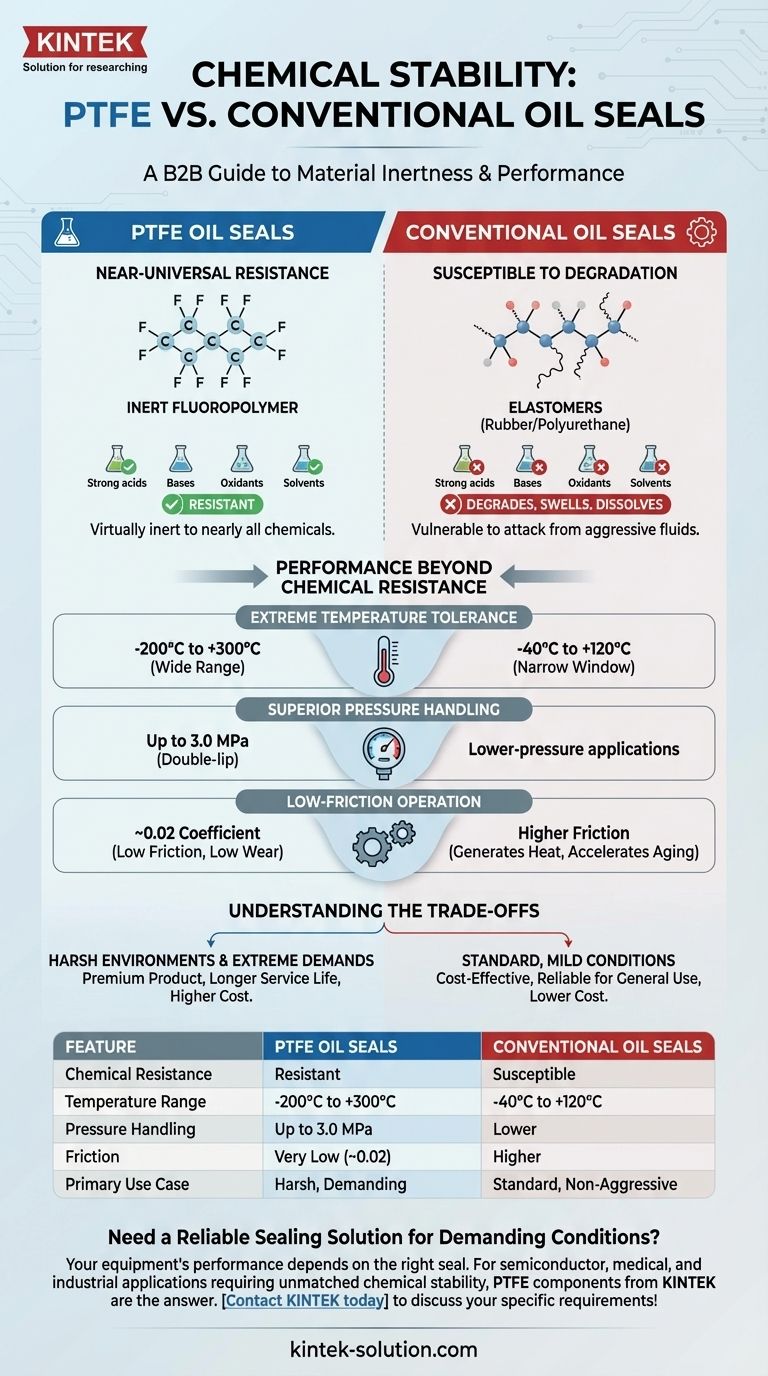
In terms of chemical stability, PTFE oil seals are vastly superior to conventional seals. Made from polytetrafluoroethylene, PTFE seals are virtually inert, allowing them to resist erosion from nearly all chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and oxidants. In contrast, conventional seals made from rubber or polyurethane are susceptible to degradation, swelling, or dissolution when exposed to certain solvents and aggressive fluids.
The core difference is specialization versus general use. PTFE seals offer near-universal chemical resistance for harsh, demanding environments, while conventional rubber seals provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for standard applications where aggressive chemicals are not a factor.

The Fundamental Difference in Material Inertness
The stark contrast in chemical stability comes down to the molecular structure of the materials used in each type of seal. Understanding this is key to selecting the right component for your equipment.
The Power of PTFE's Molecular Bond
PTFE seals are made from polytetrafluoroethylene, a fluoropolymer. Its carbon-fluorine bonds are exceptionally strong and stable, making the material almost completely non-reactive.
This inherent inertness is why PTFE is the material of choice for equipment handling a wide and aggressive range of chemicals.
The Vulnerability of Conventional Elastomers
Conventional seals are typically made from rubber or polyurethane materials. While effective in many scenarios, their chemical structure is more susceptible to attack.
Solvents, oils, and other aggressive chemicals can break down the polymer chains, causing the seal to harden, swell, or lose its sealing capability, leading to premature failure.
Performance Beyond Chemical Resistance
While chemical stability is a primary differentiator, PTFE's advantages extend to several other critical performance metrics. These factors often go hand-in-hand in demanding industrial applications.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
PTFE seals demonstrate remarkable thermal stability, operating effectively in an extremely wide temperature range from -200°C to +300°C.
Conventional rubber seals have a much narrower operating window, typically between -40°C and +120°C, and are more prone to degradation from temperature fluctuations.
Superior Pressure Handling
Engineered for more demanding tasks, PTFE seals can withstand significantly higher pressures. A single-lip PTFE seal can handle up to 1.0 MPa, while a double-lip design can manage up to 3.0 MPa.
Conventional seals are generally designed for lower-pressure applications and are best suited for general-purpose mechanical sealing.
Low-Friction Operation
PTFE has an exceptionally low friction coefficient of around 0.02. This minimizes energy loss and heat generation during operation, which reduces wear on both the seal and the shaft.
Conventional seals have higher friction, which can generate heat that accelerates material aging and degrades sealing performance over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a seal is not simply about picking the one with the highest specifications. It's about matching the component to the application's true requirements and budget.
The Critical Role of Cost
The primary advantage of conventional oil seals is their cost-effectiveness. Their lower manufacturing cost makes them the standard choice for countless common applications.
PTFE seals are a premium product with a higher price point, reflecting their advanced material properties and manufacturing process.
Matching the Seal to the Environment
Over-engineering can be as inefficient as under-engineering. For many standard applications without extreme temperatures, high pressures, or aggressive chemicals, a conventional seal performs reliably and is the more economical choice.
The superior performance of PTFE only provides a true return on investment in environments that would cause a conventional seal to fail quickly.
Service Life and Reliability
Due to its resistance to chemical attack, temperature extremes, and wear, a PTFE seal offers a significantly longer service life in harsh conditions. This translates to greater equipment uptime and reduced maintenance costs.
In a mild environment, the lifespan difference between the two types of seals may be less pronounced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct oil seal requires a clear understanding of your operational demands. Your decision should be guided by the specific challenges the component will face.
- If your primary focus is operating in harsh chemical environments: PTFE is the only reliable choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is managing extreme temperatures or high pressure: The superior thermal stability and pressure ratings of PTFE are necessary for safe and reliable operation.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for standard, non-aggressive conditions: A conventional rubber or polyurethane seal is the more economical and perfectly suitable option.
By matching the seal's material properties to your specific operational demands, you ensure both equipment reliability and long-term cost-efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Oil Seals | Conventional Oil Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to nearly all chemicals (acids, bases, oxidants) | Susceptible to degradation from solvents and aggressive fluids |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +300°C | -40°C to +120°C |
| Pressure Handling | Up to 3.0 MPa (double-lip) | Lower-pressure applications |
| Friction Coefficient | ~0.02 (very low) | Higher |
| Primary Use Case | Harsh, demanding environments | Standard, non-aggressive conditions |
Need a Reliable Sealing Solution for Demanding Conditions?
Your equipment's performance depends on the right seal. For semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications requiring unmatched chemical stability, temperature tolerance, and pressure handling, PTFE components from KINTEK are the answer.
We specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, and labware. Whether you need a custom prototype or a high-volume order, we deliver components built to withstand your harshest environments.
Ensure your equipment's reliability and longevity. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for seals? Unlock Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key advantages of PTFE rotary seals over traditional rubber seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance



















