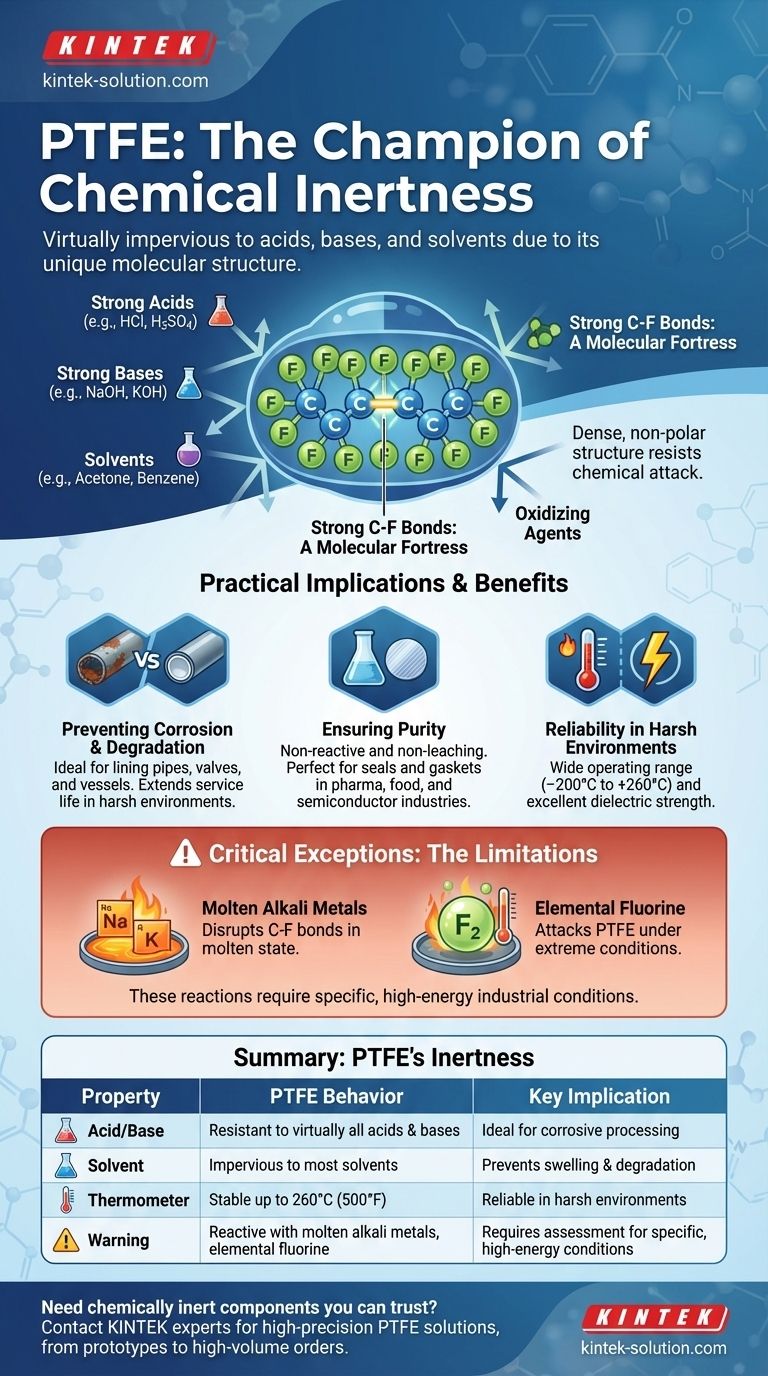
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically inert materials known. Its molecular structure makes it virtually impervious to chemical attack from nearly all acids, bases, solvents, and reactive chemicals. This remarkable resistance is why it is a default material choice in highly demanding industrial, laboratory, and processing environments.
PTFE's extreme chemical resistance is not a surface-level feature but a direct result of its incredibly stable molecular bonds. While it is inert to almost everything, a few highly reactive substances under specific conditions can attack it, making it critical to know these exceptions.

The Foundation of PTFE's Inertness
The chemical behavior of PTFE is not an accident; it is engineered at a molecular level. Understanding this foundation explains why it performs so reliably across such a wide range of applications.
A Stable Molecular Structure
The PTFE molecule consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon is completely sheathed by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This creates a dense, non-polar, and tightly bonded molecular "fortress" that is exceptionally difficult for other chemicals to break into and react with.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Because of this stable structure, PTFE does not react with corrosive substances like strong acids, alkalis, and potent oxidizing agents. It remains physically and chemically unchanged when exposed to these materials.
This property ensures that components made from PTFE will not degrade, dissolve, or swell, even during long-term contact with aggressive chemicals.
Practical Implications Across Industries
PTFE's inertness is not just a scientific curiosity; it is a critical performance attribute that solves real-world challenges in a variety of sectors.
Preventing Corrosion and Degradation
In chemical, petrochemical, and manufacturing industries, PTFE is used to line pipes, valves, and vessels. It provides a non-reactive barrier that protects equipment from corrosive substances, extending service life and preventing costly failures.
Ensuring Purity in Sensitive Processes
For pharmaceutical, food, and semiconductor manufacturing, preventing contamination is paramount. Since PTFE does not react with or leach into materials it contacts, it is an ideal choice for seals, gaskets, tubing, and processing equipment.
Reliability in Harsh Environments
PTFE's chemical resistance complements its other properties, such as its wide operating temperature range (–200°C to +260°C) and excellent dielectric strength. This makes it a superior material for wire insulation and components used in chemically aggressive and high-temperature settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Exceptions
No material is perfect, and true expertise lies in knowing its limitations. While PTFE is almost universally inert, there are a few specific, high-energy exceptions where it can be attacked.
Molten Alkali Metals
Highly reactive alkali metals in their molten state, such as sodium and potassium, have enough energy to disrupt the carbon-fluorine bond and react with PTFE.
Elemental Fluorine
While PTFE is a fluoropolymer, it can be attacked by elemental fluorine itself, particularly at elevated temperatures and pressures. Certain related compounds, like chlorine trifluoride, are also aggressive enough to react with PTFE.
Use Under Pressure and Temperature
These reactions are rare and require very specific, high-energy industrial conditions. For the vast majority of applications, PTFE remains completely inert and reliable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material selection should always be guided by the specific chemical environment and operating conditions of your project.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive acids, bases, or solvents: PTFE is an exceptionally reliable choice that will not degrade or react under almost all common chemical processing conditions.
- If your primary focus is purity for food, pharma, or laboratory use: PTFE's inertness ensures it will not leach substances or contaminate your process, making it an ideal material for wetted parts.
- If your environment involves molten alkali metals or elemental fluorine: You must avoid PTFE, as these are the rare conditions under which its chemical structure will break down, leading to material failure.
Understanding both PTFE's remarkable inertness and its specific limitations is the key to leveraging it safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Behavior | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Acid & Base Resistance | Resistant to virtually all acids and bases | Ideal for corrosive chemical processing |
| Solvent Resistance | Impervious to most solvents | Prevents swelling and degradation |
| High-Temperature Limit | Stable up to 260°C (500°F) | Reliable performance in harsh environments |
| Critical Exceptions | Reactive with molten alkali metals, elemental fluorine | Requires assessment for specific, high-energy conditions |
Need chemically inert components you can trust?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment is protected from even the most aggressive chemicals, guaranteeing purity, preventing contamination, and extending service life.
Let us provide you with a reliable solution tailored to your specific chemical environment. Contact our experts today for a consultation on custom PTFE fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some additional physical properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Discover PTFE's Elite Thermal & Chemical Resistance
- Why is PTFE's low friction coefficient significant? Unlock Superior Efficiency and Longevity
- Can PTFE be modified with additives? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are the hydrophobic properties of PTFE? The Science of Permanent Water Repellency
- How does PTFE function as a lubricant? Master Low-Friction Performance in Harsh Environments
- What are the key properties of PTFE? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What makes PTFE a valuable material in industrial applications? Its Unique Properties Solve Critical Challenges
- Are there any chemicals that have severe effects on PTFE? Understanding the Limits of Its Inertness



















