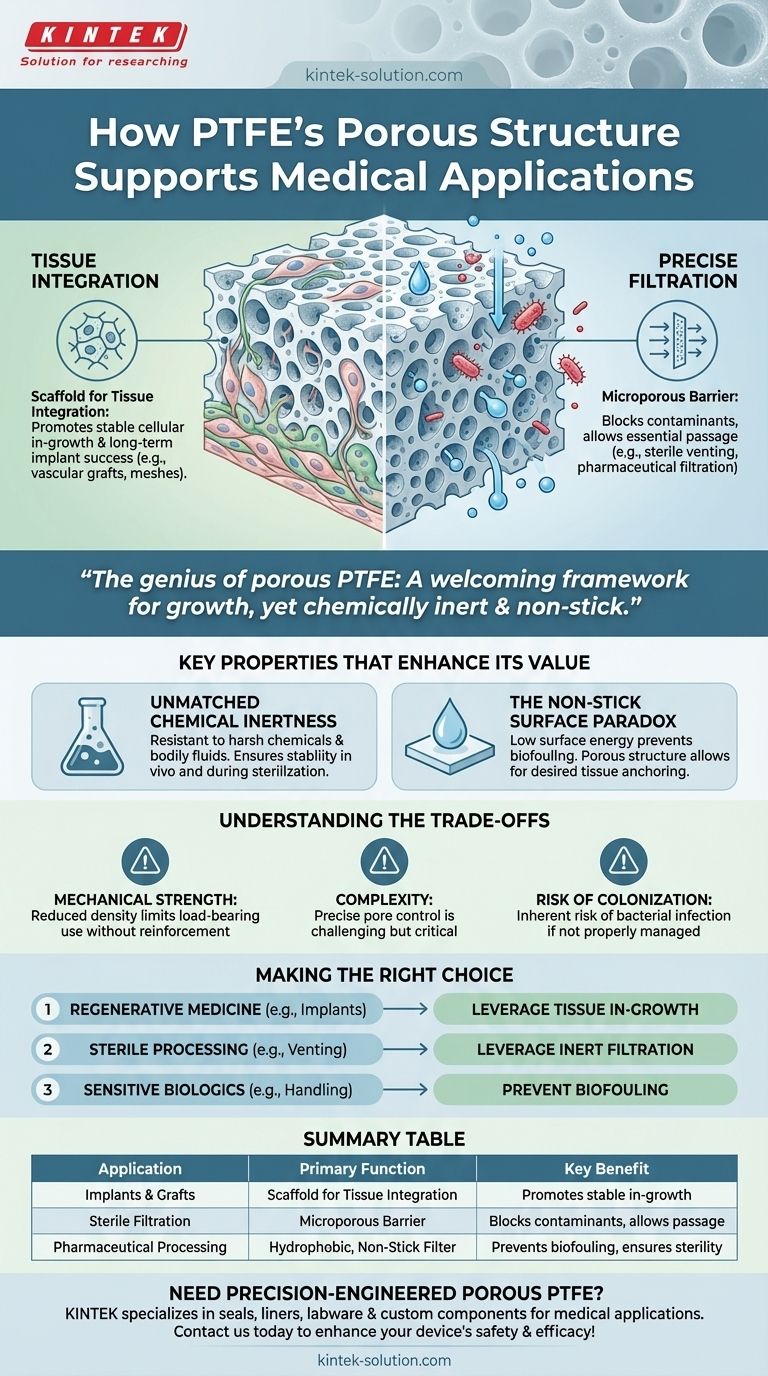
At its core, porous Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) uniquely supports medical applications by providing a biocompatible physical scaffold. This structure allows for two primary functions: promoting the integration of bodily tissue for implants and enabling highly specific filtration for sterile processes.
The genius of porous PTFE in medicine lies in its dual nature: its microscopic structure acts as a welcoming framework for cellular growth, while the material itself remains one of the most chemically inert and non-stick substances known, ensuring stability and safety within the human body.

The Functional Advantage of a Porous Structure
The defining feature of this material is its network of interconnected voids. The size and distribution of these pores are carefully engineered to achieve specific medical outcomes that a solid material could never accomplish.
A Scaffold for Tissue Integration
Porous PTFE acts as a framework for the body's own cells to grow into. This process, known as tissue integration, is fundamental for the long-term success of many implantable devices.
The structure provides a physical space for cells to anchor, proliferate, and form new tissue, effectively making the implant a part of the patient's body. This is critical in applications like vascular grafts or surgical meshes.
A Barrier for Precise Filtration
The material's small, consistent pore sizes create a highly effective physical barrier. This allows it to function as a microporous filter, blocking contaminants like bacteria while allowing essential liquids or gases to pass through.
This capability is vital for sterile venting on medical bags, protecting sensitive electronic sensors from fluids, and in pharmaceutical filtration processes.
Key Properties That Enhance Its Medical Value
The benefits of the porous structure are amplified by the inherent properties of the base PTFE material. Without these foundational characteristics, its use in medicine would be impossible.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is exceptionally resistant to degradation from harsh chemicals, acids, and bodily fluids. This ensures that a porous PTFE implant or filter will not break down over time.
This stability is critical for devices that undergo repeated, aggressive sterilization cycles or that will remain in the body for years.
The Non-Stick Surface Paradox
PTFE is famous for its low surface energy, which makes it extremely non-stick. This property prevents the undesirable adhesion of proteins or blood cells, a common cause of implant failure known as biofouling.
This creates a beneficial paradox: while the surface of the material resists adhesion, the porous structure provides the physical scaffolding needed to mechanically anchor and support desired cellular in-growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, porous PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to its proper application.
Mechanical Strength
Creating pores inherently reduces the material's overall density and tensile strength. Porous PTFE is not suitable for high-load-bearing applications, such as orthopedic joint replacements, without significant structural reinforcement.
Complexity in Manufacturing
Producing porous PTFE with a highly controlled and consistent pore size is a complex process. The performance of the final device—whether for filtration or tissue integration—is entirely dependent on the quality and uniformity of this microstructure.
Risk of Colonization
Any porous implant carries an inherent risk. If bacteria manage to colonize the intricate network of pores before the body's own tissue can, the resulting infection can be very difficult to eradicate with antibiotics alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use porous PTFE should be driven by the primary technical challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is regenerative medicine or long-term implants: Leverage its ability to promote stable, organized tissue in-growth, making it ideal for grafts and soft-tissue scaffolding.
- If your primary focus is sterile processing or device protection: Its function as a chemically inert, hydrophobic filter is its greatest asset for venting and filtration applications.
- If your primary focus is handling sensitive biologics: The combination of a non-stick surface and controlled porosity prevents biofouling while allowing for necessary fluid or gas transport.
Ultimately, porous PTFE's value comes from its unique ability to combine a physically interactive structure with profound chemical stability, solving problems other materials cannot.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function of Porous Structure | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Implants & Grafts | Scaffold for Tissue Integration | Promotes stable cellular in-growth and long-term implant success |
| Sterile Filtration | Microporous Barrier | Blocks contaminants (e.g., bacteria) while allowing gas/liquid passage |
| Pharmaceutical Processing | Hydrophobic, Non-Stick Filter | Prevents biofouling and ensures sterile fluid handling |
Need precision-engineered porous PTFE components for your medical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the precise porous structure required for optimal tissue integration or filtration performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your medical device's safety and efficacy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















