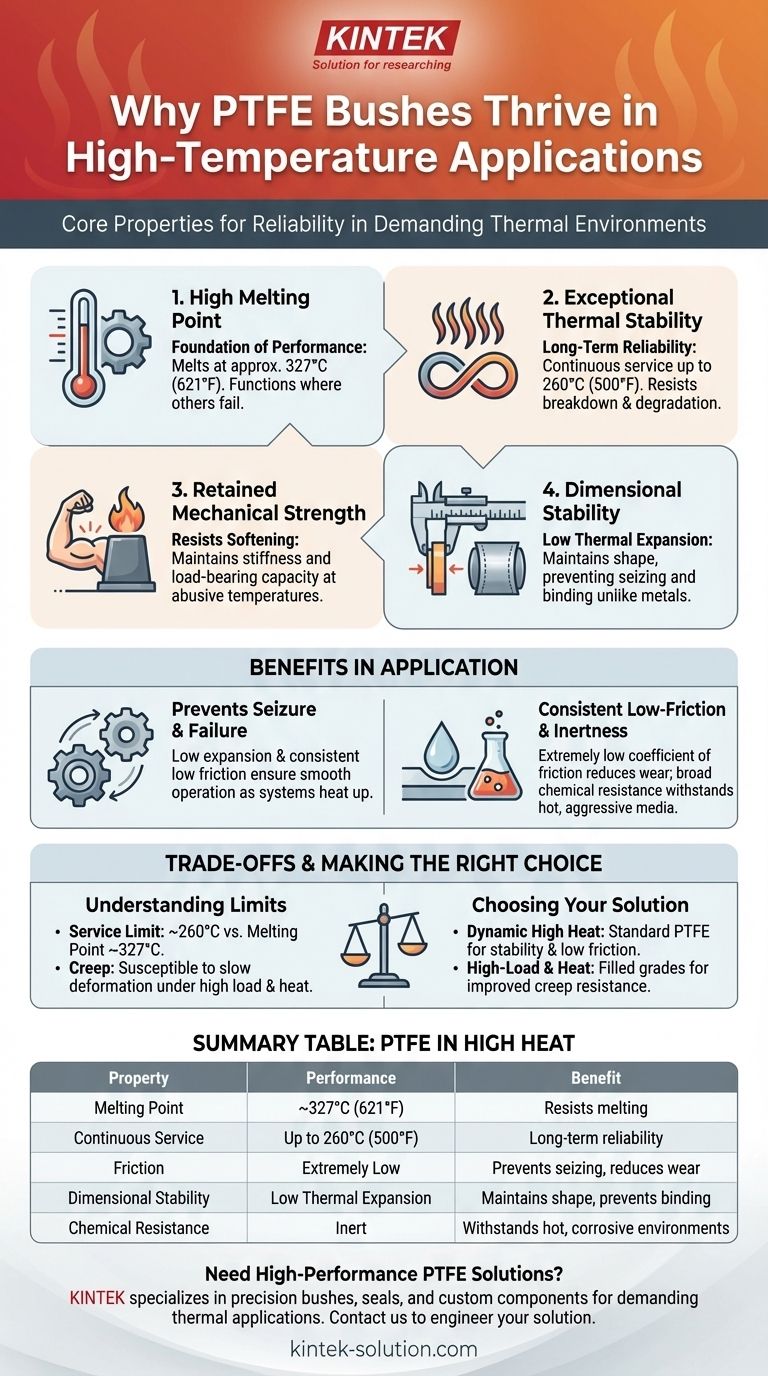
At its core, PTFE's suitability for high-temperature applications stems from its exceptionally high melting point and its unique ability to retain critical mechanical properties—like low friction and dimensional stability—even when exposed to extreme heat. Unlike many materials that deform, degrade, or fail, PTFE maintains its structural and functional integrity.
The true value of PTFE in hot environments isn't just that it resists melting. It's that it continues to perform its primary functions—providing a low-friction, stable, and chemically inert surface—at temperatures where other materials would have already failed.

The Core Properties of PTFE at High Temperatures
To understand why PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) bushes are so reliable in demanding thermal environments, we must look at a combination of its intrinsic material properties.
High Melting Point
The foundation of PTFE's performance is its high melting temperature, which is approximately 327°C (621°F). This is significantly higher than most common plastics, allowing it to function in applications where others would simply melt.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Beyond just resisting melting, PTFE demonstrates excellent thermal stability. It can withstand repeated exposure to high temperatures up to its continuous service limit of 260°C (500°F) without breaking down or chemically degrading.
This stability ensures longevity and reliability in systems that cycle through different temperature ranges.
Retained Mechanical Strength
Many materials soften and lose their strength long before they reach their melting point. PTFE, however, retains a significant amount of its stiffness and strength even at abusive temperatures.
This property is crucial for a bushing, which must support a load without deforming.
Dimensional Stability
PTFE resists significant thermal expansion, meaning it maintains its shape and size when heated. This is a critical advantage over metal bushes, which can expand with heat, potentially causing parts to seize or fail.
Why These Properties Matter in Application
These fundamental properties translate directly into tangible performance benefits in real-world engineering scenarios.
Preventing Seizure and Failure
In rotating or sliding applications, the combination of low thermal expansion and consistent low friction prevents parts from binding or seizing as the system heats up. This ensures smooth, continuous operation.
Consistent Low-Friction Performance
PTFE is famous for having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. Crucially, it maintains this extremely low friction characteristic even at high temperatures, ensuring efficiency and reducing wear on moving parts.
Broad Chemical Inertness
High temperatures often accelerate chemical reactions and corrosion. PTFE is almost completely inert, meaning it resists degradation even when exposed to hot and aggressive chemicals, fluids, or gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While exceptional, PTFE is not without its operational limits. A clear understanding of these trade-offs is essential for proper material selection.
Continuous Service vs. Melting Point
It is critical to distinguish between the melting point (~327°C) and the practical continuous service temperature (~260°C). While PTFE can survive short excursions to higher temperatures, reliable, long-term performance under mechanical load should be kept within the service limit.
Considerations for Mechanical Load
While PTFE retains strength at high temperatures, it is a relatively soft material overall and can be susceptible to "creep"—a slow, permanent deformation under sustained load. This effect can be more pronounced at higher temperatures.
For applications involving both high heat and high mechanical stress, filled grades of PTFE (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled) are often used to improve creep resistance and durability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is dynamic performance in high heat: PTFE is an outstanding choice due to its combination of thermal stability and consistently low friction, preventing seizure.
- If your primary focus is sealing hot, corrosive materials: PTFE's unparalleled chemical inertness at high temperatures makes it one of the most reliable options available.
- If your primary focus is a high-load structural component in extreme heat: Standard PTFE may not be sufficient; investigate filled PTFE grades or alternative high-performance materials to mitigate the risk of creep.
Ultimately, understanding both the strengths and limitations of PTFE allows you to engineer a more reliable and effective solution.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance at High Temperatures | Benefit for Bushes |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | ~327°C (621°F) | Resists melting in extreme heat |
| Continuous Service | Up to 260°C (500°F) | Long-term reliability without degradation |
| Friction Coefficient | Remains extremely low | Prevents seizing and reduces wear on moving parts |
| Dimensional Stability | Low thermal expansion | Maintains shape and prevents binding, unlike metals |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most chemicals | Withstands hot, corrosive fluids and gases |
Need high-performance PTFE components that won't fail under heat?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision-manufactured PTFE bushes, seals, liners, and labware designed to thrive in the most demanding thermal environments. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a solution tailored to your exact temperature, load, and chemical resistance requirements.
Let's engineer a solution for your high-temperature challenge. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















