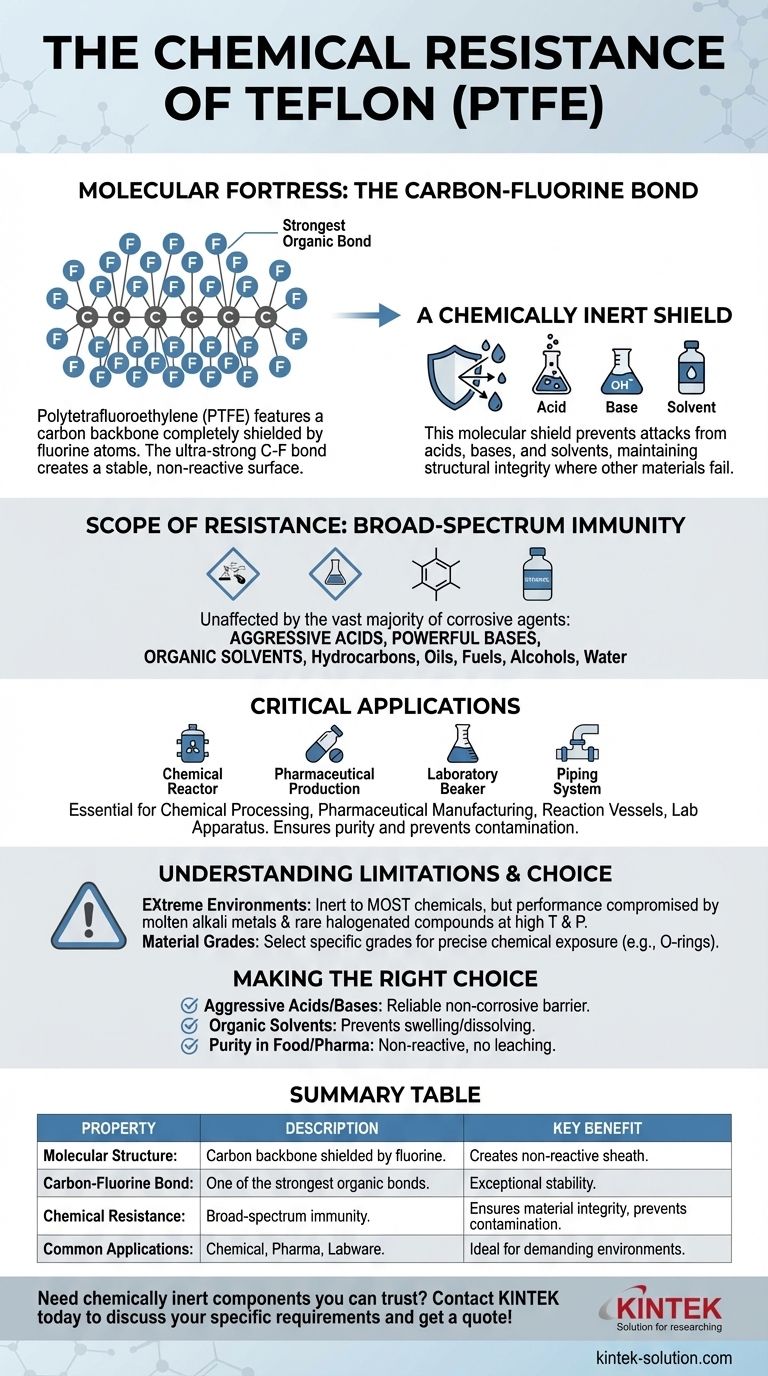
The chemical resistance of Teflon is a direct result of its molecular structure. This material, technically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is built upon a chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bonds are among the strongest known in organic chemistry, creating a stable, non-reactive surface that is impervious to nearly all common acids, bases, and solvents.
At its core, Teflon's chemical inertness isn't a complex feature—it's the simple, brute strength of the carbon-fluorine bond. This bond creates a molecular fortress that aggressive chemicals cannot breach, preventing any reaction from taking place.
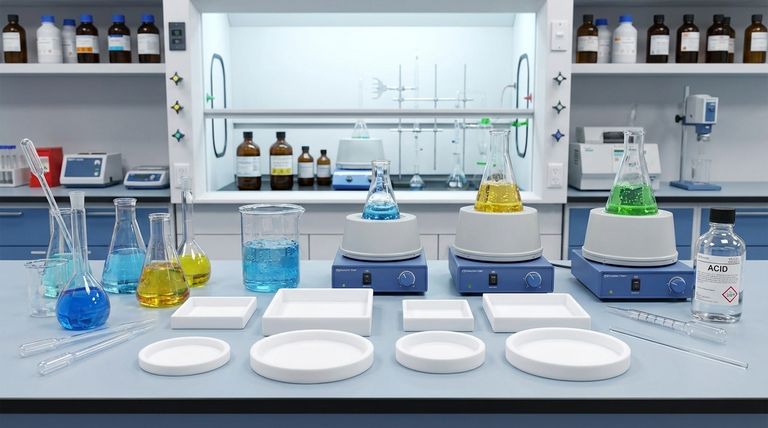

The Molecular Fortress of PTFE
To truly understand Teflon's resilience, we must look at its chemical composition. The material's properties are not an accident; they are a direct consequence of its tightly-bound and well-protected atomic structure.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The defining feature of PTFE is the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond. This bond is exceptionally strong and stable.
Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it holds onto its electrons very tightly. When bonded to carbon, it creates a short, powerful connection that requires a tremendous amount of energy to break.
A Chemically Inert Shield
Because these C-F bonds are so stable, they do not react with other chemicals. The fluorine atoms effectively form a protective, non-stick sheath around the carbon backbone of the polymer.
This molecular shield prevents acids, bases, or solvents from attacking and breaking down the underlying structure, a common failure point for materials like metals or rubbers.
The Scope of Teflon's Resistance
Teflon's robust molecular structure gives it one of the widest ranges of chemical resistance of any commercially available material. This makes it an essential component in demanding industrial and scientific settings.
Broad-Spectrum Immunity
Teflon remains completely unaffected by the vast majority of corrosive agents.
This includes aggressive acids, powerful bases, and nearly all organic solvents, as well as hydrocarbons, oils, fuels, water, and alcohols.
Where This Resistance Matters Most
This unparalleled inertness makes Teflon invaluable in environments where chemical purity and material integrity are non-negotiable.
You will find it used extensively in chemical processing equipment, pharmaceutical manufacturing, reaction vessels, piping, and critical laboratory apparatus. Its non-reactive nature ensures it will not contaminate the substances it contacts.
Understanding the Limitations
While Teflon's chemical resistance is exceptional, no material is infinitely impervious under all conceivable conditions. Understanding its boundaries is key to proper application.
Extreme Chemical Environments
Teflon is inert to most chemicals. However, its performance can be compromised by a very small number of highly reactive substances, such as molten alkali metals and some rare, halogenated compounds at high temperatures and pressures.
The Importance of Material Grades
For critical applications, chemical resistance is often measured and rated for specific compounds and concentrations. As noted with products like Teflon-encapsulated O-rings, a rating scale helps engineers select the precise material grade that guarantees performance against a specific chemical exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a material requires matching its intrinsic properties to the demands of the task. Teflon's value is clearest in scenarios where other materials would quickly fail.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive acids and bases: Teflon provides a reliable, non-corrosive barrier where metals and most other plastics would degrade.
- If your primary focus is working with organic solvents: Teflon's inertness prevents it from swelling, dissolving, or weakening, a common failure point for many rubbers and elastomers.
- If your primary focus is ensuring purity in food or pharmaceuticals: Teflon's non-reactive surface ensures it will not leach chemicals, react with, or contaminate the end product.
Ultimately, leveraging Teflon's properties allows you to engineer for stability in environments where chemical reactivity is the primary obstacle to success.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Structure | Carbon backbone shielded by fluorine atoms. | Creates a non-reactive, protective sheath. |
| Carbon-Fluorine Bond | One of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry. | Provides exceptional stability against chemical attack. |
| Chemical Resistance | Broad-spectrum immunity to acids, bases, and solvents. | Ensures material integrity and prevents contamination. |
| Common Applications | Chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, labware. | Ideal for demanding environments where purity is critical. |
Need chemically inert components you can trust?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment maintains purity and performance, even when exposed to the most aggressive chemicals.
Leverage our custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders, to solve your toughest chemical resistance challenges.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation



















