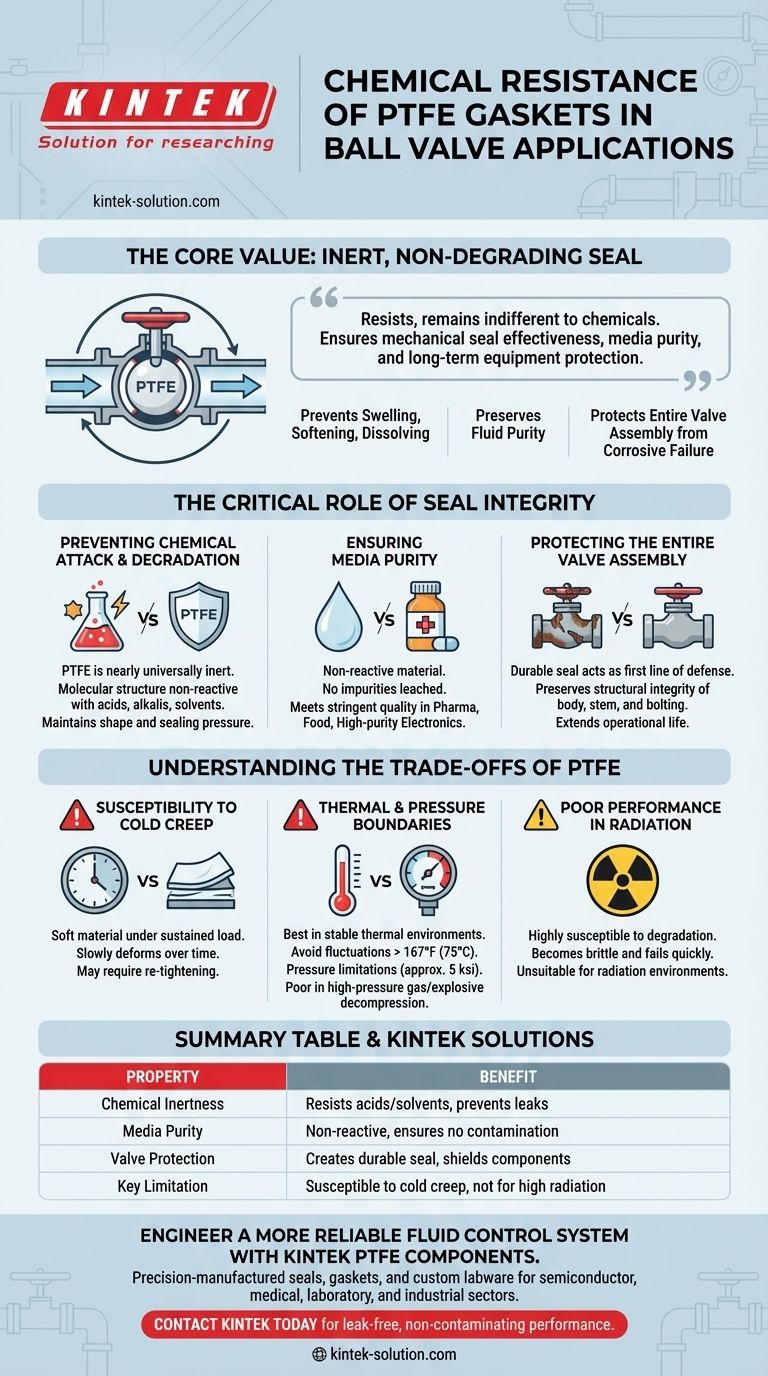
The fundamental benefit of PTFE's chemical resistance is its ability to create an inert, non-degrading seal. In a ball valve, this property ensures that the gasket will not swell, soften, or dissolve when exposed to aggressive acids, solvents, or alkalis. This stability prevents leaks, preserves the purity of the fluid, and protects the entire valve assembly from corrosive failure.
The core value of a PTFE gasket in a ball valve isn't just that it resists chemicals—it's that it remains completely indifferent to them. This ensures the mechanical seal remains effective, the process media stays uncontaminated, and the equipment is protected over the long term.

The Critical Role of Seal Integrity
A ball valve's reliability is entirely dependent on its seals. While the ball itself controls the flow, the gaskets and seats are what prevent internal and external leaks.
Preventing Chemical Attack and Degradation
When a gasket material is not compatible with the process fluid, it can fail rapidly. Other materials might swell, shrink, or become brittle upon chemical exposure.
PTFE, or Polytetrafluoroethylene, is nearly universally inert. Its molecular structure makes it non-reactive with almost all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents.
This means a PTFE gasket maintains its physical shape and sealing pressure, preventing the primary cause of chemical-related leaks.
Ensuring Media Purity
In industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, or high-purity electronics, contamination is unacceptable. The gasket material cannot react with or leach particles into the fluid it contains.
Because PTFE is non-reactive, it does not introduce impurities into the system. This guarantees that the final product meets stringent quality and safety standards.
Protecting the Entire Valve Assembly
A leaking gasket does more than just release fluid. It allows corrosive media to escape the primary flow path and attack other components of the valve, such as the body, stem, and bolting.
By providing a durable, long-lasting seal, a PTFE gasket acts as the first line of defense, preserving the structural integrity and extending the operational life of the entire valve.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE
While its chemical resistance is unmatched, PTFE is not the solution for every application. A true technical evaluation requires acknowledging its physical limitations.
Susceptibility to Cold Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained compressive load from the valve flanges, it can slowly deform over time, a phenomenon known as cold creep or "cold flow."
This can eventually reduce the sealing pressure and may require periodic re-tightening of flange bolts to maintain a tight seal.
Thermal and Pressure Boundaries
PTFE gaskets perform best in stable thermal environments. They should not be used in applications with temperature fluctuations greater than 167°F (75°C), as this can compromise seal integrity.
Furthermore, standard PTFE has pressure limitations, often cited around 5 ksi, and its performance degrades in high-pressure gas service where explosive decompression can be a risk.
Poor Performance in Radiation
PTFE is highly susceptible to degradation from radiation. In nuclear or other radiation-heavy environments, the material can become brittle and fail quickly, making it an unsuitable choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right gasket material requires matching its properties to the specific operational demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals at stable temperatures: PTFE is an industry-standard choice for ensuring a reliable, long-lasting, and non-contaminating seal.
- If your application involves high pressures or significant temperature cycling: You must carefully evaluate PTFE's limitations and consider alternative materials or filled-PTFE variants designed to resist cold creep.
- If media purity is non-negotiable (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food production): PTFE's inert, non-reactive nature makes it one of the safest and most effective sealing materials available.
Ultimately, understanding both the unmatched chemical resilience and the specific physical limitations of PTFE allows you to engineer a truly robust and reliable fluid control system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit in Ball Valve Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists acids, solvents, and alkalis; prevents gasket degradation and leaks. |
| Media Purity | Non-reactive; ensures no contamination in pharmaceuticals, food, or electronics. |
| Valve Protection | Creates a durable seal, shielding valve body and components from corrosive attack. |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to cold creep under sustained load; not ideal for high radiation. |
Engineer a more reliable and durable fluid control system with KINTEK PTFE components.
Our precision-manufactured PTFE seals, gaskets, and custom labware are designed to deliver unmatched chemical resistance for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or high-volume production, we prioritize the precision and material integrity required for your most critical applications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure leak-free, non-contaminating performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation



















