At a fundamental level, PTFE is the superior electrical performer for high-frequency applications due to its significantly lower dielectric constant and dissipation factor. In contrast, standard FR4 material, while having higher signal losses at frequency, provides excellent and cost-effective insulation and voltage handling for the vast majority of mainstream electronics.
The core decision between FR4 and PTFE is not about finding the "better" material, but about matching the material's properties to your application's frequency and budget. FR4 is the default for a reason—it's good enough for most things—while PTFE is a specialized tool for high-performance needs.

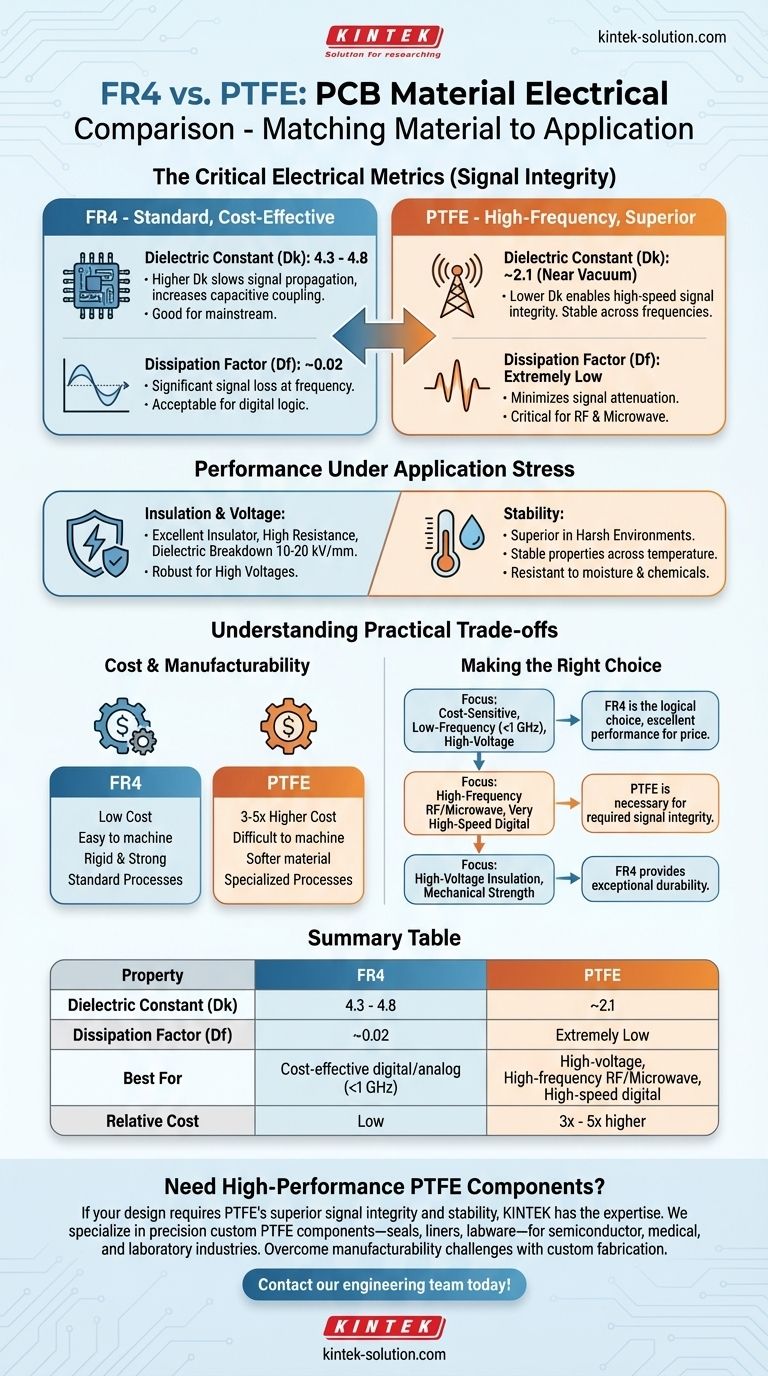
The Critical Electrical Metrics: Dk and Df
The primary electrical differences between FR4 and PTFE are defined by two key parameters: the dielectric constant (Dk) and the dissipation factor (Df). These properties directly impact signal integrity, especially as frequency increases.
Dielectric Constant (Dk): The Speed and Integrity Factor
A material's dielectric constant (Dk) measures its ability to store electrical energy. A lower Dk is almost always better for high-speed signal integrity.
PTFE has a Dk of approximately 2.1, which is very close to a vacuum and highly stable across a wide frequency range.
FR4 has a much higher Dk, typically between 4.3 and 4.8. This higher value can slow down signal propagation and increase unwanted capacitive coupling between traces.
Dissipation Factor (Df): The Signal Loss Factor
The dissipation factor (Df), or loss tangent, quantifies how much of a signal's energy is absorbed and lost as heat within the PCB material itself.
PTFE exhibits an extremely low Df, minimizing signal attenuation. This is critical for preserving the strength of high-frequency signals as they travel across the board.
FR4 has a significantly higher Df of around 0.02. This level of loss is often acceptable for digital logic and low-frequency analog signals but becomes a major source of signal degradation in RF and microwave circuits.
Performance Under Application Stress
While Dk and Df are critical for signal integrity, other properties define a material's suitability for general-purpose and high-power use.
Insulation and Voltage Handling
FR4 is an excellent insulator. It features very high insulation resistance, preventing current leakage between layers and traces.
Furthermore, FR4 has a high dielectric breakdown voltage of 10-20 kV/mm, making it a robust and reliable choice for applications involving high voltages where signal frequency is not the primary concern.
Stability in Operating Environments
PTFE offers superior performance in harsh environments. Its properties remain stable across a wide range of temperatures, and it is highly resistant to moisture absorption and chemical exposure.
FR4, while robust, can see its electrical properties shift with significant changes in temperature and humidity, a factor that can be problematic for highly sensitive circuits.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
The decision to use a specific PCB material is never based on electrical properties alone. Cost and manufacturability are often the deciding factors.
Cost: The Dominant Consideration
The cost difference is stark. A PTFE-based PCB can be 3 to 5 times more expensive than an equivalent board made from FR4.
This premium is due to both the higher cost of the raw PTFE material and the specialized manufacturing processes required to fabricate it effectively.
Manufacturability and Mechanical Properties
FR4 is a rigid, strong material reinforced with fiberglass. It is easy to drill, mill, and process using standardized, cost-effective techniques.
PTFE is a much softer material, which makes it more difficult to machine with precision. This adds complexity and cost to the fabrication process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Design
Selecting the correct material requires aligning your primary design goal with the material's strengths.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive digital logic or low-frequency analog (below ~1 GHz): FR4 is the clear and logical choice, offering excellent performance for the price.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency RF, microwave, or very high-speed digital circuits: PTFE is necessary to maintain the required signal integrity and minimize loss.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation and mechanical strength: FR4 provides exceptional performance and durability at a fraction of the cost of specialized materials.
Ultimately, choosing the right PCB material is about using the right tool for the job to meet your performance targets without over-engineering your solution.
Summary Table:
| Property | FR4 | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | 4.3 - 4.8 | ~2.1 |
| Dissipation Factor (Df) | ~0.02 | Extremely Low |
| Best For | Cost-effective digital/analog (<1 GHz), High-voltage insulation | High-frequency RF/Microwave, High-speed digital |
| Relative Cost | Low | 3x - 5x higher |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Critical Application?
If your design requires the superior signal integrity and stability of PTFE, KINTEK has the expertise to deliver. We specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries.
We help you overcome the manufacturability challenges of PTFE, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let's discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance. Contact our engineering team today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















