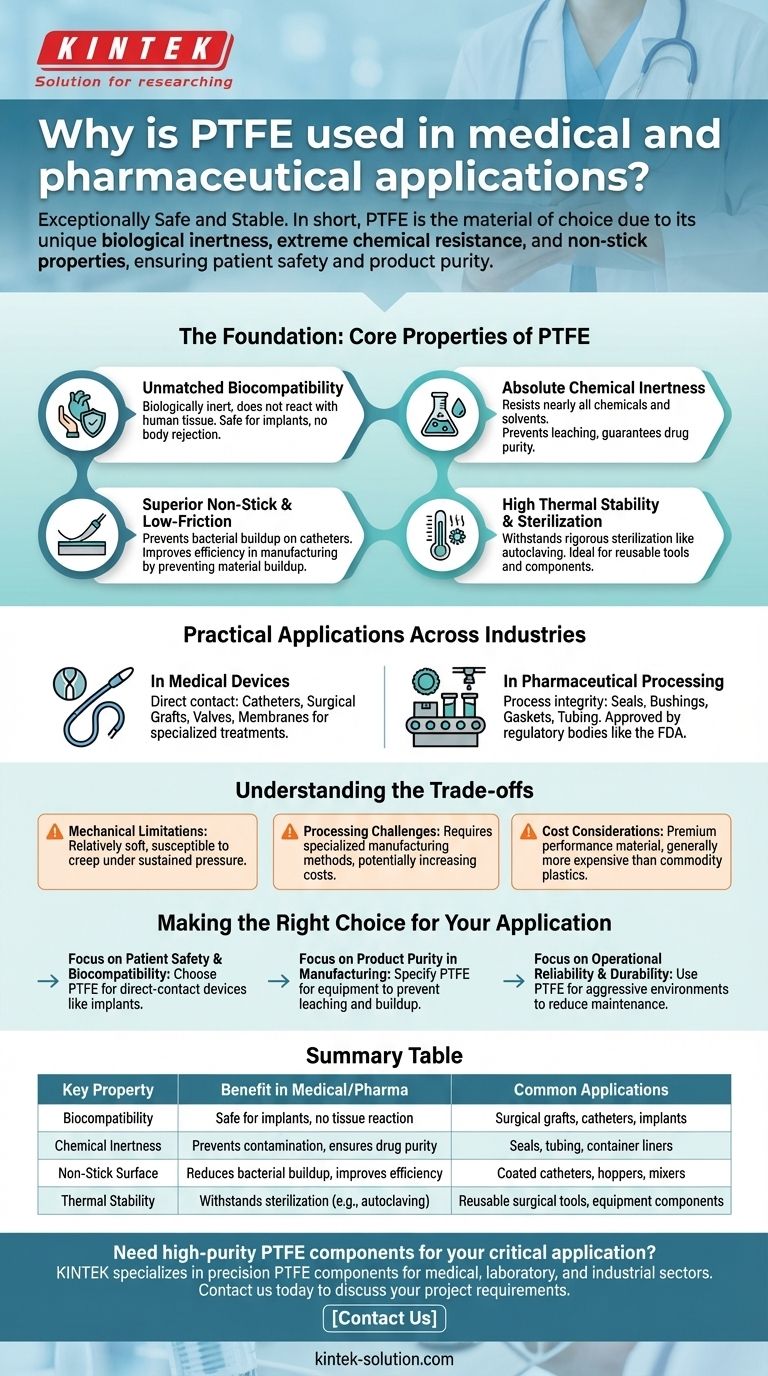
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of choice in medical and pharmaceutical applications because it is exceptionally safe and stable. Its unique combination of biological inertness, extreme chemical resistance, and non-stick properties ensures that it will not react with the human body, contaminate sensitive drug products, or degrade when exposed to harsh chemicals or sterilization processes.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread adoption goes beyond a single feature. It is the material's unique ability to simultaneously ensure patient safety, guarantee product purity, and enhance operational reliability in highly regulated and demanding environments.

The Foundation: Core Properties of PTFE
To understand why PTFE is so trusted, we must first examine its fundamental characteristics. These properties work in concert to deliver the safety and performance required in medical and pharmaceutical settings.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
PTFE is biologically inert, meaning it does not react with human tissue or bodily fluids. This is the single most important property for any material used inside the body.
Because of this, components like surgical grafts and implants made from PTFE are not rejected by the body. Even microscopic debris from PTFE seals in processing equipment can pass through the body without consequence.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
The material is renowned for its resistance to nearly all chemicals, including aggressive solvents and strong oxidizers used in drug manufacturing.
This property is critical for applications like tubing, container liners, and seals. It guarantees that the PTFE component will not degrade and, more importantly, will not leach harmful substances into a pharmaceutical product, ensuring its purity and safety.
Superior Non-Stick and Low-Friction Surface
PTFE's famous non-stick surface is a significant advantage in both medical and manufacturing contexts.
In medical devices, this low-friction quality is used to coat catheters, which makes them easier to insert and helps inhibit the buildup of bacteria that can lead to infections.
In pharmaceutical processing, it prevents valuable and often sticky drug compounds from building up on equipment like hoppers and mixers, which improves production efficiency and reduces cross-contamination between batches.
High Thermal Stability and Sterilization
PTFE has a high melting point and excellent thermal stability.
This allows medical devices and equipment components made from PTFE to withstand rigorous sterilization methods, such as autoclaving, which is a mandatory step for reusable surgical tools and other critical items.
Practical Applications Across the Industries
These core properties translate directly into tangible benefits and a wide range of uses across both the medical and pharmaceutical fields.
In Medical Devices
PTFE is a component in countless medical devices where direct contact with the body is required. Common examples include catheters, surgical grafts, valves, and membranes used in specialized treatments like glaucoma surgery. Its inertness is paramount for patient safety.
In Pharmaceutical Processing
In drug manufacturing, PTFE ensures process integrity. It is used for seals, bushings, gaskets, and tubing in equipment that handles corrosive chemicals. Its durability and non-stick nature keep production lines running smoothly and prevent contamination.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
PTFE's long history of safe use means it is recognized and approved by regulatory bodies like the FDA for use in pharmaceutical applications. Selecting PTFE can simplify the compliance process for new equipment and devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its advantages are clear, PTFE is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to metals or other high-performance polymers. It is not ideal for high-load, structural applications and can be susceptible to creep under sustained pressure.
Processing Challenges
Unlike many common plastics, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-extrusion or injection molding techniques. This requires specialized manufacturing methods that can influence component design and increase costs.
Cost Considerations
PTFE is a premium performance material and is generally more expensive than commodity plastics. Its use is best justified in applications where its specific properties of inertness, chemical resistance, or low friction are critical requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use PTFE should be driven by the most critical requirement of your project.
- If your primary focus is patient safety and biocompatibility: PTFE is an industry standard for direct-contact devices like implants, catheters, and surgical grafts due to its inert nature.
- If your primary focus is product purity in manufacturing: Specify PTFE for processing equipment like tubing, liners, and seals to prevent chemical leaching and material buildup.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability and durability: Choose PTFE for components exposed to aggressive chemicals or high temperatures to reduce maintenance, minimize downtime, and extend equipment lifespan.
Choosing PTFE is a decision to prioritize safety, purity, and performance in applications where there is no room for compromise.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Medical/Pharma | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Safe for implants, no tissue reaction | Surgical grafts, catheters, implants |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination, ensures drug purity | Seals, tubing, container liners |
| Non-Stick Surface | Reduces bacterial buildup, improves efficiency | Coated catheters, hoppers, mixers |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands sterilization (e.g., autoclaving) | Reusable surgical tools, equipment components |
Need high-purity PTFE components for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your products meet the highest standards of safety, purity, and reliability, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and learn how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















