In radio frequency (RF) circuits, PTFE is considered a critical material because its exceptional electrical properties are uniquely suited for preserving signal integrity at high frequencies. Its very low dielectric constant (Dk) and low dissipation factor (Df or loss tangent) ensure that minimal signal energy is lost or distorted as it travels through the printed circuit board (PCB).
The core challenge in RF PCB design is that the board material itself can absorb and degrade the signal. PTFE is valued because it behaves more like a vacuum or "air" than typical materials, providing a near-transparent path for high-frequency signals, which is essential for performance and reliability.

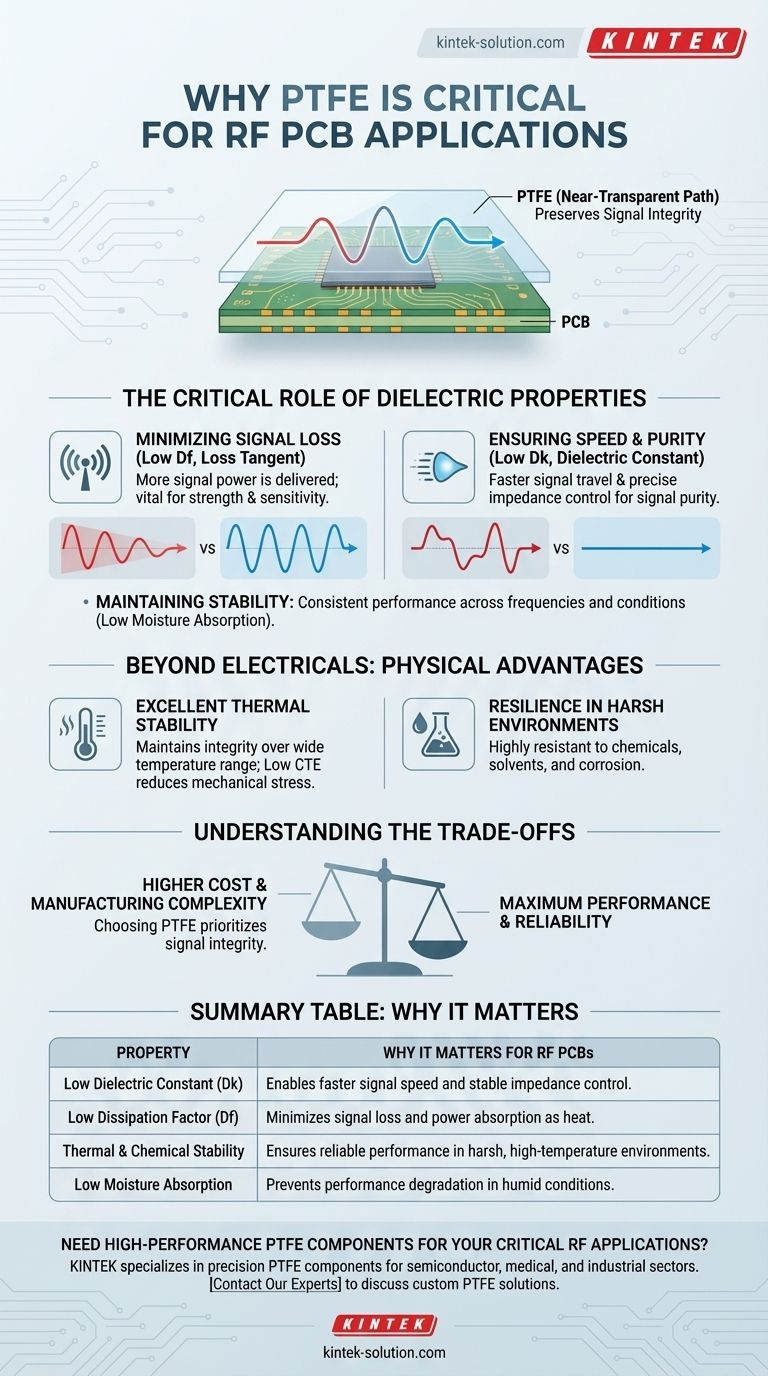
The Critical Role of Dielectric Properties in RF
For high-frequency applications, the physical substrate of a PCB is not just a mechanical support structure; it is an active component in the circuit. PTFE's properties directly address the primary challenges of high-frequency design.
Minimizing Signal Loss (Low Dielectric Loss)
At RF frequencies, a portion of the signal's electromagnetic energy can be absorbed by the PCB material and converted into heat. This phenomenon is quantified by the material's dissipation factor (Df), or loss tangent.
PTFE has an extremely low dissipation factor. This means less signal power is wasted, which is vital for preserving the strength of transmitted signals and the sensitivity of receivers.
Ensuring Signal Speed and Purity (Low Dielectric Constant)
The dielectric constant (Dk) of a material determines how fast an electrical signal travels through it. A lower Dk allows for higher signal propagation speed.
PTFE's very low and stable dielectric constant (as low as 2.2) provides two key benefits. First, it enables faster signal travel. Second, and more importantly, its consistency makes it easier to design and maintain precise trace impedance, which is crucial for preventing signal reflections and preserving signal purity.
Maintaining Stability Across Conditions
A material's electrical properties are useless if they change with operating conditions. PTFE exhibits remarkable stability.
Its Dk and Df remain consistent across a very wide frequency range, making it ideal for broadband applications. Furthermore, PTFE has very low moisture absorption, ensuring its electrical performance does not degrade in humid environments.
Beyond Electricals: The Physical Advantages of PTFE
While its electrical characteristics are primary, PTFE's physical properties reinforce its suitability for demanding RF applications.
Excellent Thermal Stability
High-frequency circuits can generate significant heat. PTFE maintains its structural and electrical integrity over a wide temperature range.
It also has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). This means the material expands and contracts very little with temperature changes, reducing mechanical stress on solder joints, traces, and vias, which significantly improves long-term reliability.
Resilience in Harsh Environments
PTFE is highly resistant to chemicals, solvents, and corrosion. This inertness makes it an ideal choice for PCBs deployed in harsh industrial, automotive, or aerospace environments.
This chemical resistance, combined with its performance at extremely low temperatures, ensures reliable operation where other materials would fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is a superior performer, it is not a universal solution. Its advantages come with practical considerations.
The Cost Factor
PTFE-based laminates are significantly more expensive than standard PCB materials like FR-4. This cost must be justified by the performance requirements of the application.
Manufacturing Complexity
PTFE is a softer material, which can present challenges during PCB fabrication, such as drilling and multilayer lamination. These processing difficulties can increase manufacturing time and overall board cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right PCB material requires balancing performance needs with project constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance at very high frequencies (e.g., microwave or mmWave): PTFE's ultra-low loss and stable dielectric constant are often non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical reliability in extreme environments (aerospace, defense): PTFE's thermal stability and chemical resistance make it a leading candidate.
- If your project is cost-sensitive or operates at lower RF frequencies: You should evaluate whether specialized FR-4 or other high-frequency laminates provide a sufficient price-to-performance ratio.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is an engineering decision to prioritize signal integrity and reliability above all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for RF PCBs |
|---|---|
| Low Dielectric Constant (Dk) | Enables faster signal speed and stable impedance control. |
| Low Dissipation Factor (Df) | Minimizes signal loss and power absorption as heat. |
| Thermal & Chemical Stability | Ensures reliable performance in harsh, high-temperature environments. |
| Low Moisture Absorption | Prevents performance degradation in humid conditions. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical RF applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get components that meet the exacting demands of RF circuitry.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's signal integrity and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















