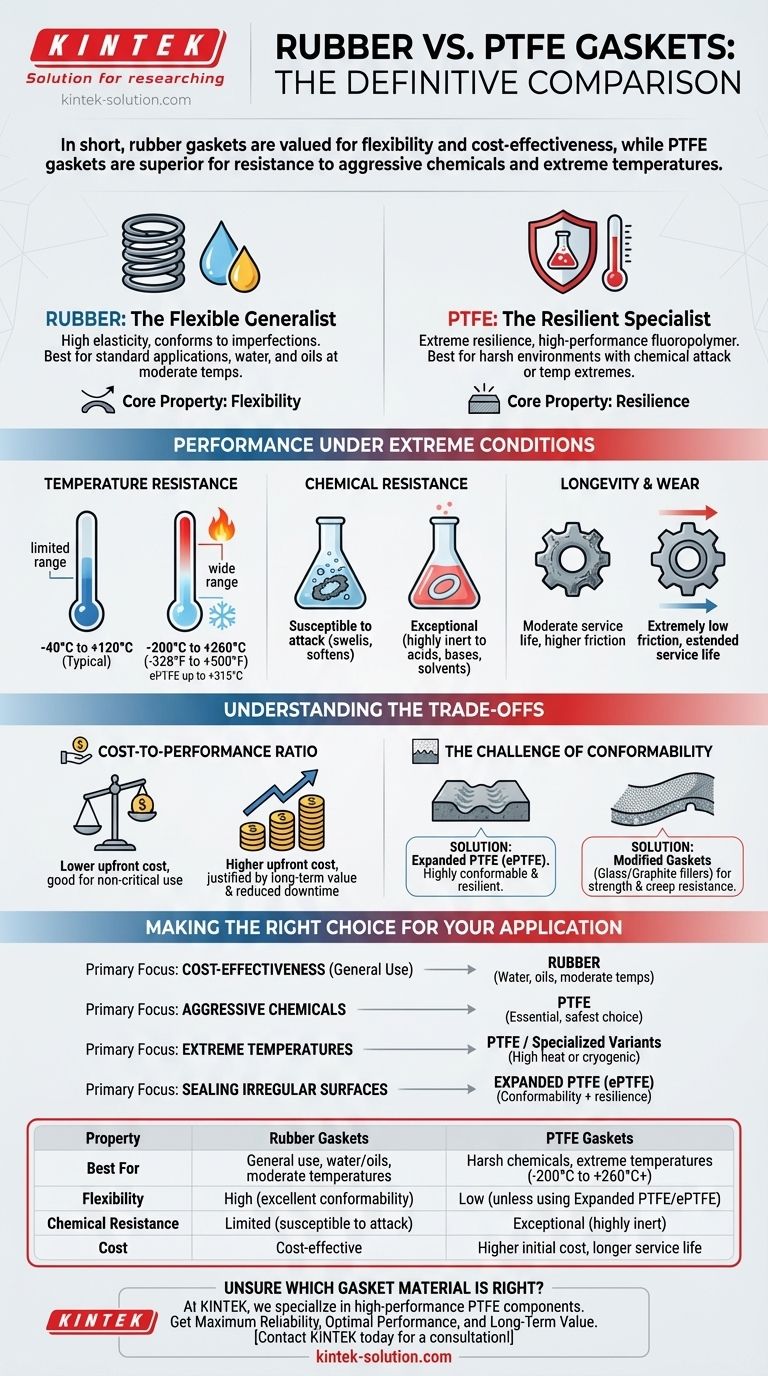
In short, rubber gaskets are valued for their flexibility and cost-effectiveness in general applications, while PTFE gaskets are superior for their exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures. Rubber is a reliable, economical choice for sealing water or oil in moderate conditions. In contrast, PTFE is the definitive material for harsh industrial environments where failure due to chemical attack or temperature degradation is not an option.
The decision between rubber and PTFE is not about which material is universally "better," but which is optimally suited for the specific operating conditions. The choice hinges on a critical trade-off between cost, flexibility, and the material's inherent resilience to thermal and chemical stress.

Core Properties: Flexibility vs. Resilience
The fundamental differences between rubber and PTFE stem from their molecular structures, which dictate how they perform under pressure, heat, and chemical exposure.
Rubber: The Flexible Generalist
Rubber is known for its high elasticity, allowing it to conform easily to surface imperfections and create a tight seal with relatively low bolt force.
This makes it an excellent, cost-effective choice for a wide range of standard applications, particularly those involving water and oils at moderate temperatures.
PTFE: The Resilient Specialist
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance fluoropolymer. Its primary characteristic is its extreme resilience.
It is engineered to withstand conditions that would cause most other materials, including rubber, to fail quickly. Its value lies in its stability and reliability in demanding environments.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
When evaluating gaskets for industrial use, performance at the operational extremes is the most critical factor. Here, the advantages of PTFE become clear.
Temperature Resistance: A Clear Winner
PTFE gaskets exhibit superior thermal stability, capable of operating for long durations in temperatures from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
Some specialized variants, like expanded PTFE, can handle an even broader range, from -268°C to 315°C (-450°F to 600°F). This makes PTFE the only viable choice for cryogenic or high-heat processes.
Chemical Resistance: The PTFE Advantage
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert substances known. It can handle a vast array of aggressive acids, bases, and solvents without degrading.
Rubber, by contrast, is susceptible to chemical attack and will swell, soften, or dissolve when exposed to incompatible fluids, leading to seal failure.
Longevity and Wear
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient offriction, creating a smooth, non-stick surface.
This characteristic significantly reduces wear on both the gasket and the sealing surfaces, extending the service life of the equipment and maintaining a more reliable seal over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gasket requires acknowledging the compromises between different materials and even different versions of the same material.
The Cost-to-Performance Ratio
Rubber is significantly more cost-effective on a per-unit basis, making it ideal for large-scale, non-critical applications.
However, the higher upfront cost of a PTFE gasket is often justified by its much longer service life and the prevention of costly downtime or hazardous leaks in critical systems.
The Challenge of Conformability
Traditional rubber's elasticity gives it an advantage in sealing rough or uneven flange surfaces. Pure, rigid PTFE can sometimes struggle to conform to these imperfections.
This is where Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is invaluable. It is created to be highly conformable and flexible while retaining the exceptional chemical and temperature resistance of PTFE.
The Evolution of PTFE: Modified Gaskets
To enhance mechanical properties, pure PTFE is often modified with fillers like glass fiber or graphite.
These additions improve the gasket's strength, durability, and resistance to "creep" (deformation under load), making them superior to pure PTFE for high-pressure applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by the demands of your specific operating environment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general use: Choose rubber for non-critical applications involving water, oils, and moderate temperatures.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is the essential and safest choice due to its near-total chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability: PTFE or its specialized variants are required for any process operating at very high or cryogenic temperatures.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular surfaces in a harsh environment: Select Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) to get the ideal combination of conformability and resilience.
Ultimately, selecting the correct gasket material is a foundational element of ensuring system safety, reliability, and long-term operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Property | Rubber Gaskets | PTFE Gaskets |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | General use, water/oils, moderate temperatures | Harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures (-200°C to +260°C+) |
| Flexibility | High (excellent conformability) | Low (unless using Expanded PTFE/ePTFE) |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited (susceptible to attack) | Exceptional (highly inert) |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Higher initial cost, longer service life |
Unsure which gasket material is right for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals and gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get a sealing solution that guarantees:
- Maximum Reliability: Prevent costly downtime and hazardous leaks in critical systems.
- Optimal Performance: Benefit from our custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific temperature and chemical requirements.
- Long-Term Value: Our precision-engineered PTFE components offer superior longevity, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Let our experts help you select or design the perfect seal. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















