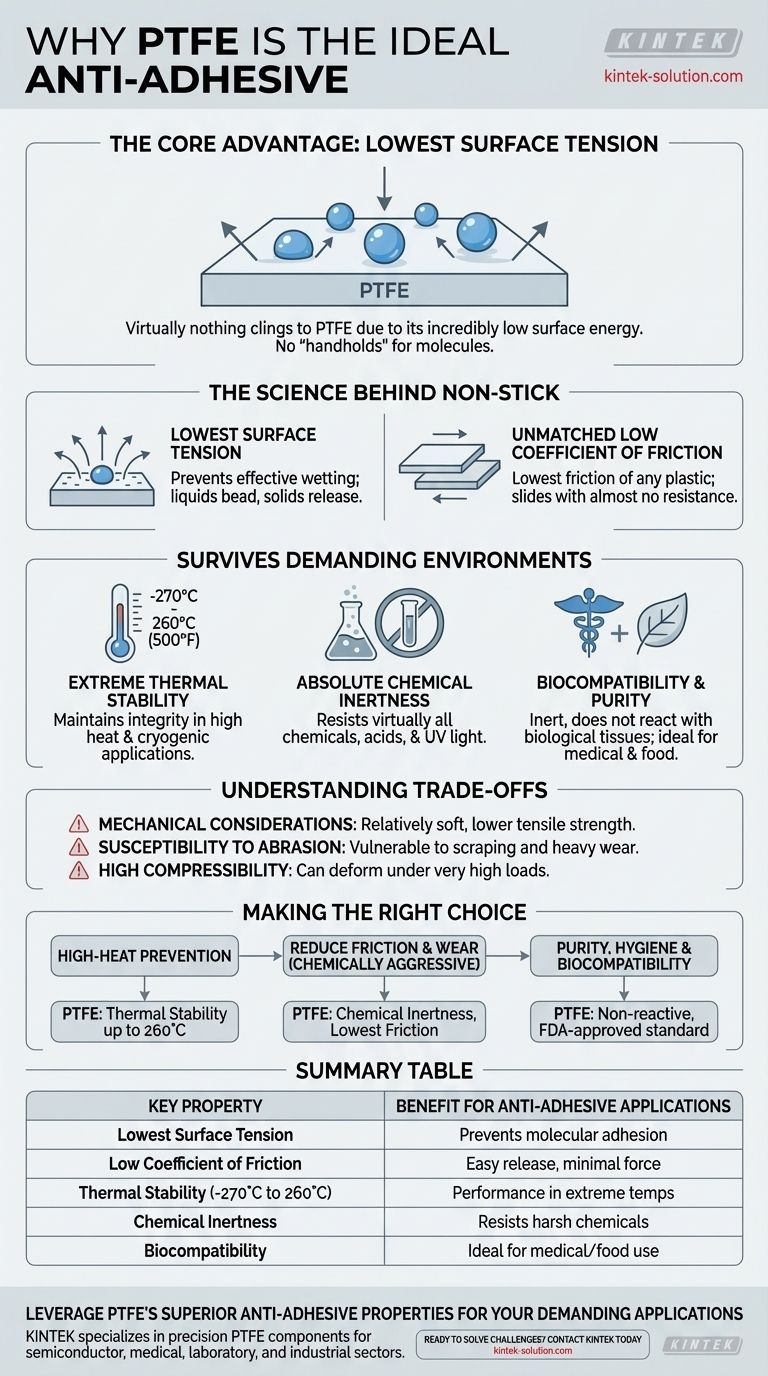
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the ideal anti-adhesive material because it has the lowest surface tension of any known solid. This unique molecular property means other substances have virtually nothing to cling to, preventing them from sticking. When this is combined with an extremely low coefficient of friction and exceptional resilience, it creates the uniquely slick, non-stick surface for which PTFE is famous.
While PTFE's non-stick quality originates from its low surface tension, its true value comes from its ability to maintain this property under extreme conditions. It is the combination of a non-stick surface with elite thermal stability and chemical inertness that makes it a definitive solution for so many demanding applications.
The Science Behind PTFE's Non-Stick Surface
To understand PTFE's effectiveness, we must look at two distinct but related properties that work in tandem. One prevents adhesion at a molecular level, while the other addresses friction at a mechanical level.
The Lowest Surface Tension
The primary reason nothing sticks to PTFE is its incredibly low surface energy. Think of it as a surface that offers no "handholds" for other molecules to grab.
This prevents any substance from effectively wetting the surface, causing liquids to bead up and solids to release effortlessly.
An Unmatched Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has the lowest coefficient of friction of any plastic, meaning surfaces slide past it with almost no resistance.
This property complements its low surface energy perfectly. Even if a substance is resting on a PTFE surface, it requires minimal force to move it, reinforcing its non-stick and easy-release characteristics. This often eliminates the need for external lubrication.
Why It Survives in Demanding Environments
A non-stick surface is only useful if it can endure its operating environment. PTFE's secondary properties are what make its primary anti-adhesive feature practical for real-world use in industry, medicine, and consumer products.
Extreme Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity across a vast temperature range, from as low as -270°C to a continuous 260°C (500°F).
This makes it the material of choice for applications involving high heat, such as non-stick cookware, or in cryogenic applications where other materials would become brittle and fail.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert, offering high resistance to almost all common chemicals, acids, and UV light.
This ensures that the anti-adhesive surface will not degrade or corrode when exposed to harsh substances, making it invaluable for gaskets, seals, and liners in the chemical processing and aerospace industries.
Biocompatibility and Purity
This same inert behavior makes PTFE biocompatible, meaning it does not react with biological tissues.
This feature, combined with its non-stick surface that resists contamination, makes it a critical material for medical transplants, implants, and equipment used in food production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and understanding PTFE's limitations is key to using it effectively. Its unique strengths are balanced by specific mechanical considerations.
Mechanical Considerations
While PTFE has good dimensional stability and creep resistance for a fluoropolymer, it is a relatively soft material. It does not possess the rigidity or high tensile strength of engineering plastics or metals.
Susceptibility to Abrasion
Because it is soft, PTFE can be susceptible to wear from scraping and heavy abrasion. In applications requiring extreme physical durability, the non-stick surface may be applied as a coating on a more robust metal substrate.
High Compressibility
PTFE's high compressibility is beneficial for creating tight seals in gaskets but means it can deform under very high loads. This must be accounted for in component design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about leveraging its unique combination of properties. Your primary goal will determine if it is the optimal choice for your application.
- If your primary focus is preventing sticking in high-heat environments: PTFE's combination of low surface tension and thermal stability up to 260°C (500°F) is its defining advantage.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear in a chemically aggressive environment: Its chemical inertness and the lowest friction coefficient of any plastic make it ideal for seals, gaskets, and industrial liners.
- If your primary focus is purity, hygiene, and biocompatibility: PTFE's inert, non-reactive nature makes it a standard for critical medical devices and FDA-approved food processing equipment.
Ultimately, PTFE is a premier problem-solving material for any challenge where adhesion, friction, or reactivity must be eliminated.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Anti-Adhesive Applications |
|---|---|
| Lowest Surface Tension | Prevents substances from adhering at a molecular level |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Allows easy release with minimal force |
| Thermal Stability (-270°C to 260°C) | Maintains performance in extreme temperatures |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists degradation from harsh chemicals and acids |
| Biocompatibility | Ideal for medical and food-grade applications |
Leverage PTFE's superior anti-adhesive properties for your most demanding applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom fabrications—for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components maintain non-stick performance under extreme conditions.
Ready to solve your adhesion and friction challenges? Contact our team today to discuss custom PTFE solutions from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















