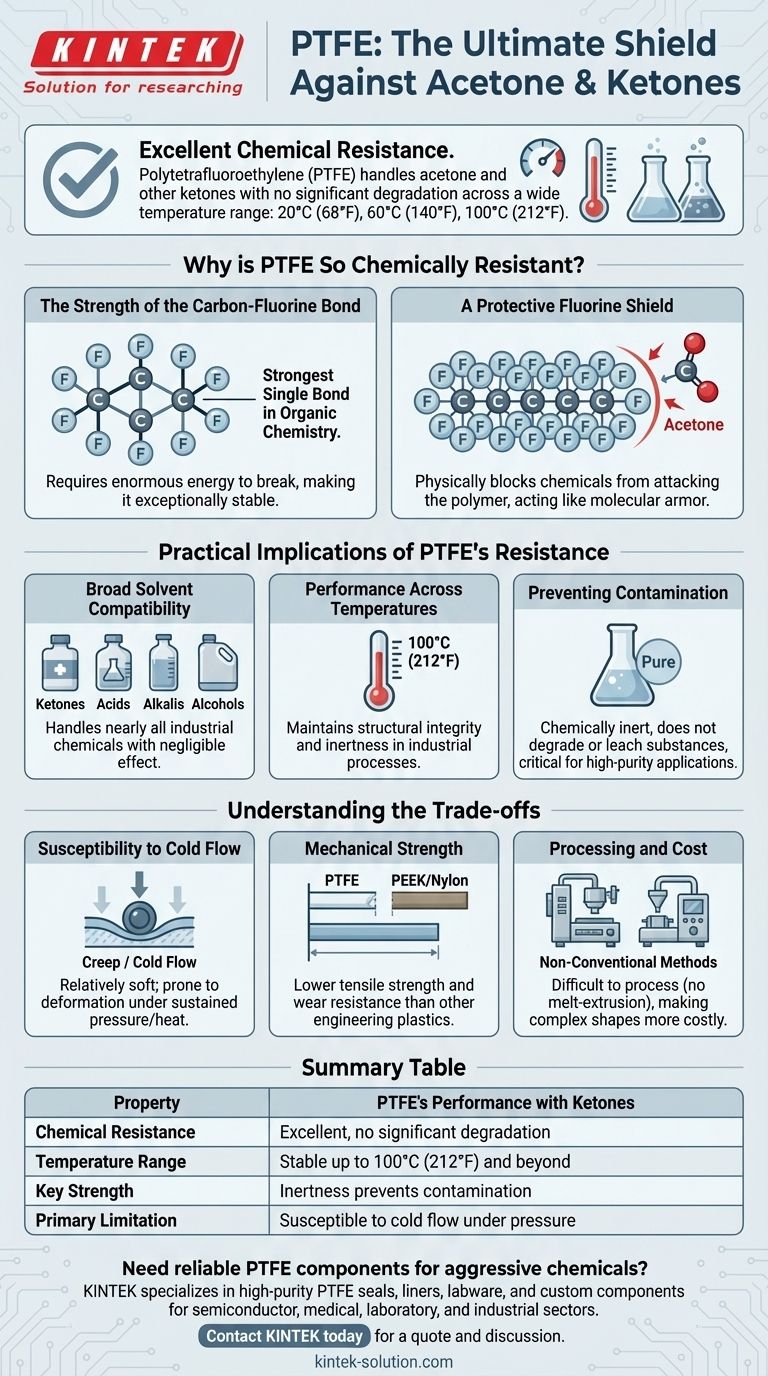
To put it directly, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has excellent chemical resistance to acetone and other ketones. This high level of resistance is maintained across a wide functional temperature range, with no significant degradation observed at temperatures of 20°C (68°F), 60°C (140°F), or even 100°C (212°F). Its compatibility is not limited to ketones; it extends to most acids, solvents, and alkalis.
The question isn't just whether PTFE can resist acetone, but why it's such a reliable choice for aggressive chemical applications. The answer lies in its unique molecular structure, which makes it one of the most chemically inert polymers available.

Why is PTFE So Chemically Resistant?
Understanding the source of PTFE's resilience is key to trusting it in a critical application. Its near-universal chemical inertness is not an accident; it is a direct result of its molecular architecture.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE is a long chain of carbon atoms, but each carbon is completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This incredible bond strength means that an enormous amount of energy is required to break it, making the molecule exceptionally stable and non-reactive.
A Protective Fluorine Shield
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. They effectively form a tight, dense, and seamless sheath around the vulnerable carbon backbone.
This "fluorine shield" physically blocks aggressive chemicals like acetone from ever reaching and attacking the polymer chain, acting like a suit of molecular armor.
Practical Implications of PTFE's Resistance
This fundamental stability translates into tangible benefits for engineering, laboratory, and industrial applications.
Broad Solvent Compatibility
While your question is about ketones, PTFE's resistance is famously broad. It can safely handle nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, alkalis, alcohols, and other organic solvents with negligible effect.
Performance Across Temperatures
The data confirms that PTFE's resistance isn't limited to room temperature. It maintains its structural integrity and inertness when exposed to ketones even at 100°C (212°F), a temperature common in many industrial processes.
Preventing Contamination
Because PTFE is so chemically inert, it does not degrade or leach substances into the chemicals it contains. This is critical for high-purity applications in pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and analytical chemistry where product purity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its chemical resistance is nearly unmatched, PTFE is not the perfect material for every situation. Its limitations are primarily mechanical, not chemical.
Susceptibility to Cold Flow
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, it can be prone to creep or cold flow, where the material slowly deforms over time. This is a critical design consideration for high-pressure seals and gaskets.
Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics like PEEK or nylon, PTFE has lower tensile strength and wear resistance. It is not typically chosen for high-load structural components.
Processing and Cost
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-extrusion or injection molding techniques, which can make manufacturing complex shapes more difficult and costly compared to other polymers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires balancing chemical needs with mechanical and environmental demands.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical handling: PTFE is an exceptional choice due to its non-reactivity and low potential for leaching or contamination.
- If you are designing a high-pressure seal: PTFE is suitable for its chemical inertness, but you must account for potential cold flow by using fillers (like glass or carbon) or proper mechanical design.
- If you need chemical transfer tubing or liners: PTFE's flexibility and broad temperature and chemical resistance make it a reliable and safe option.
Ultimately, you can confidently specify PTFE for applications involving acetone and other ketones, provided its mechanical properties meet the demands of your system.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE's Performance with Ketones |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, no significant degradation |
| Temperature Range | Stable up to 100°C (212°F) and beyond |
| Key Strength | Inertness prevents contamination |
| Primary Limitation | Susceptible to cold flow under pressure |
Need reliable PTFE components for handling aggressive chemicals like acetone?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-purity PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get components that guarantee chemical integrity and prevent contamination.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements and get a quote for PTFE solutions you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















