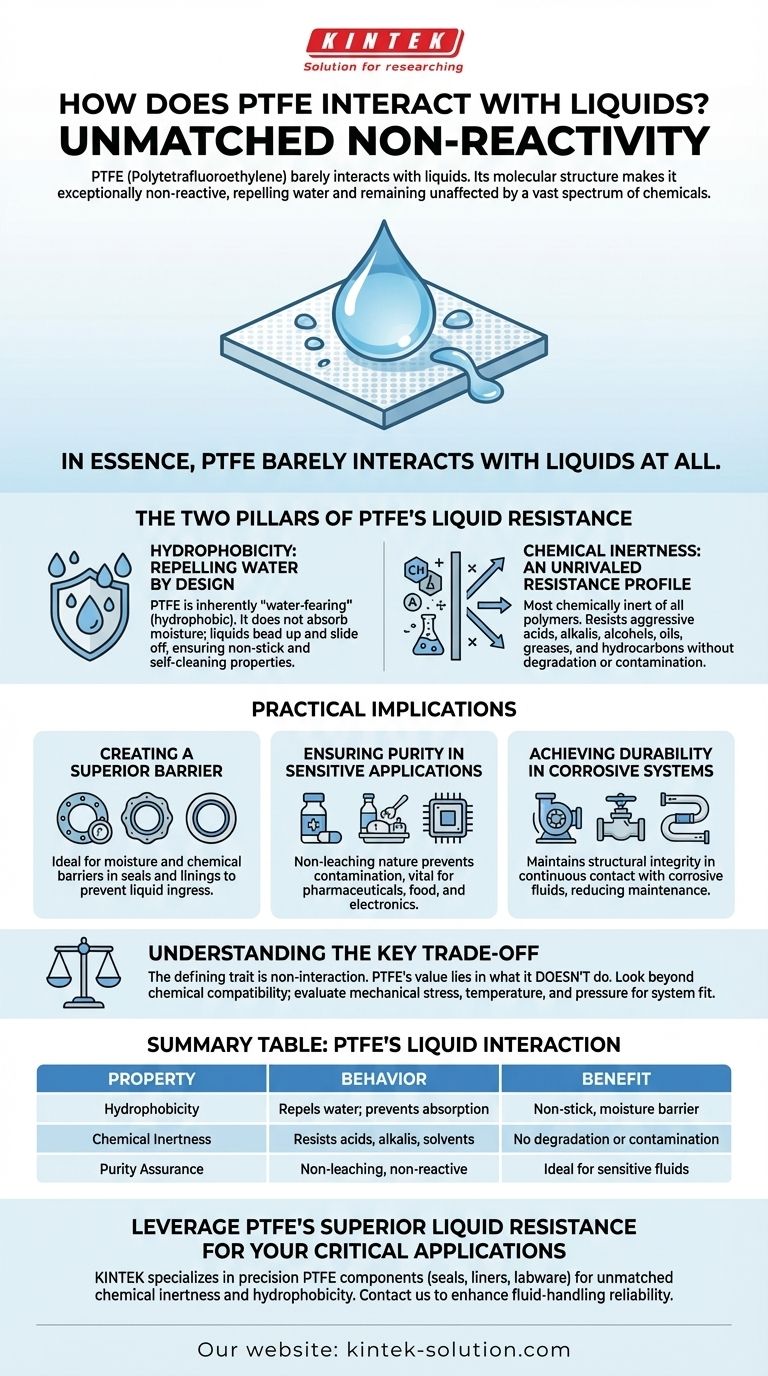
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) barely interacts with liquids at all. Its unique molecular structure makes it exceptionally non-reactive, causing it to powerfully repel water and remain completely unaffected by a vast spectrum of chemicals. This behavior makes it a premier material for the most demanding fluid-handling and barrier applications.
The defining characteristic of PTFE is its extreme inertness. It is both highly hydrophobic (water-repelling) and chemically non-reactive, making it one of the most reliable materials for creating barriers and handling corrosive substances without degrading or contaminating them.

The Two Pillars of PTFE's Liquid Resistance
PTFE's performance is not based on a single property but on two distinct and powerful characteristics: its relationship with water (hydrophobicity) and its relationship with nearly everything else (chemical inertness).
Hydrophobicity: Repelling Water by Design
PTFE is fundamentally hydrophobic, a term that literally means "water-fearing." This is not a coating or a treatment but an inherent property of the material itself.
This property ensures that PTFE does not absorb moisture and actively repels water and water-based liquids.
As a result, liquids bead up and slide off its surface with very little resistance, contributing to its well-known non-stick and self-cleaning capabilities.
Chemical Inertness: An Unrivaled Resistance Profile
Beyond water, PTFE is renowned for being the most chemically inert of all polymers, making it suitable for the harshest environments.
It shows outstanding resistance to a wide range of aggressive liquids, including concentrated and dilute acids, alkalis, alcohols, oils, greases, and hydrocarbons.
This profound non-reactivity means the material will not degrade, swell, or dissolve when exposed to even the most corrosive industrial chemicals.
Practical Implications of This Behavior
Understanding these core properties allows engineers and designers to leverage PTFE to solve specific, critical challenges in fluid systems.
Creating a Superior Barrier
Because PTFE repels water and prevents absorption, it functions as an exceptional moisture and chemical barrier.
This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and protective linings where preventing liquid ingress is absolutely critical to system performance and longevity.
Ensuring Purity in Sensitive Applications
The inert nature of PTFE means it will not leach chemicals or otherwise contaminate the liquids it contains.
This is a vital characteristic in industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing, where maintaining absolute fluid purity is paramount.
Achieving Durability in Corrosive Systems
Components made from PTFE, such as pump linings, valve seats, and tubing, maintain their structural integrity over long service lives, even in continuous contact with highly corrosive fluids.
This reliability reduces maintenance costs, minimizes downtime, and prevents catastrophic failures in chemical processing plants and other demanding industrial settings.
Understanding the Key Trade-off
When selecting a material, it is crucial to understand its limitations. However, in the case of PTFE's interaction with liquids, its primary "limitation" is simply a consequence of its greatest strength.
The Defining Trait is Non-Interaction
The core value of PTFE in liquid applications comes from what it doesn't do: it does not absorb, react, dissolve, or adhere.
Its performance is defined by this extreme lack of interaction. This makes it a specialist material, chosen specifically when non-reactivity is the most important design requirement.
Look Beyond Chemical Compatibility
While its chemical resistance is nearly universal, a successful application requires looking at the entire system.
Engineers must also evaluate factors like mechanical stress, temperature limits, and pressure ratings to ensure PTFE is the right physical fit for the design. Chemical inertness alone does not guarantee success.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Use this knowledge to specify PTFE when your primary design goal aligns with its core strengths.
- If your primary focus is moisture protection or a non-stick surface: Rely on PTFE's inherent hydrophobicity to repel water and prevent unwanted adhesion.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive or corrosive chemicals: Leverage its unmatched chemical inertness for long-term material stability and system safety.
- If your primary focus is maintaining the purity of a sensitive fluid: Choose PTFE for its non-leaching, non-contaminating properties.
Understanding PTFE's fundamental non-reactivity empowers you to design more reliable, durable, and safer systems for handling nearly any liquid.
Summary Table:
| Property | Behavior with Liquids | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobicity | Repels water; prevents absorption | Non-stick, moisture barrier |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists acids, alkalis, solvents | No degradation or contamination |
| Purity Assurance | Non-leaching, non-reactive | Ideal for sensitive fluids (e.g., pharma, semiconductors) |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Liquid Resistance for Your Critical Applications
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to labware—that deliver unmatched chemical inertness and hydrophobic performance. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures your systems handle corrosive liquids or maintain purity without failure.
Ready to enhance your fluid-handling reliability? Contact our team today to discuss prototypes or high-volume orders tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















