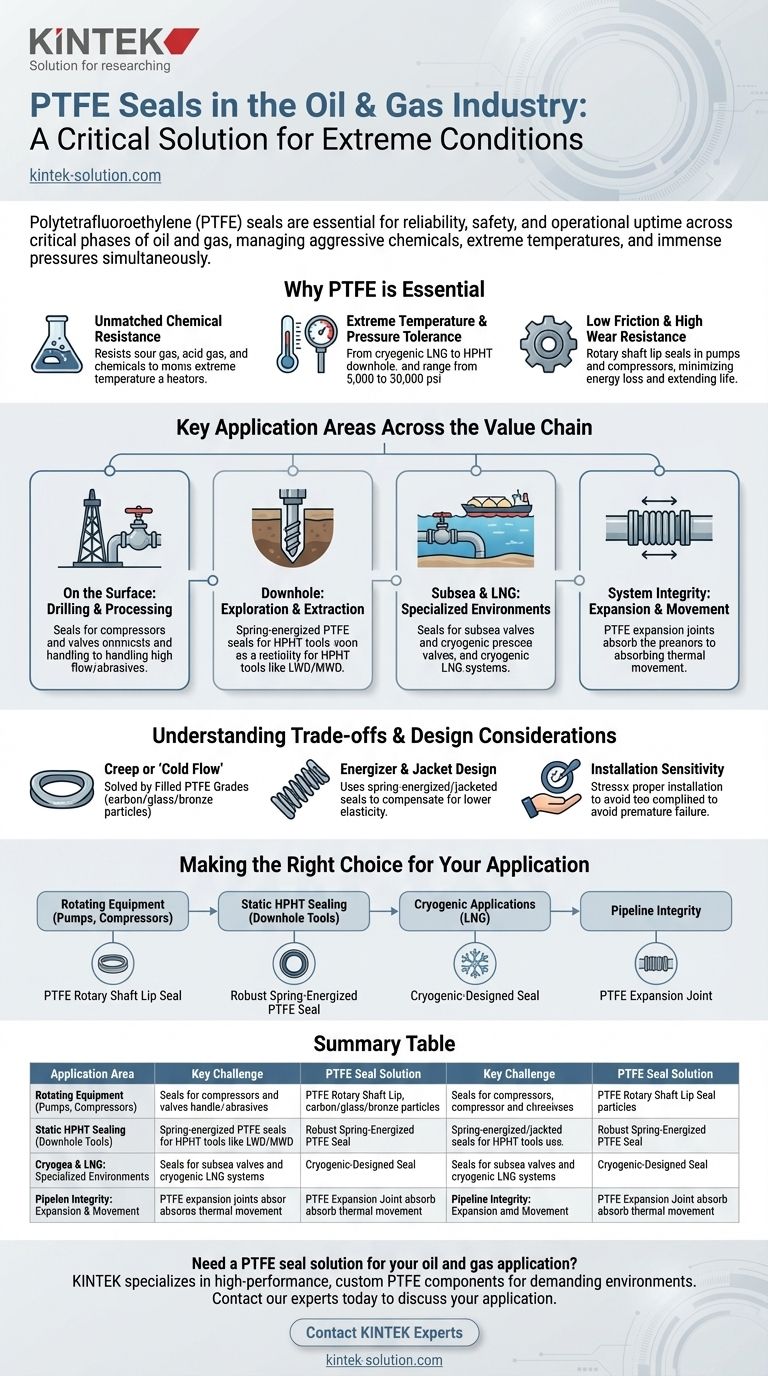
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) seals are applied in nearly every critical phase of the oil and gas industry due to their unique ability to withstand the sector's extreme operating conditions. They are found in everything from surface drilling equipment and LNG pipelines to downhole tools operating in high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) environments deep within the earth. Their reliability is essential for preventing leaks, ensuring safety, and maintaining operational uptime.
The core challenge in oil and gas is managing aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and immense pressures simultaneously. PTFE seals are the default solution because their chemical inertness and physical resilience are unmatched by most other materials, making them indispensable for ensuring the integrity and safety of critical equipment.

Why PTFE is Essential for Oil & Gas Operations
The selection of a sealing material is not a trivial decision; it is a fundamental engineering choice that impacts safety, efficiency, and profitability. PTFE has become a cornerstone material because it directly solves the most severe challenges inherent to oil and gas extraction and processing.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
Oil and gas streams are rarely pure. They often contain highly corrosive materials like sour gas (hydrogen sulfide) and acid gas (carbon dioxide), along with steam and various aggressive chemicals used in the extraction process. PTFE is virtually chemically inert, meaning it will not degrade or swell when exposed to these substances, ensuring a long-lasting and reliable seal.
Extreme Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
Operations can range from the cryogenic temperatures required for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) to the extreme heat of downhole environments. PTFE seals, particularly spring-energized designs, maintain their integrity across this vast temperature spectrum. They are engineered to handle immense pressures, routinely performing in environments from 5,000 to 30,000 psi (345 to 2070 bar), which is critical for subsea and deep-well operations.
Low Friction and High Wear Resistance
Much of the equipment in the oil and gas industry involves constant motion. Rotary shaft lip seals made from PTFE are vital for pumps, compressors, motors, and gearboxes. The material's inherently low coefficient of friction minimizes energy loss and heat generation, while its excellent wear resistance extends the service life of both the seal and the equipment itself.
Key Application Areas Across the Value Chain
PTFE seals are not a single product but a category of solutions tailored to specific needs. Their application can be seen across the entire operational landscape, from the surface to the seabed.
On the Surface: Drilling and Processing
Surface equipment like drilling rigs, pumps, and valves handle high flow rates and abrasive materials. PTFE seals are used here to provide reliable sealing in compressors and valves that control the flow of hydrocarbons, preventing leaks that could be hazardous and costly.
Downhole: Exploration and Extraction
This is one of the most demanding environments on Earth. Downhole tools, including Logging While Drilling (LWD) and Measurement While Drilling (MWD) instruments, rely on PTFE seals to protect sensitive electronics from extreme HPHT conditions. Here, spring-energized PTFE seals are critical for maintaining integrity under immense pressure and heat.
Subsea and LNG: Specialized Environments
Subsea equipment faces the dual challenge of high external pressure and corrosive seawater. PTFE seals ensure the long-term reliability of subsea valves and connectors. In LNG facilities, PTFE's excellent performance at cryogenic temperatures makes it the ideal choice for seals in pipes, valves, and loading systems, preventing the volatile gas from escaping.
System Integrity: Expansion and Movement
Pipelines and processing systems are subject to constant temperature fluctuations, causing them to expand and contract. PTFE expansion joints are installed to absorb this movement, preventing stress fractures and maintaining system stability and safety, especially when handling corrosive fluids.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While highly effective, PTFE is not without its limitations. A true expert understands that proper material selection and design are crucial for success.
Creep or "Cold Flow"
Standard PTFE has a tendency to deform or "creep" over time when subjected to a constant load. This is mitigated by using filled PTFE grades, where materials like carbon, glass, or bronze are added to the polymer. This enhances mechanical strength and resistance to deformation, making the seal more robust for high-pressure applications.
Energizer and Jacket Design
For the most demanding applications, a simple PTFE ring is insufficient. Spring-energized or jacketed seals use a metallic spring to provide a constant force against the sealing surface. This design compensates for the material's lower elasticity, ensuring a tight seal during pressure fluctuations, temperature changes, and wear over time. The choice of spring material and seal profile is critical to performance.
Installation Sensitivity
The performance of high-tech seals is highly dependent on correct installation. Scratches on the seal or mating hardware, improper lubrication, or incorrect sizing can lead to premature failure. Ensuring that installation is performed by trained personnel according to precise specifications is non-negotiable for critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE seal configuration depends entirely on the specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is rotating equipment (pumps, compressors): A low-friction, wear-resistant PTFE rotary shaft lip seal is the optimal choice to ensure efficiency and longevity.
- If your primary focus is static HPHT sealing (downhole tools): A robust spring-energized PTFE seal made from a filled grade is necessary to resist creep and maintain integrity under extreme forces.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic applications (LNG): A seal designed specifically for cryogenic service, with an appropriate energizer and PTFE grade, is critical to prevent embrittlement and leakage.
- If your primary focus is pipeline integrity: A PTFE expansion joint is the correct component to manage thermal movement and chemical corrosion, protecting the entire system.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of PTFE in oil and gas is about matching the right design and material composite to the precise challenges of the environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Challenge | PTFE Seal Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Drilling & Processing | Abrasive materials, high flow rates | PTFE seals for compressors and valves |
| Downhole Tools (HPHT) | Extreme pressure & temperature (>30,000 psi) | Spring-energized PTFE seals |
| Subsea Equipment | High external pressure, corrosive seawater | PTFE seals for valves and connectors |
| LNG Facilities | Cryogenic temperatures | PTFE seals for pipes, valves, and loading systems |
Need a PTFE seal solution for your oil and gas application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production ensures your equipment operates safely and efficiently, from prototype to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can provide a reliable, application-specific PTFE sealing solution for your critical operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















