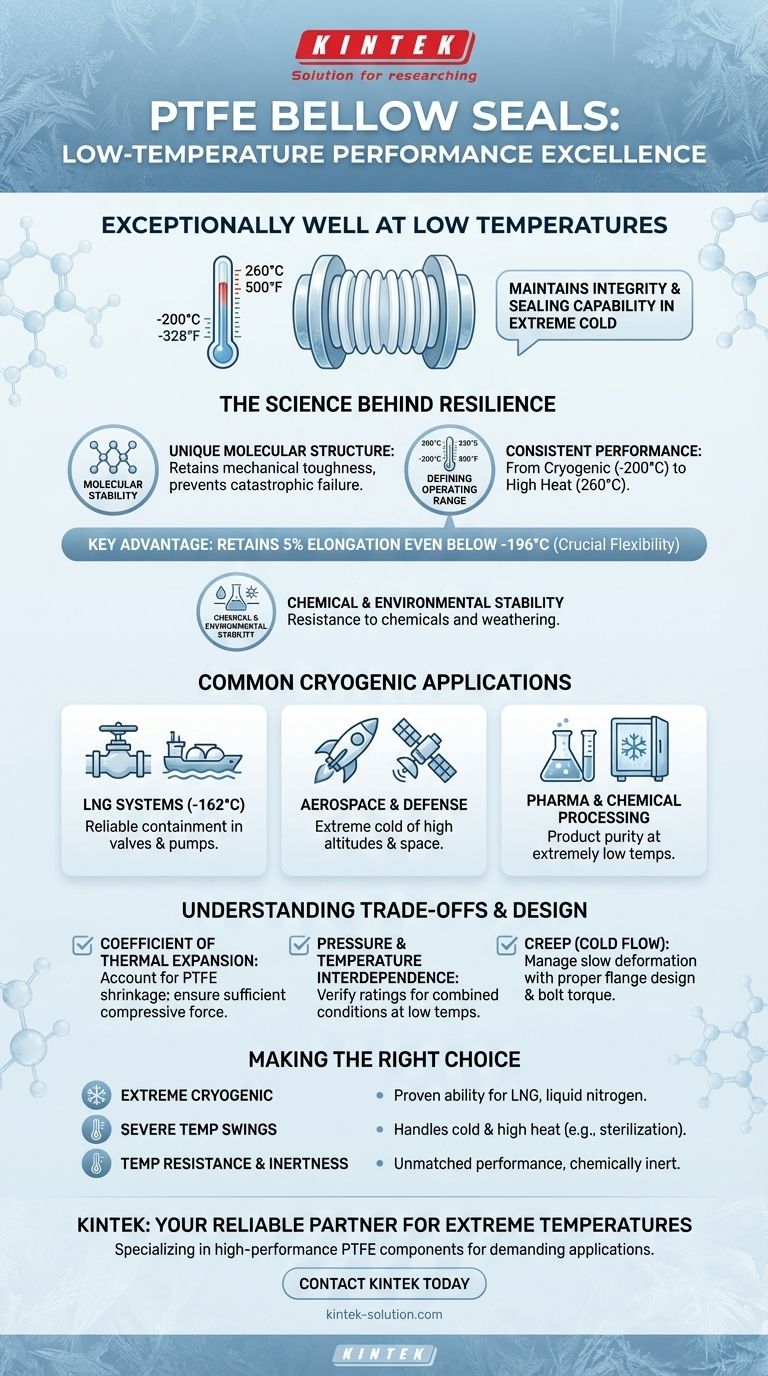
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) bellow seals perform exceptionally well at low temperatures. They are specifically engineered to maintain their integrity and sealing capability in extreme cold. Due to their inherent mechanical toughness, PTFE seals can operate effectively in temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F) and can even maintain critical flexibility at cryogenic temperatures below -196°C (-321°F).
While many materials become brittle and fail in extreme cold, PTFE's unique molecular stability allows it to retain mechanical toughness and prevent catastrophic seal failure. This makes it a primary choice for cryogenic and severe low-temperature applications where reliability is non-negotiable.

The Science Behind PTFE's Low-Temperature Resilience
To understand why PTFE is so effective in the cold, we need to look at its core material properties. Its performance isn't an accident; it's a direct result of its molecular structure.
Defining the Operating Range
PTFE is renowned for its incredibly wide functional temperature range. It provides consistent and reliable performance from cryogenic conditions around -200°C (-328°F) all the way up to 260°C (500°F).
Retaining Mechanical Toughness
The most critical attribute for a low-temperature seal is its ability to avoid becoming brittle. PTFE excels here, maintaining 5% elongation even at temperatures below -196°C.
This means the material can still stretch slightly and flex under load without cracking, which is essential for maintaining a tight seal as components contract and shift in the cold.
Inherent Chemical and Environmental Stability
PTFE is virtually inert and highly resistant to weathering. This means its low-temperature performance is not degraded by exposure to harsh chemicals or environmental conditions, ensuring a long and predictable service life.
Common Applications in Cryogenic Environments
The reliability of PTFE at low temperatures makes it a go-to material for some of the most demanding industries.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
In LNG systems, seals are constantly exposed to temperatures around -162°C (-260°F). PTFE bellow seals are used in valves, pumps, and transfer lines to provide reliable containment and prevent dangerous leaks.
Aerospace and Defense
Components in aerospace applications are often exposed to the extreme cold of high altitudes or space. PTFE seals are used for handling cryogenic rocket propellants and in systems that must function reliably in freezing environments.
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Processing
Many pharmaceutical and specialized chemical processes require extremely low temperatures. PTFE bellow seals ensure product purity and operational safety by providing a stable, non-reactive seal that withstands both the cold and the processed media.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While PTFE is an exceptional material, its successful application depends on understanding its behavior and designing the system accordingly.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high rate of thermal contraction compared to metals. When designing a sealed joint, engineers must account for how much the PTFE seal will shrink in the cold. A proper design ensures that sufficient compressive force (load) is maintained on the seal at the lowest operating temperature to prevent leaks.
Pressure and Temperature Interdependence
A seal's performance is a function of both pressure and temperature. A PTFE seal rated for a specific pressure at ambient temperature may have a different rating at -190°C. Always verify that the specific seal is rated for the combined pressure and temperature of your application.
Creep (Cold Flow)
Under a constant compressive load, PTFE can exhibit "creep," or a slow deformation over time. While less pronounced at very low temperatures, it is a factor that must be managed through proper flange design and bolt torque procedures to ensure a long-lasting, leak-free seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure optimal performance, match the seal's capabilities to your primary operational need.
- If your primary focus is extreme cryogenic service (e.g., LNG, liquid nitrogen): PTFE is an excellent first choice due to its proven ability to maintain toughness and flexibility at these temperatures.
- If your primary focus is reliability in environments with severe temperature swings: PTFE's ability to handle both extreme cold and high heat (e.g., systems that are steam-sterilized and then run cold) makes it uniquely versatile.
- If your primary focus is both temperature resistance and chemical inertness: PTFE is nearly unmatched, providing a reliable seal that will not degrade when exposed to aggressive media, regardless of the temperature.
By understanding PTFE's inherent strengths and key design considerations, you can confidently specify bellow seals for the most demanding low-temperature services.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance at Low Temperatures |
|---|---|
| Operating Range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Flexibility (Elongation) | Maintains 5% elongation even below -196°C |
| Key Advantage | Resists brittleness, prevents catastrophic seal failure |
| Common Applications | LNG systems, aerospace, pharmaceutical processing |
Need a reliable seal for extreme temperatures?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including bellow seals, for demanding applications in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a seal that delivers unwavering reliability in cryogenic environments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific low-temperature sealing requirements and leverage our material expertise for your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















