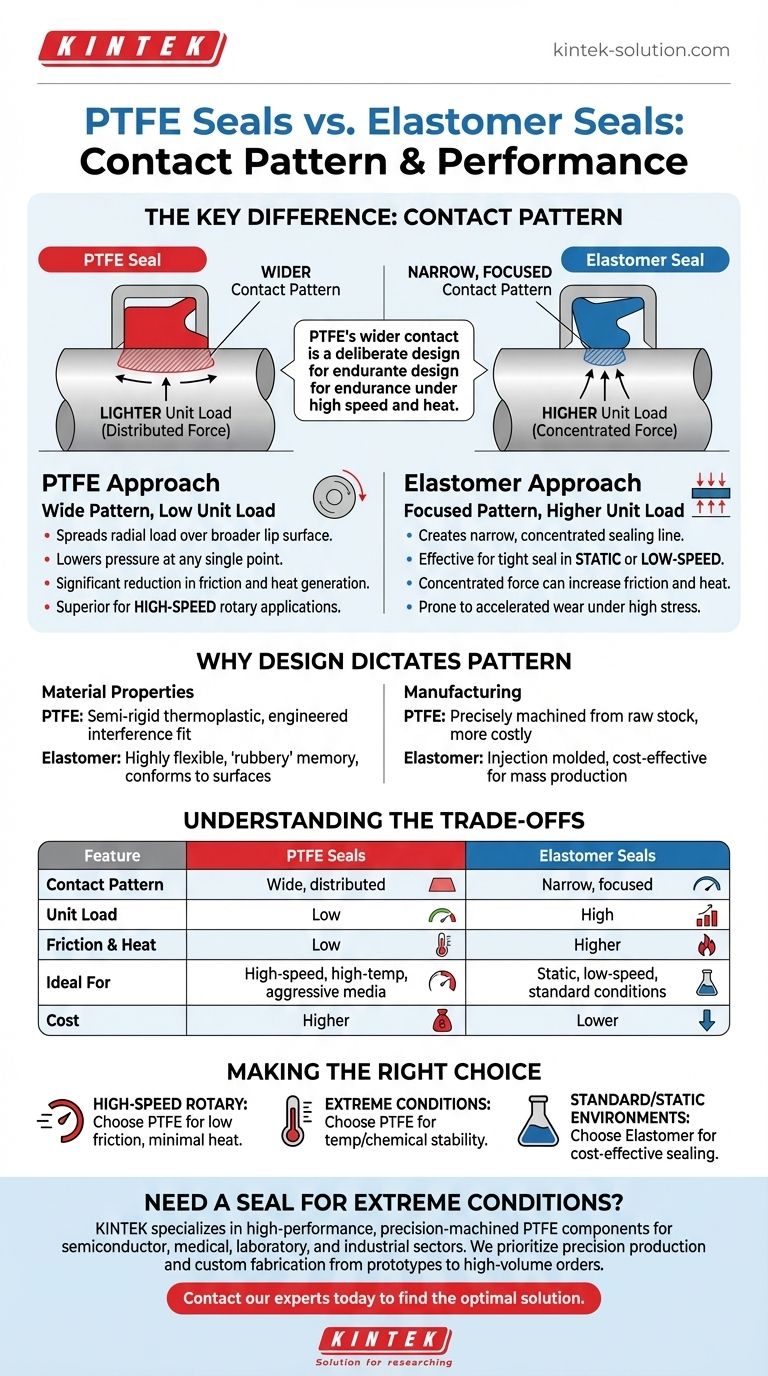
In short, PTFE seals have a wider contact pattern than their elastomeric counterparts. This is a deliberate design choice that distributes the sealing force over a larger surface area, resulting in a lighter unit load. This fundamental difference is the key to PTFE's superior performance in high-stress applications.
The difference in contact pattern isn't just a geometric detail; it's the core of the performance trade-off between PTFE and elastomer seals. PTFE's wider, lighter-pressure footprint is engineered for endurance under high speed and heat, while an elastomer's focused contact provides effective sealing in less demanding conditions at a lower cost.
The Anatomy of Seal Contact: Width vs. Force
The effectiveness and longevity of any seal are dictated by the relationship between the contact area (the "pattern") and the force applied over that area.
The PTFE Approach: Wide Pattern, Low Unit Load
PTFE seals are designed to spread the radial load across a broader lip surface. This design intentionally lowers the pressure at any single point on the seal.
The primary benefit is a significant reduction in friction and subsequent heat generation. This characteristic makes PTFE seals the superior choice for high-speed rotary applications where heat is the primary cause of seal failure.
The Elastomer Approach: Focused Pattern, Higher Unit Load
Elastomeric seals, due to their flexible, rubbery nature, typically create a narrower, more concentrated sealing line.
This focused pressure is highly effective for creating a tight seal in static or low-speed applications. However, in high-stress conditions, this concentrated force can increase friction, accelerate wear, and lead to premature failure.
Why Design Dictates the Contact Pattern
The difference in contact patterns is a direct result of the materials' inherent properties and the manufacturing processes used to create them.
Material Properties and Seal Mechanics
PTFE is a semi-rigid thermoplastic. PTFE seals generate their sealing force from the material's carefully engineered interference fit and lip geometry, rather than from extension springs common in elastomer designs.
Elastomers are highly flexible and rely on their "rubbery" memory to conform to surfaces and maintain a seal. This compliance allows for a different design philosophy focused on concentrated pressure.
The Impact of Manufacturing
PTFE cannot be injection molded like an elastomer. It must be precisely machined from raw stock and then press-fitted into a metal casing. This process allows for tight control over the seal's geometry but is more costly.
Elastomers can be directly molded onto metal components, a process that is highly efficient and cost-effective for mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between PTFE and elastomer seals requires an objective look at their performance characteristics, lifespan, and cost implications.
Performance Under Stress
PTFE excels in extreme conditions. It maintains its integrity and sealing capability in extreme temperatures (-53°C to 232°C), at very high surface speeds (over 35 m/s), and in the presence of aggressive chemical media.
Elastomers are the workhorse for standard operating conditions but will quickly degrade and fail when exposed to these types of extremes.
Durability and Wear Life
The wider, low-pressure contact pattern of PTFE seals directly translates to lower wear rates and a significantly longer operational life, especially in demanding rotary applications.
The focused contact of an elastomer seal can lead to faster wear and material breakdown under continuous high stress due to heat and friction.
Cost and Complexity
PTFE seals are more expensive. This is due to both the higher cost of the raw PTFE material and the more complex, multi-step machining and assembly process.
Elastomeric seals are far more economical to produce, making them the default choice for a vast range of applications where extreme performance is not a requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based on the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotary performance: Choose PTFE for its wide contact pattern and low-friction characteristics, which minimize heat generation and wear.
- If your application involves extreme temperatures or aggressive media: PTFE's material stability and engineered contact provide reliability where elastomers would fail.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a standard environment: An elastomer seal's focused contact provides excellent sealing for static or low-duty applications at a much lower cost.
Understanding the contact pattern moves you beyond a simple geometric comparison and empowers you to select a seal based on the fundamental principles of load, friction, and material science.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Seals | Elastomer Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Pattern | Wide, distributed | Narrow, focused |
| Unit Load | Low | High |
| Friction & Heat | Low | Higher |
| Ideal For | High-speed, high-temperature, aggressive media | Static, low-speed, standard conditions |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Need a Seal That Can Handle Extreme Conditions?
Understanding the contact pattern is the first step to selecting the right seal for your application's specific demands of load, friction, and temperature. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, precision-machined PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure your equipment operates reliably under stress.
Let's discuss your sealing challenge. Contact our experts today to find the optimal solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















