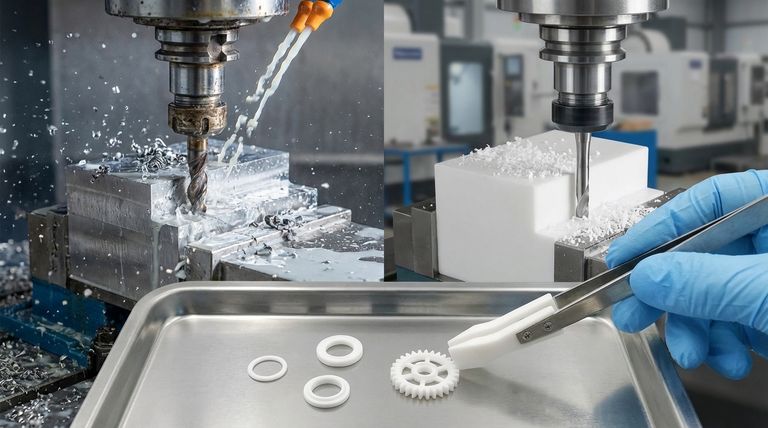
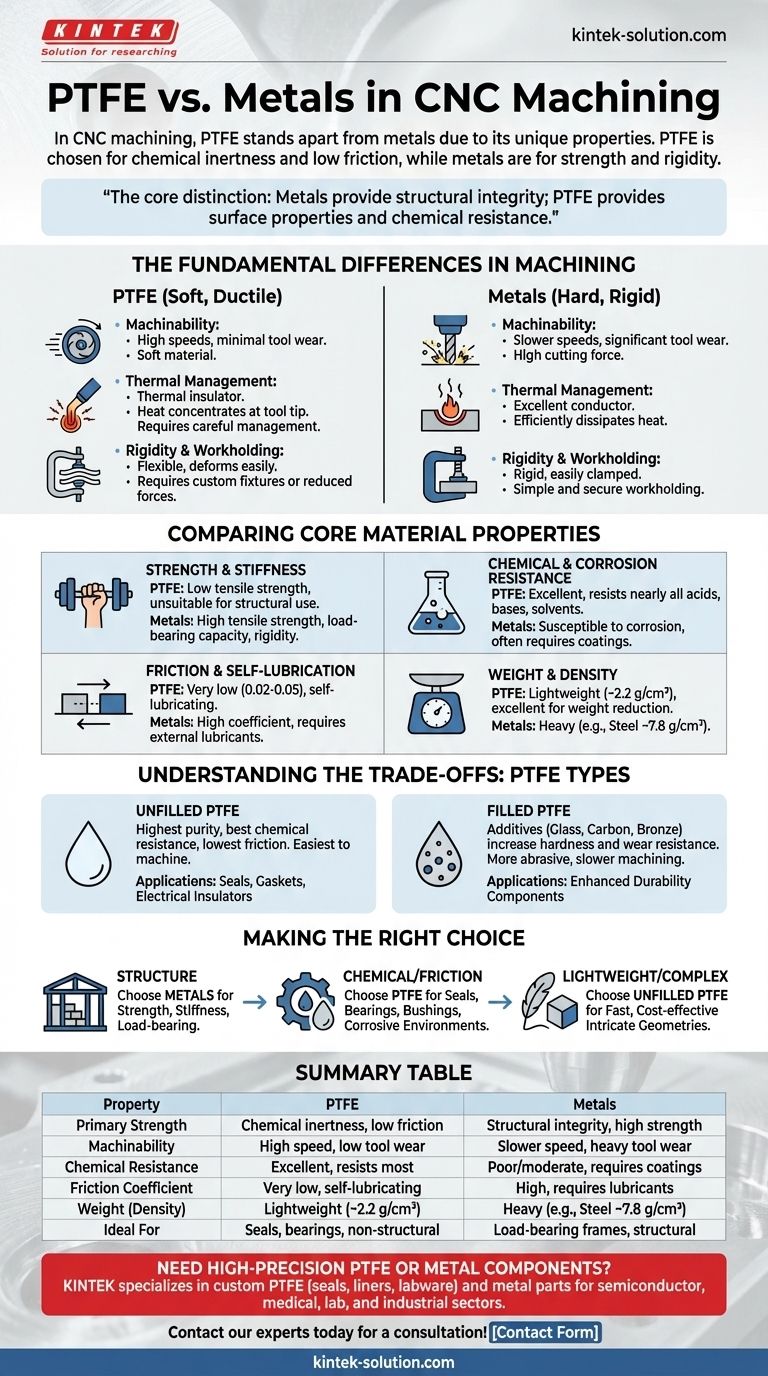
In CNC machining, PTFE stands apart from metals due to its unique combination of properties. Unlike metals such as steel or aluminum, which are chosen for strength and rigidity, PTFE is selected for its exceptional chemical inertness, extremely low friction, and ease of machining. While it is far weaker than any metal, it offers performance characteristics that metals cannot achieve without secondary coatings or lubricants.
The core distinction is one of purpose. Metals provide structural integrity and high strength, whereas PTFE provides unparalleled surface properties and chemical resistance in non-structural applications. Your choice depends entirely on which of these functions is critical for your component.

The Fundamental Differences in Machining
While both material classes can be shaped via CNC machining, the process and considerations are vastly different. Understanding these differences is key to successful part design and manufacturing.
Machinability and Cutting Speeds
Metals are hard and require significant force to cut, leading to slower cutting speeds and noticeable tool wear. PTFE, particularly unfilled grades, is exceptionally soft and ductile. This allows for very high cutting speeds and feeds with minimal wear on cutting tools, often enabling faster and less costly production runs for complex geometries.
Thermal Management
Metals are excellent thermal conductors, efficiently drawing heat away from the cutting tool. In contrast, PTFE is a thermal insulator. Heat generated during machining concentrates at the tool tip instead of dissipating through the material, which can cause the PTFE to melt or deform if not managed with sharp tools, proper coolants, and optimized cutting strategies.
Material Rigidity and Workholding
Metals are rigid, making them simple to clamp securely in a CNC machine. PTFE is soft and flexible, easily deforming under pressure. This requires careful workholding strategies, such as using custom fixtures or reduced clamping forces, to avoid compressing or distorting the part and compromising dimensional accuracy.
Comparing Core Material Properties
The ideal application for each material becomes clear when comparing their inherent properties beyond just the machining process itself.
Strength and Stiffness
This is the most significant advantage for metals. Materials like steel and aluminum offer high tensile strength, rigidity, and hardness, making them the default choice for load-bearing frames, brackets, and structural components. PTFE is a soft material with low tensile strength and is unsuitable for applications requiring structural integrity.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Here, PTFE has a decisive advantage. It is one of the most chemically inert substances known, resistant to nearly all common acids, bases, and solvents. Most metals, with the exception of noble metals or specialized alloys, are susceptible to corrosion or chemical attack, requiring protective coatings for use in harsh environments.
Friction and Self-Lubrication
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often cited between 0.02 and 0.05. This makes it naturally "slippery" and self-lubricating. Metals have a much higher coefficient of friction and require external lubricants like oil or grease to operate in sliding applications.
Weight and Density
PTFE is significantly lighter than even the lightest structural metals. Its density is roughly 2.2 g/cm³, whereas aluminum is ~2.7 g/cm³ and steel is ~7.8 g/cm³. This makes PTFE an excellent choice for applications where weight reduction is a primary goal.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Unfilled vs. Filled PTFE
Not all PTFE is the same. The addition of fillers dramatically changes its properties, bridging some of the gap between it and harder materials.
The Purity of Unfilled PTFE
Unfilled, or virgin, PTFE offers the highest purity, best chemical resistance, and lowest coefficient of friction. It is also the softest and easiest to machine. It is the ideal choice for seals, gaskets, and electrical insulators where these pure properties are paramount.
The Durability of Filled PTFE
Filled PTFE contains additives like glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance specific properties. These fillers increase hardness, wear resistance, and resistance to "creep" (deformation under load). However, this comes at a cost: filled grades are more abrasive, requiring harder tooling and slower machining speeds, and their chemical resistance may be slightly reduced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting between PTFE and metal is not a matter of which is superior, but which is appropriate for the task.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Choose metals like aluminum or steel for their unparalleled strength, stiffness, and load-bearing capacity.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance or low friction: Choose PTFE for components like seals, bearings, bushings, and pump parts exposed to corrosive media.
- If your primary focus is a complex, lightweight, non-structural part: Choose unfilled PTFE, as its exceptional machinability makes it ideal for producing intricate geometries quickly and cost-effectively.
Ultimately, your material selection is determined by a clear understanding of whether your design prioritizes mechanical strength or specialized properties like inertness and lubricity.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | Metals (e.g., Steel, Aluminum) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Chemical inertness, low friction | Structural integrity, high strength |
| Machinability | High speed, low tool wear | Slower speed, significant tool wear |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists most acids/bases | Poor to moderate, often requires coatings |
| Friction Coefficient | Very low (0.02-0.05), self-lubricating | High, requires external lubricants |
| Weight (Density) | Lightweight (~2.2 g/cm³) | Heavy (e.g., steel ~7.8 g/cm³) |
| Ideal For | Seals, bearings, non-structural parts | Load-bearing frames, structural components |
Need High-Precision PTFE or Metal Components?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing custom PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) and metal parts for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver precision production from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your parts meet exact specifications for performance and durability.
Let us help you select the ideal material and manufacturing process for your project. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















