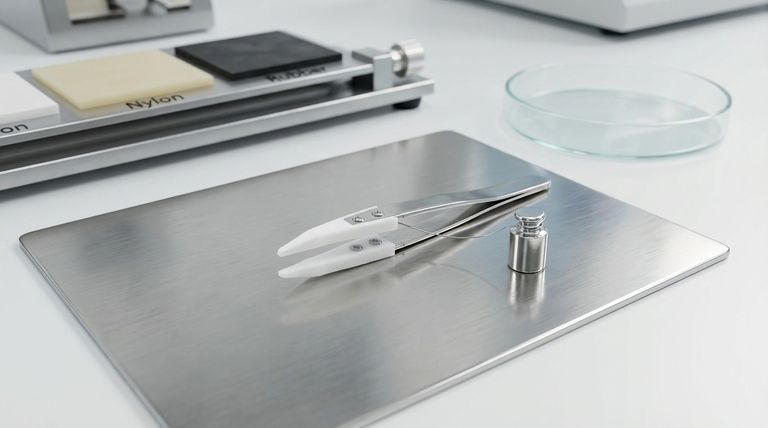
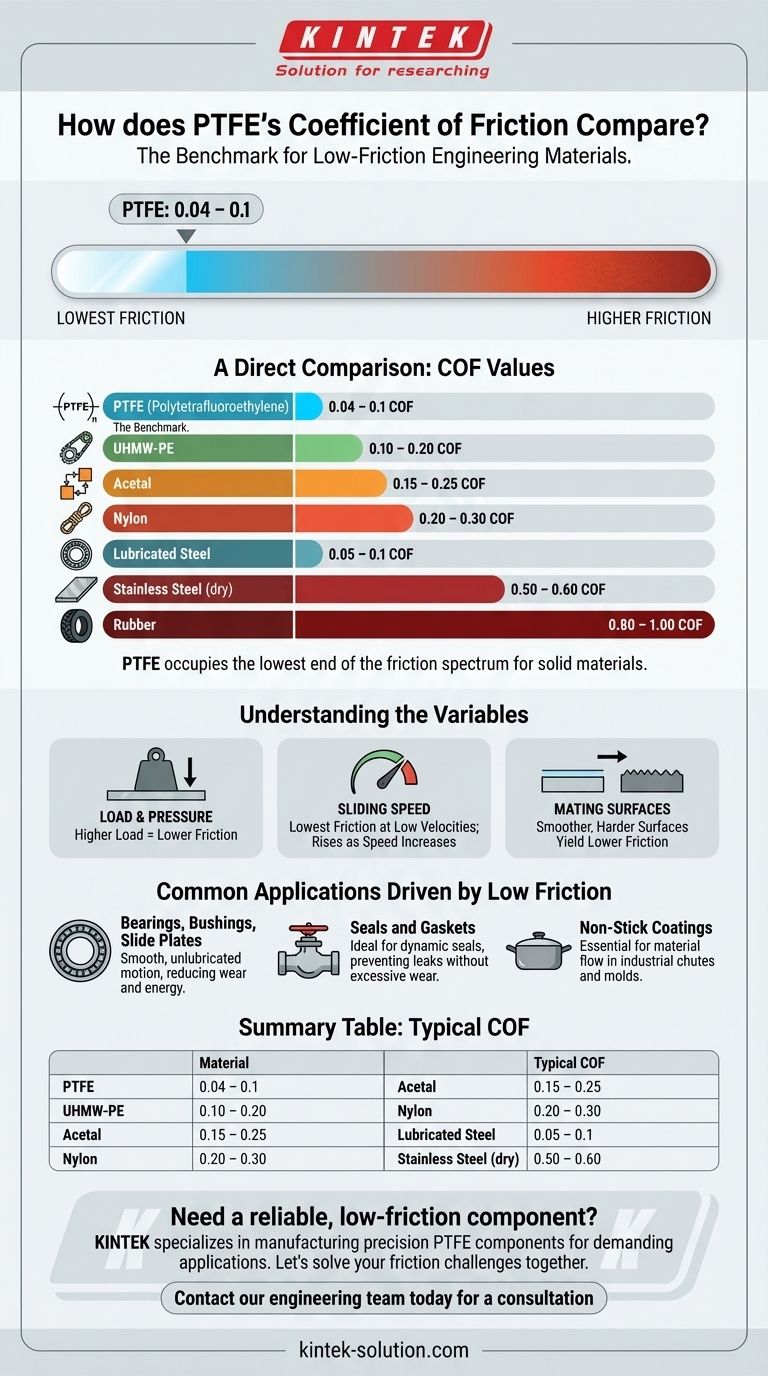
When measured against other solid engineering materials, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) consistently exhibits one of the lowest coefficients of friction available. Its typical dynamic coefficient of friction ranges from 0.04 to 0.1, making it significantly "slicker" than other common polymers like Nylon or Acetal, and even superior to lubricated steel in many conditions. This exceptionally low friction is the defining characteristic that drives its use in countless demanding applications.
The core takeaway is that while PTFE is the benchmark for low-friction surfaces, its coefficient of friction is not a single static number. It is a dynamic value that varies based on critical operating factors like pressure, sliding velocity, and temperature.

A Direct Comparison: PTFE vs. Other Materials
To understand PTFE's unique position, it's best to compare its performance directly against other well-known materials. The coefficient of friction (COF) is a ratio that indicates the resistance to sliding motion between two surfaces; a lower number means less resistance.
Against Other Polymers
PTFE's performance is most striking when compared to other plastics. Its non-stick molecular structure gives it a significant advantage where smooth, effortless motion is required.
- PTFE: 0.04 – 0.1
- UHMW-PE (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene): 0.10 – 0.20
- Acetal: 0.15 – 0.25
- Nylon: 0.20 – 0.30
Against Metals and Elastomers
Even when compared to lubricated metals, PTFE often comes out ahead, especially in static friction, which is the force needed to initiate movement.
- PTFE: 0.04 – 0.1
- Lubricated Steel: 0.05 (kinetic) to 0.1 (static)
- Stainless Steel (dry): 0.50 – 0.60
- Rubber: 0.80 – 1.00
This data clearly establishes PTFE as an outlier, occupying the lowest end of the friction spectrum for solid materials.
Understanding the Variables That Affect Performance
The coefficient of friction cited for PTFE in technical data sheets is a guideline, not an absolute constant. The real-world performance depends heavily on the specific conditions of the application. Understanding these variables is critical for accurate engineering design.
The Effect of Load and Pressure
For PTFE, a higher load or surface pressure generally results in a lower coefficient of friction. This is a key reason it excels in high-load bearing applications where other materials might seize.
The Influence of Sliding Speed
Conversely, the coefficient of friction for PTFE tends to be at its lowest at low sliding velocities. As speeds increase (e.g., above 10 ft./min), the friction can begin to rise from its lowest values.
The Impact of Mating Surfaces
The nature of the surface sliding against the PTFE component has a significant impact. Smoother, harder mating surfaces will typically yield lower friction values than rough or soft ones.
Test Methods and Conditions
The discrepancies in published data (from 0.02 to 0.2) are often due to different testing methodologies, temperatures, and surface preparations. This highlights the need to consider the entire system, not just the material in isolation.
Common Applications Driven by Low Friction
The unique properties of PTFE make it the material of choice for components where minimizing resistance and preventing stick-slip motion is the primary goal.
Bearings, Bushings, and Slide Plates
In these applications, PTFE allows for smooth, unlubricated motion between mechanical parts, reducing wear, noise, and energy consumption.
Seals and Gaskets
PTFE's low friction and chemical inertness make it ideal for dynamic seals in pumps and valves, preventing leaks without causing excessive wear on moving shafts.
Non-Stick Coatings
The non-stick property, a direct result of low surface energy and a low COF, is famously used in cookware but is also critical for industrial applications like chutes, hoppers, and molds where material flow is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires balancing friction requirements with other mechanical and environmental needs.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute lowest friction: PTFE is the benchmark, especially in high-load, low-speed applications where self-lubrication is needed.
- If your application involves high speeds or requires greater structural rigidity: You must evaluate how PTFE's COF may increase and consider alternatives like filled-PTFE grades or other polymers like UHMW-PE which may offer a better balance of properties.
- If you are performing engineering calculations: Start with a conservative COF value from the typical range (e.g., 0.05 to 0.1) and adjust your assumptions based on the specific pressures and speeds of your system.
By understanding the factors that influence its performance, you can effectively harness PTFE's exceptional slipperiness to solve your most demanding friction challenges.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Coefficient of Friction (COF) |
|---|---|
| PTFE | 0.04 – 0.1 |
| UHMW-PE | 0.10 – 0.20 |
| Acetal | 0.15 – 0.25 |
| Nylon | 0.20 – 0.30 |
| Lubricated Steel | 0.05 – 0.1 |
| Stainless Steel (dry) | 0.50 – 0.60 |
Need a reliable, low-friction component for your application?
PTFE's exceptional slipperiness, chemical resistance, and self-lubricating properties make it ideal for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware.
We partner with you from prototype to high-volume production to ensure your components meet exact performance requirements. Let's solve your friction challenges together.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















