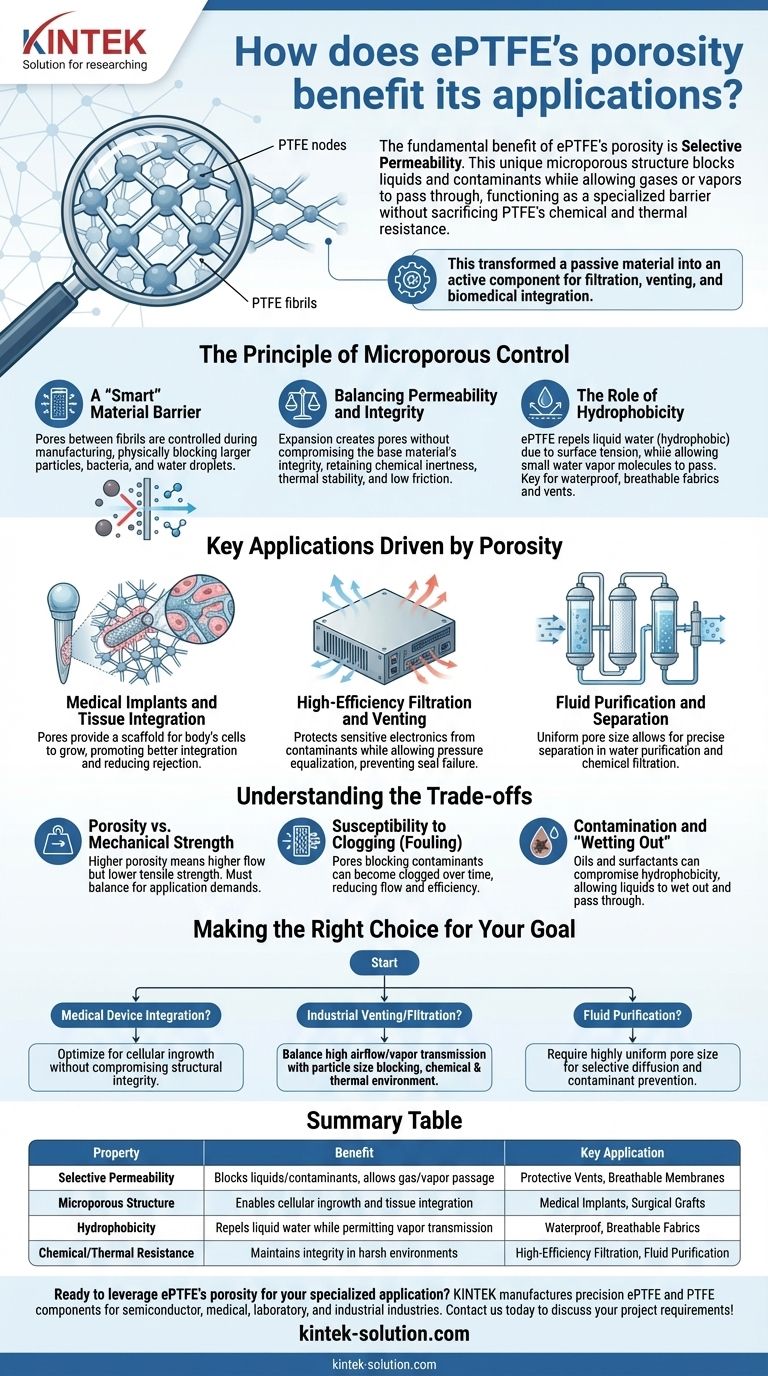
The fundamental benefit of ePTFE's porosity is selective permeability. This unique microporous structure, formed by stretching solid PTFE, creates a material that can block liquids and contaminants while allowing gases or vapors to pass through. This capability allows ePTFE to function as a highly specialized barrier without sacrificing the exceptional chemical and thermal resistance inherent to PTFE.
The porosity of ePTFE is not simply a series of holes; it is an engineered network that allows designers to precisely control how a material interacts with its environment. This transforms a passive material into an active component for filtration, venting, and biomedical integration.

The Principle of Microporous Control
The value of expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is rooted in the "expansion" process itself. This process creates a microscopic architecture of solid nodes interconnected by thin fibrils, resulting in a material that is mostly empty space but remains structurally sound.
A "Smart" Material Barrier
Think of the ePTFE structure as a highly sophisticated screen. The size of the pores between the fibrils can be controlled during manufacturing to a very fine degree.
This allows the material to act as a "smart" barrier, physically blocking particles, bacteria, or liquid water droplets that are larger than the pores.
Balancing Permeability and Integrity
Crucially, the expansion process creates these pores without compromising the base material's integrity.
The resulting ePTFE membrane retains the remarkable properties of solid PTFE: it is chemically inert, stable across a wide range of temperatures, and has a very low coefficient of friction.
The Role of Hydrophobicity
ePTFE is naturally hydrophobic, meaning it repels liquid water. This property works in tandem with its porosity.
While the pores are large enough to allow small water vapor molecules (gas) to pass through easily, the material's surface tension prevents liquid water from penetrating them. This is the key principle behind its use in waterproof, breathable fabrics and protective vents.
Key Applications Driven by Porosity
The ability to control what passes through a material has unlocked critical applications across multiple industries. Each use case leverages the porous structure in a distinct way.
Medical Implants and Tissue Integration
In medical applications like surgical grafts or implants, the pores of ePTFE provide a scaffold.
This structure allows the body's own cells to grow into the material, promoting better integration, reducing the chance of rejection, and creating a more durable and natural bond between the implant and the surrounding tissue.
High-Efficiency Filtration and Venting
For industrial and electronics applications, ePTFE serves as a high-performance filter or vent.
It can protect sensitive electronics from water, dust, and dirt while allowing heat and pressure to equalize with the outside environment, preventing seal failure. This dual function of protection and breathability is a direct result of its controlled porosity.
Fluid Purification and Separation
In specialized filtration systems, ePTFE membranes are used to separate components in a fluid stream.
The uniform pore size allows for precise separation, enabling applications like water purification or filtering aggressive chemicals that would destroy other membrane materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the porous nature of ePTFE is not without practical limitations that must be considered in any design.
Porosity vs. Mechanical Strength
There is an inherent trade-off between porosity and strength. A material with higher porosity (and thus higher flow rates) will generally have lower tensile strength than a denser ePTFE variant or solid PTFE.
Engineers must select a grade that balances the required permeability with the mechanical demands of the application.
Susceptibility to Clogging (Fouling)
In any filtration application, the pores that block contaminants can eventually become clogged by them.
This phenomenon, known as fouling, can reduce flow rates and efficiency over time, potentially requiring cleaning cycles or eventual replacement of the ePTFE membrane.
Contamination and "Wetting Out"
While hydrophobic, the surface of ePTFE can be compromised by oils or surfactants. These contaminants can lower the surface tension and allow liquids to "wet out" the membrane, enabling them to pass through the pores and defeating its barrier function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal ePTFE configuration depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is medical device integration: You need a pore structure optimized for cellular ingrowth without compromising the implant's long-term structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is industrial venting or filtration: You must balance a high airflow or vapor transmission rate with the specific particle size you need to block, all while considering the chemical and thermal environment.
- If your primary focus is fluid purification: You require a highly uniform and controlled pore size to ensure selective diffusion and prevent the breakthrough of contaminants under operational pressures.
Ultimately, leveraging ePTFE's porosity is about precisely controlling the boundary between two environments to achieve a specific technical outcome.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Selective Permeability | Blocks liquids/contaminants, allows gas/vapor passage | Protective Vents, Breathable Membranes |
| Microporous Structure | Enables cellular ingrowth and tissue integration | Medical Implants, Surgical Grafts |
| Hydrophobicity | Repels liquid water while permitting vapor transmission | Waterproof, Breathable Fabrics |
| Chemical/Thermal Resistance | Maintains integrity in harsh environments | High-Efficiency Filtration, Fluid Purification |
Ready to leverage ePTFE's porosity for your specialized application? KINTEK manufactures precision ePTFE and PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom membranes—for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial industries. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in microporous control ensures optimal performance for filtration, venting, or biomedical integration. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Purity for Your Samples
- What is PTFE (Teflon) and what are its key properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How do PTFE properties benefit butterfly valve performance? Enhance Durability & Efficiency
- What are the chemical resistance properties of PTFE labware? The Ultimate Guide to Inert Labware
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE lined and hard seal butterfly valves? Ensure Optimal Performance and Safety



















