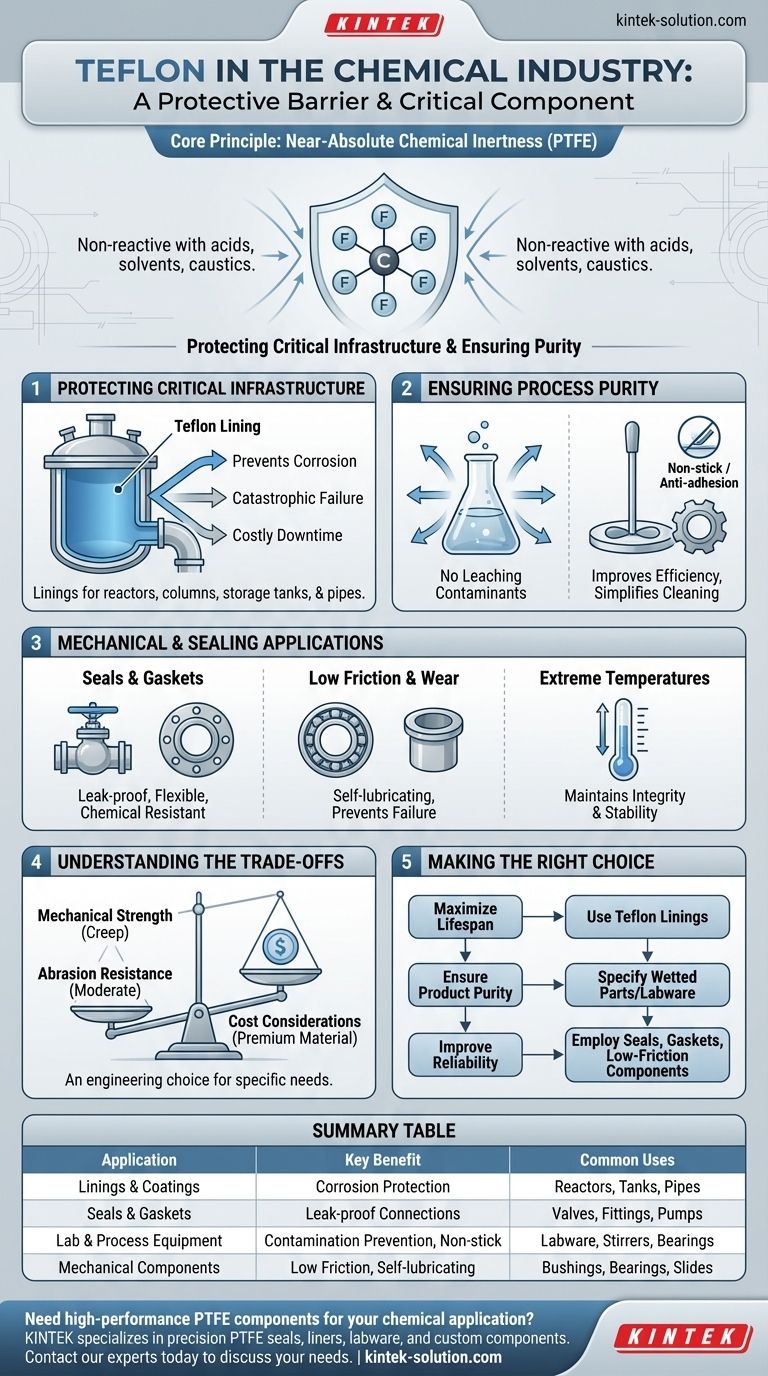
In the chemical industry, Teflon is primarily used as a protective barrier and a critical component material in environments where extreme chemical resistance is required. It is applied as a lining for reactors, pipes, and storage tanks, and fabricated into essential parts like gaskets, seals, and laboratory equipment to prevent corrosion, ensure product purity, and improve operational reliability.
Teflon’s value is not just in its resistance to chemicals, but in its near-total chemical inertness. This core property allows it to protect critical, expensive infrastructure from corrosion while simultaneously preventing any contamination of the chemical processes themselves.

The Core Principle: Near-Absolute Chemical Inertness
Teflon, technically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a fluoropolymer. Its molecular structure, consisting of a strong carbon-fluorine bond, is the source of its remarkable and defining characteristic: it is non-reactive with nearly every known acid, solvent, and caustic chemical.
Protecting Critical Infrastructure
In chemical processing, equipment is constantly exposed to highly corrosive substances. Teflon acts as an indispensable shield.
It is applied as a durable lining for reactors, distillation columns, and storage tanks. This prevents the aggressive chemicals from eating away at the underlying metal, which would lead to catastrophic equipment failure and costly downtime.
Similarly, pipes are often coated or lined with Teflon. This ensures the safe transport of hazardous materials throughout a facility without risk of leaks caused by corrosion.
Ensuring Process Purity
Just as Teflon protects the equipment from the chemicals, it also protects the chemicals from the equipment.
Because it is so inert, Teflon does not leach contaminants into the chemical mixtures. This is critical for producing high-purity chemicals where even trace amounts of metal ions could ruin an entire batch.
Its anti-adhesion and low-friction properties are also key. Materials do not stick to its surface, which is why it is used for coating stirring bars and other process components, improving efficiency and simplifying cleaning.
Beyond Linings: Mechanical and Sealing Applications
While its role as a protective barrier is primary, Teflon's unique combination of properties makes it essential for moving parts and connection points within a chemical plant.
The Importance of Seals and Gaskets
Every chemical plant relies on thousands of connections between pipes, vessels, and valves. Leaks are not an option.
Teflon is fabricated into seals, gaskets, and gland fillers because it can withstand corrosive chemicals while remaining flexible enough to create a perfect, durable seal.
Reducing Friction and Wear
In machinery where parts are in constant motion, friction leads to wear, heat, and eventual failure.
Teflon's extremely low coefficient of friction makes it an ideal material for bushings, bearings, and other machinery components. It provides a self-lubricating surface where traditional wet lubricants would be impractical or would contaminate the process.
Handling Extreme Temperatures
Many chemical reactions occur at high temperatures. Teflon maintains its structural integrity and chemical stability across a wide temperature range, making it reliable in demanding thermal conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and choosing Teflon requires understanding its limitations. It is an engineering choice driven by specific needs, not a universal solution.
Mechanical Strength
Teflon is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep," or slow deformation over time when placed under a constant high load. In high-pressure applications, this must be accounted for in the design.
Abrasion Resistance
While excellent for sliding friction, Teflon has only moderate resistance to abrasion from hard, sharp particles. In environments with abrasive slurries, other materials may be more suitable.
Cost Considerations
Teflon is a premium, high-performance polymer. Its cost is significantly higher than many standard plastics or metals. Its use is therefore justified in applications where its unique chemical inertness and performance are absolutely necessary to prevent failure or contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use Teflon should be based on the primary challenge you are trying to solve within your chemical process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Use Teflon as a lining for any tank, reactor, or pipe that comes into contact with highly corrosive substances.
- If your primary focus is ensuring product purity: Specify Teflon for all wetted parts, including lab equipment, seals, and anti-adhesion coatings, to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is improving mechanical reliability: Employ Teflon in seals, gaskets, and low-friction components like bushings to prevent leaks and reduce wear in moving parts.
Ultimately, Teflon serves as the definitive material for creating a chemically invisible and mechanically smooth surface in the world's most aggressive environments.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Linings & Coatings | Protects metal from corrosion | Reactors, storage tanks, pipes |
| Seals & Gaskets | Creates leak-proof connections | Valves, pipe fittings, pumps |
| Lab & Process Equipment | Prevents contamination, non-stick | Labware, stirrers, bearings |
| Mechanical Components | Low friction, self-lubricating | Bushings, bearings, slides |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your chemical application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your equipment is protected from corrosion and your processes remain contaminant-free.
Contact our experts today to discuss your custom fabrication needs, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















