breaks due to its superior mechanical and thermal properties.
The Importance of Proper Installation
The effectiveness of a thermal break depends entirely on its correct placement and installation. It must be integrated seamlessly into the structural connection to ensure both thermal separation and load transfer are handled as designed.
Aligning with Modern Building Standards
The increasing adoption of PTFE thermal breaks is directly linked to the push for more sustainable building practices. Meeting standards like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) often requires a meticulous approach to eliminating thermal bridging, making these components essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency: Specify thermal breaks at all major structural penetrations of the building envelope, particularly steel-to-steel and steel-to-concrete connections.
- If your primary focus is long-term structural integrity: Ensure the specified PTFE material has the documented compressive strength and durability to handle the calculated structural loads for the life of the building.
- If your primary focus is achieving LEED certification: Incorporating high-performance thermal breaks is a clear strategy for earning points in the "Energy and Atmosphere" credit category.
By strategically severing these hidden energy highways, you ensure the building performs as designed.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit of PTFE Thermal Breaks | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Thermal Conductivity | Acts as a highly effective insulator to stop heat/cold transfer through structural elements. |
| High Compressive Strength | Withstands immense structural loads while functioning as a bearing pad. |
| Environmental Resistance | Resistant to water, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations for long-term durability. |
| Supports Green Building | Essential for meeting modern energy standards like LEED certification. |
Achieve Superior Building Performance with KINTEK PTFE Components
Ready to eliminate thermal bridging and enhance your building's energy efficiency? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom thermal break pads and sheets, for the construction industry.
We understand the critical balance between structural integrity and thermal performance. Our PTFE components are engineered to provide:
- Reliable Insulation: Precisely fabricated to stop thermal bridging in steel-to-steel and steel-to-concrete connections.
- Proven Durability: Manufactured to withstand specific structural loads and environmental conditions.
- Custom Solutions: From prototype development to high-volume production, we tailor our fabrication to your project's exact requirements.
Don't let thermal bridging compromise your design. Contact KINTEPT today to discuss your project needs and request a quote for custom PTFE thermal break solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















