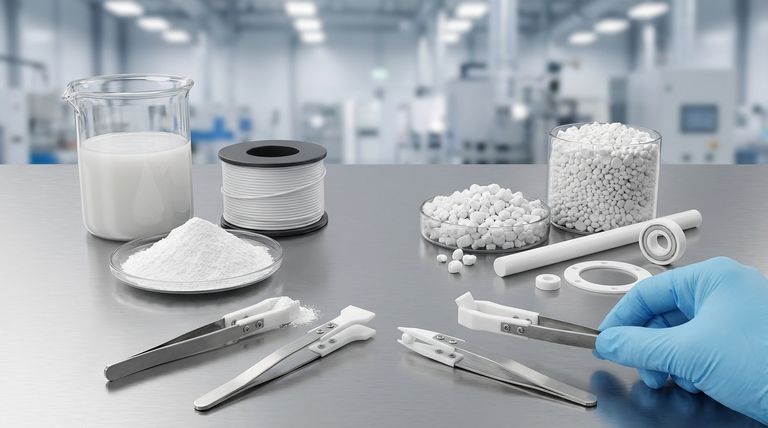
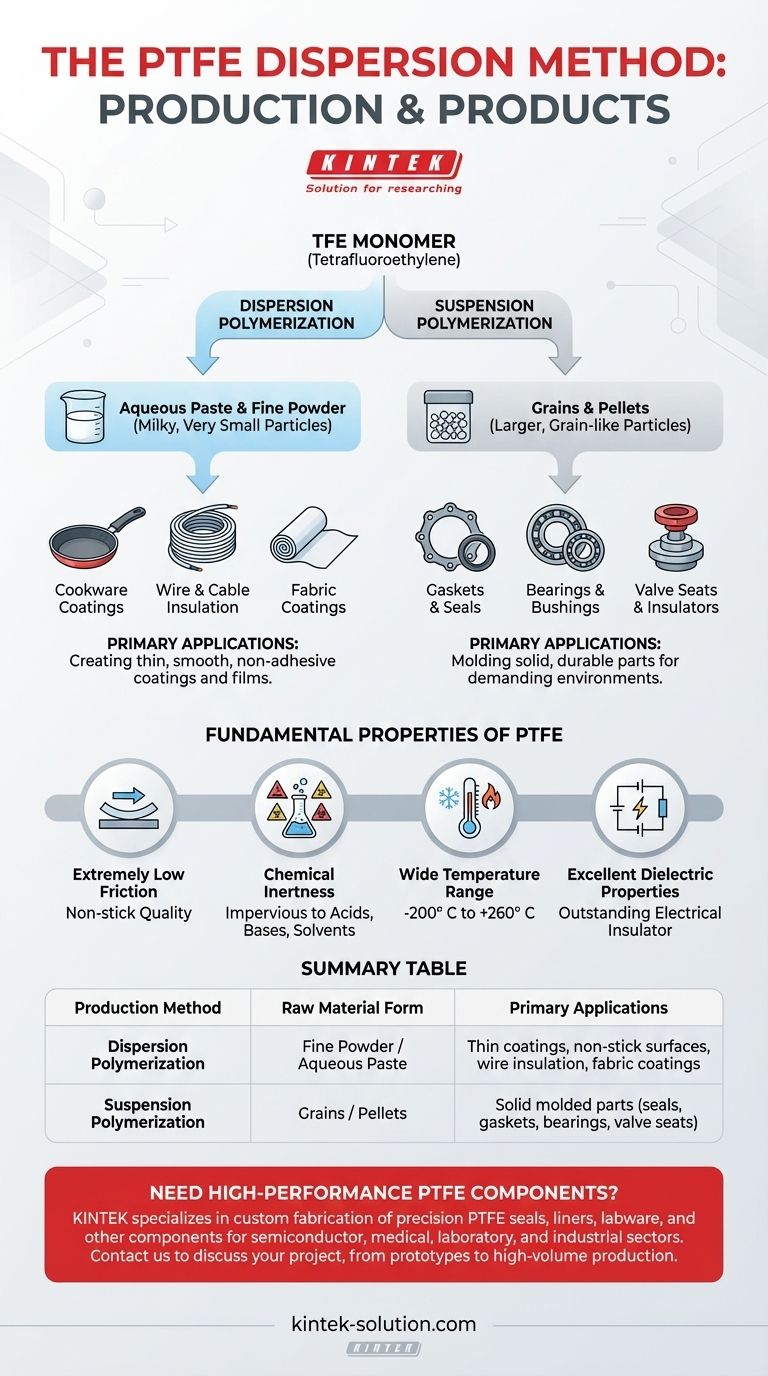
The dispersion method of producing PTFE is a polymerization process that creates the material as a milky, aqueous paste. This paste can be used directly for certain applications or further processed into a very fine powder, both of which are primarily intended for creating thin coatings and films.
The core distinction lies in the final form and its intended application. The dispersion method yields fine powders and pastes ideal for thin coatings, while the alternative suspension method produces larger grains and pellets suited for molding solid parts.

The Two Paths of PTFE Production
To fully understand the dispersion method, it is essential to contrast it with its counterpart. The manufacturing process fundamentally determines the physical form of the raw PTFE and, consequently, how it can be used in commercial products.
Dispersion Polymerization: For Coatings and Films
The dispersion method involves polymerizing the tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) monomer in water to create a stable dispersion of very small PTFE particles. This results in the milky paste mentioned earlier.
The fine particle size of this paste or the derived powder is critical. It allows the PTFE to be applied smoothly and evenly over surfaces, creating the thin, non-adhesive films for which the material is famous.
Suspension Polymerization: For Solid Components
In contrast, suspension polymerization also uses water but results in larger, grain-like particles of PTFE. These grains are not suitable for creating thin coatings.
Instead, these larger granules are designed to be processed into pellets. These pellets are the feedstock for manufacturing methods like compression molding and ram extrusion, which create solid PTFE shapes like rods, sheets, gaskets, and seals.
Understanding the End Products and Their Uses
The physical output of each polymerization method is tailored for a distinct set of applications. The choice of production method is therefore a choice about the final product's function.
Paste and Fine Powder (from Dispersion)
The primary products of the dispersion method are ideal for coating applications. Think of the non-stick surface on cookware, chemically resistant linings for industrial vessels, or low-friction coatings on wires and fabrics.
Their fine nature allows them to be formulated into liquid coatings that can be sprayed, rolled, or dipped onto a substrate before being cured with heat.
Grains and Pellets (from Suspension)
The grains and pellets from suspension polymerization are used when you need a solid piece of PTFE. This raw material is placed into a mold and subjected to heat and pressure to form a solid, durable component.
These are the parts you would find used as high-performance seals, bearings, valve seats, or electrical insulators in demanding industrial environments.
The Fundamental Properties Driving PTFE's Value
Regardless of the production method, the final material exhibits a unique combination of properties that make it an invaluable engineering polymer.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This is the property behind its famous "non-stick" quality.
Chemical Inertness
It is virtually impervious to chemical attack and shows excellent resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents.
Wide Temperature Range
PTFE performs reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, typically from –200° C to +260° C (–328° F to +500° F).
Excellent Dielectric Properties
It is an outstanding electrical insulator, making it a critical material in high-frequency electronics and cable insulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of raw PTFE is not a matter of quality but of function. The production method is the first and most critical decision point, as it dictates the material's physical form and subsequent application possibilities.
- If your primary focus is creating a thin, non-stick, or chemically resistant coating: You need PTFE produced via the dispersion method.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing solid, molded parts like seals, gaskets, or bearings: You need PTFE produced via the suspension polymerization method.
Understanding the production method is the key to unlocking the right form of PTFE for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Production Method | Raw Material Form | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Dispersion Polymerization | Fine Powder / Aqueous Paste | Thin coatings, non-stick surfaces, wire insulation, fabric coatings |
| Suspension Polymerization | Grains / Pellets | Solid molded parts (seals, gaskets, bearings, valve seats) |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
KINTEK specializes in the custom fabrication of precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and other components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require parts made from dispersion-grade powders for coatings or suspension-grade pellets for solid components, our expertise ensures superior chemical resistance, low friction, and reliable performance.
Let us help you solve your unique engineering challenge. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















