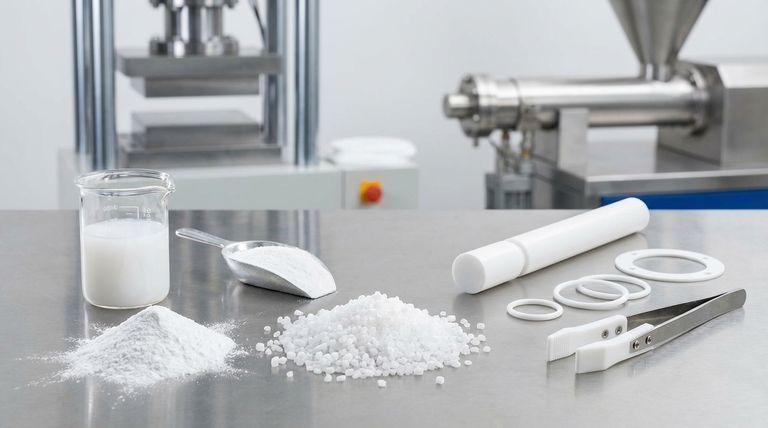
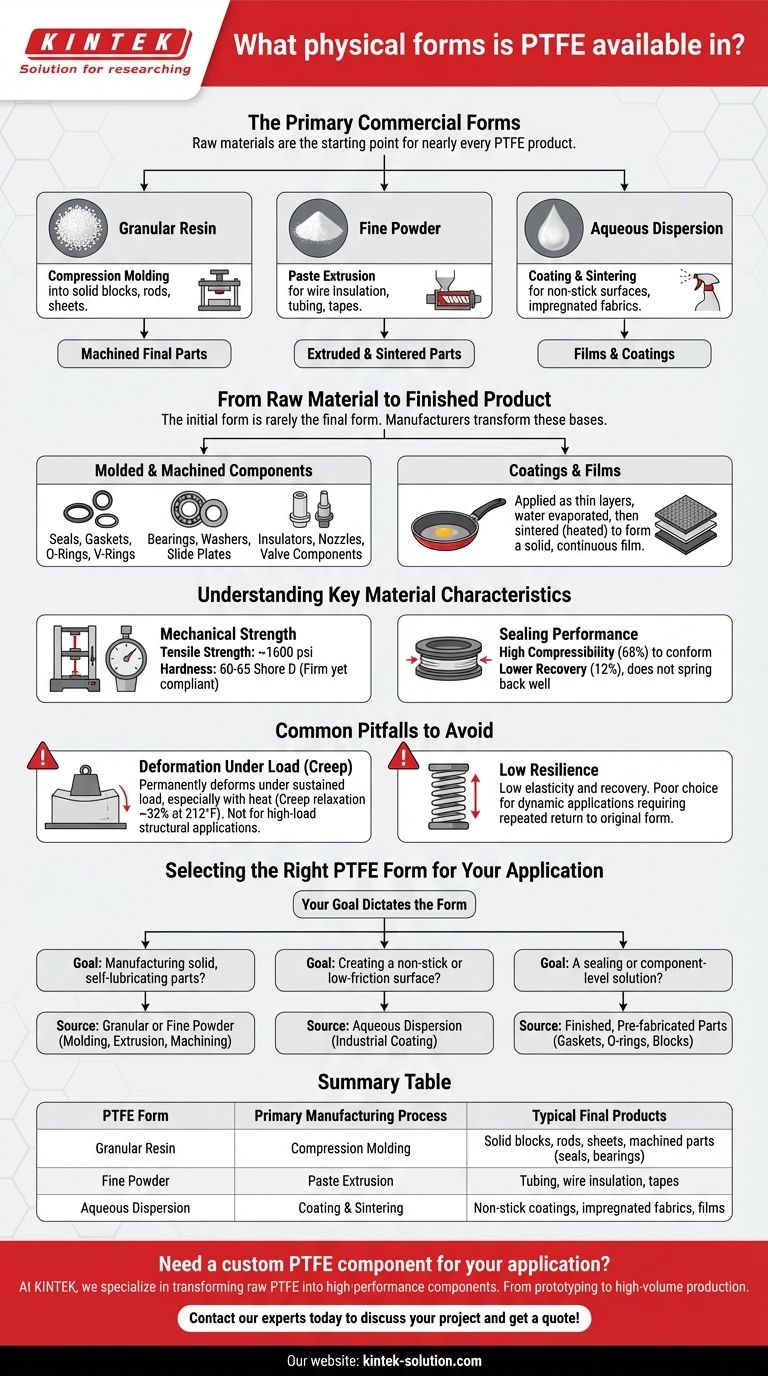
At its source, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is commercially available in three primary forms: granular resin, fine powder, and a liquid-based aqueous dispersion. These raw materials are the starting point for nearly every PTFE product, from industrial seals to non-stick coatings.
The key is to understand that PTFE's raw forms (powders and dispersions) are intermediary. Its true utility is realized when these materials are processed into a final solid component, a flexible seal, or a functional coating.

The Primary Commercial Forms
While we encounter PTFE as a solid material in finished products, it begins its lifecycle in one of three distinct raw states. Each form is optimized for a different manufacturing process.
Granular Resin
Granular PTFE is produced in a way that creates larger, more irregularly shaped particles. This form is ideal for compression molding into solid blocks, rods, and sheets. These molded shapes are then often machined into final parts.
Fine Powder
Fine powders consist of much smaller, more uniform particles than granular resins. This form is typically used in a process called paste extrusion, which is suitable for creating wire insulation, tubing, and tapes.
Aqueous Dispersion
This is a milky-white liquid where microscopic PTFE particles are suspended in water. Dispersions are the basis for coatings, most famously used for creating the non-stick surfaces on cookware. They are also used to impregnate materials like fiberglass to create high-performance composites.
From Raw Material to Finished Product
The initial form of PTFE is almost never its final form. Manufacturers use these raw materials as a base to create a vast range of functional components and surfaces.
Molded and Machined Components
The most common path for granular PTFE is transformation into solid stock shapes. These are then machined into precise, durable parts.
Common examples include:
- Seals, Gaskets, O-Rings, and V-Rings
- Bearings, Washers, and Slide Plates
- Insulators, Nozzles, and Valve Components
Coatings and Films
Aqueous dispersions are used to apply thin layers of PTFE onto other materials. After application, the water is evaporated and the PTFE is sintered (heated) to form a solid, continuous film, valued for its low-friction and non-stick properties.
Understanding Key Material Characteristics
The reason PTFE is transformed into so many shapes is due to its unique combination of physical properties. These characteristics are consistent across most solid forms of the material.
Mechanical Strength
While not as rigid as metal, PTFE offers a useful tensile strength of around 1600 psi. Its hardness is typically measured between 60 to 65 Shore D, providing a firm yet slightly compliant surface.
Sealing Performance
PTFE excels in sealing applications. It has a high compressibility (68%) allowing it to conform to surfaces, but a lower recovery (12%), meaning it doesn't spring back to its original shape as well as elastomers.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While versatile, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its unique properties create specific limitations that must be understood to prevent misapplication and failure.
Deformation Under Load (Creep)
PTFE's most significant trade-off is its tendency to creep, or slowly deform under a sustained load. Its creep relaxation is noted as 32% at 212°F, showing that it permanently deforms much more under heat. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications where tight tolerances are critical over time.
Low Resilience
Unlike rubber, PTFE has very low elasticity. Its low recovery rate means that once it is compressed into a shape, it largely stays that way. This is ideal for certain static seals but makes it a poor choice for dynamic applications that require a component to repeatedly return to its original form.
Selecting the Right PTFE Form for Your Application
Your final goal dictates which form of PTFE—raw material or finished product—you should be concerned with.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing solid, self-lubricating parts: Your process will begin with granular or fine powder PTFE for molding, extrusion, and machining.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-stick or low-friction surface: You will need to source an aqueous dispersion suitable for industrial coating processes.
- If your primary focus is a sealing or component-level solution: You should source finished, pre-fabricated parts like gaskets, O-rings, or machined blocks.
Understanding the journey from raw powder to finished product is the key to successfully leveraging PTFE's powerful properties in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Form | Primary Manufacturing Process | Typical Final Products |
|---|---|---|
| Granular Resin | Compression Molding | Solid blocks, rods, sheets, machined parts (seals, bearings) |
| Fine Powder | Paste Extrusion | Tubing, wire insulation, tapes |
| Aqueous Dispersion | Coating & Sintering | Non-stick coatings, impregnated fabrics, films |
Need a custom PTFE component for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in transforming raw PTFE into high-performance components. Whether you require precision-machined seals for the semiconductor industry, durable labware for your laboratory, or custom-fabricated parts for medical or industrial use, we deliver.
We offer end-to-end solutions from prototyping to high-volume production, ensuring your parts meet exact specifications for performance, chemical resistance, and low friction.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















