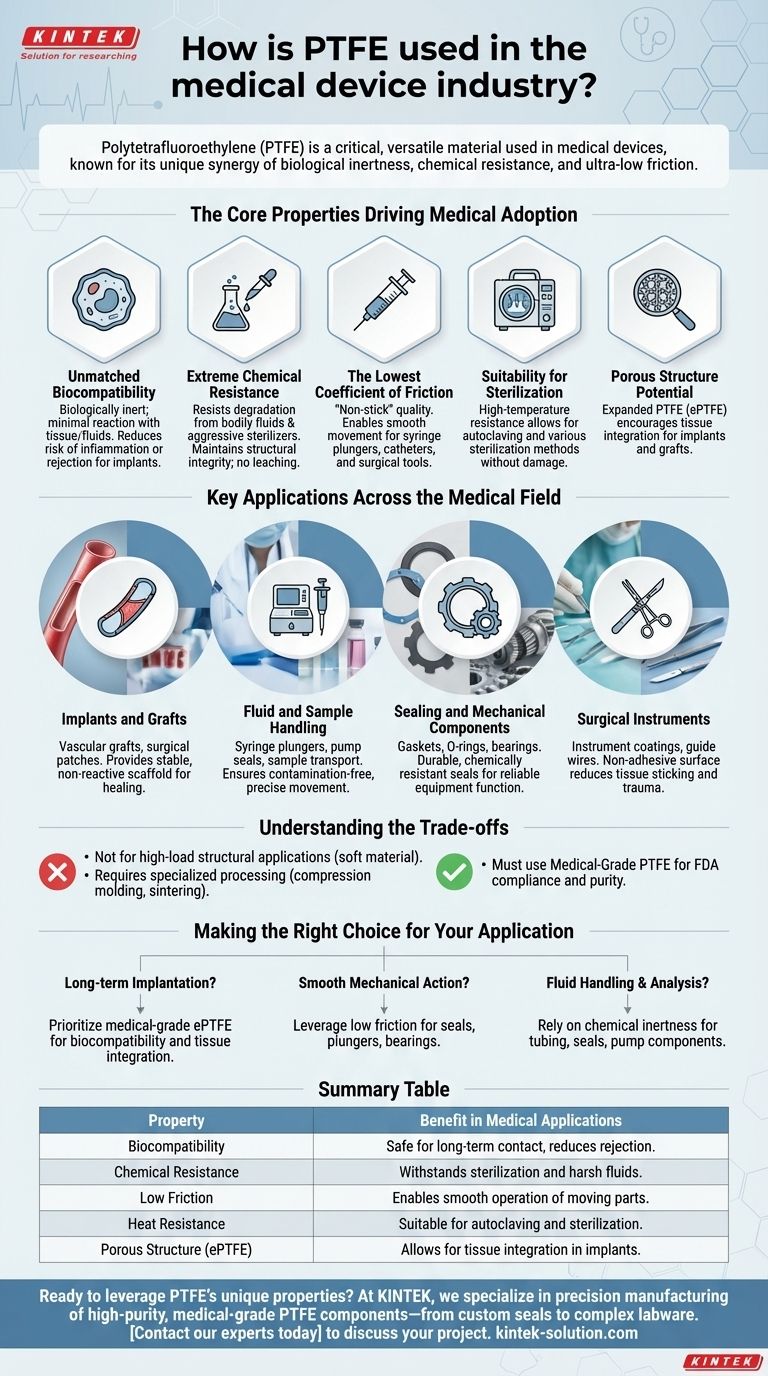
In the medical device industry, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a critical material used for everything from permanent implants and surgical grafts to essential components in diagnostic equipment like seals and syringe plungers. Its value stems from a unique combination of biological inertness, chemical resistance, and an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most versatile and reliable polymers for clinical applications.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use in medicine is its synergy of properties. It is one of the few materials that is simultaneously biocompatible for safe contact with the human body, chemically inert to resist degradation from bodily fluids and sterilizers, and exceptionally slick to enable smooth mechanical function.
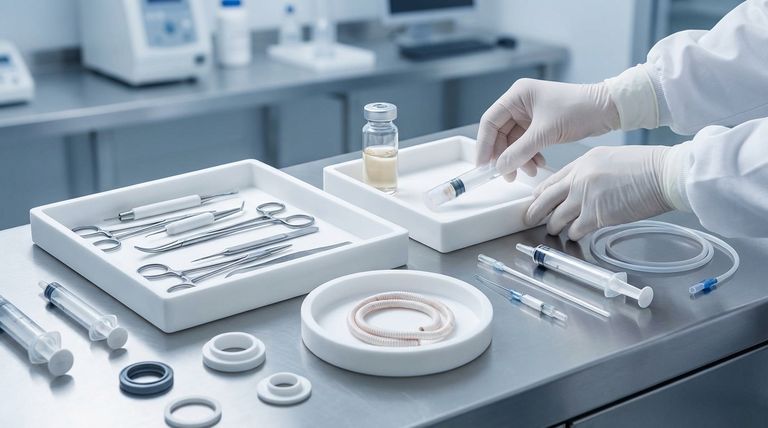

The Core Properties Driving Medical Adoption
The selection of any material for a medical device is a decision driven by safety, reliability, and performance. PTFE excels in several areas that are non-negotiable in a clinical environment.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
PTFE is biologically inert, meaning it has minimal reaction when it comes into contact with human tissue and bodily fluids. This property is paramount for any component that will be placed inside the body, significantly reducing the risk of inflammation or rejection.
Extreme Chemical Resistance
Medical components are exposed to a wide range of substances, from aggressive sterilization chemicals to complex bodily fluids. PTFE is resistant to virtually all common chemicals, ensuring the material does not degrade over time, maintaining its structural integrity and preventing the leaching of harmful substances.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
Often recognized by its trade name Teflon, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This "non-stick" quality is critical in applications requiring smooth, effortless movement, such as reducing the force needed to operate a syringe plunger or minimizing irritation from a catheter.
Suitability for Sterilization
PTFE’s high-temperature resistance allows it to withstand common sterilization methods, such as autoclaving. This ensures that devices made from or coated with PTFE can be made sterile for surgical use without compromising the material’s integrity.
Porous Structure Potential
A specific form, expanded PTFE (ePTFE), can be engineered to have a porous microstructure. This is highly valuable for implants like vascular grafts, as it encourages the patient's own cells to grow into the material, leading to better integration with the body.
Key Applications Across the Medical Field
These fundamental properties translate directly into a wide array of life-saving and function-enabling applications in medical technology.
Implants and Grafts
Due to its biocompatibility and potential for porosity, PTFE is a go-to material for synthetic vascular grafts, surgical patches, and other permanent implants. It provides a stable, non-reactive scaffold for the body to heal around.
Fluid and Sample Handling
In laboratory and diagnostic equipment, PTFE is essential. It is used for syringe plungers, pump seals, and sample transport mechanisms where its chemical inertness prevents contamination and its low friction ensures precise, repeatable movement.
Sealing and Mechanical Components
The reliability of medical equipment often depends on its seals. PTFE is widely used for gaskets, O-rings, and bearings in medical pumps and devices because it creates a durable, chemically resistant seal that won't degrade or fail unexpectedly.
Surgical Instruments
PTFE is often used as a coating on surgical instruments and guide wires. Its non-adhesive surface prevents tissue from sticking to the instrument during a procedure, which can reduce patient trauma and improve the surgeon's control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its benefits are significant, PTFE is not a universal solution. It's crucial to understand its limitations to apply it correctly.
Not a High-Strength Material
Standard PTFE is a relatively soft material and is generally not suitable for high-load, structural applications on its own. Its strength lies in its surface properties and chemical stability, not its mechanical rigidity.
Specialized Processing
PTFE does not melt and flow like common thermoplastics. It must be processed using more complex techniques like compression molding and sintering, which can influence design possibilities and manufacturing costs.
Matching Grade to Application
Not all PTFE is created equal. Medical-grade PTFE must be sourced to ensure it complies with stringent FDA regulations and has the purity required for clinical use. Using an industrial grade for a medical application is a critical failure point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material is about matching its properties to the primary goal of your device.
- If your primary focus is long-term implantation: Prioritize medical-grade ePTFE for its proven biocompatibility and porous structure that encourages tissue integration.
- If your primary focus is smooth mechanical action: Leverage PTFE's low coefficient of friction for components like seals, plungers, and bearings to ensure reliable, stick-free movement.
- If your primary focus is fluid handling and analysis: Rely on PTFE’s chemical inertness to prevent sample contamination and material degradation in tubing, seals, and pump components.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique profile makes it an indispensable tool for engineers creating safer, more reliable, and more effective medical devices.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit in Medical Applications |
|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Safe for long-term contact with tissue and bodily fluids, reducing rejection risk. |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands sterilization and harsh fluids, ensuring device integrity and safety. |
| Low Friction | Enables smooth operation of syringes, catheters, and moving parts. |
| Heat Resistance | Suitable for autoclaving and other high-temperature sterilization methods. |
| Porous Structure (ePTFE) | Allows for tissue integration in implants like vascular grafts. |
Ready to leverage PTFE's unique properties for your medical device?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-purity, medical-grade PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production for the semiconductor, medical, or laboratory industries, our expertise ensures your devices meet the highest standards of safety and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how we can bring reliability and precision to your medical solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















