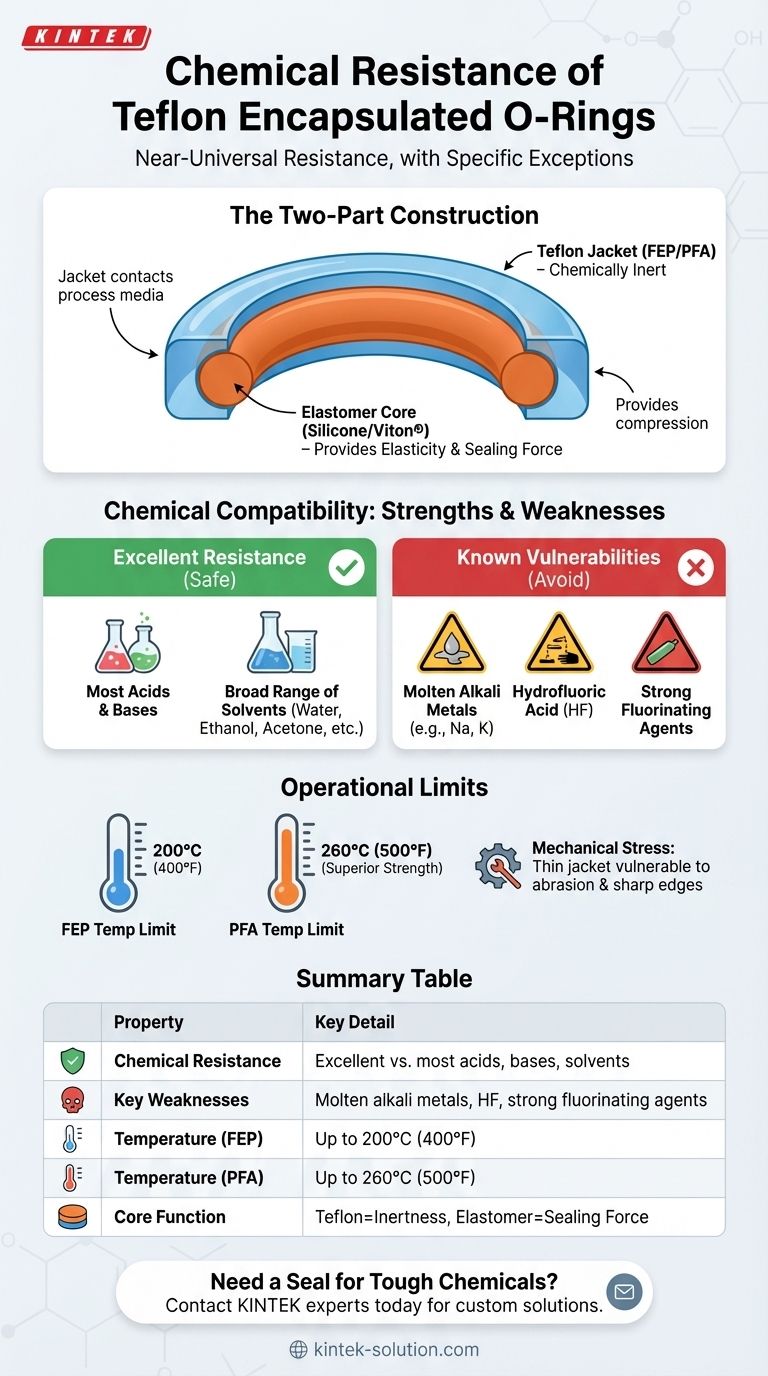
In short, Teflon encapsulated O-rings offer near-universal chemical resistance. They are designed to withstand a vast range of aggressive chemicals, including most acids, bases, and solvents, making them inert in the majority of industrial and laboratory applications. However, their performance is compromised by a specific set of chemicals, including molten alkali metals, hydrofluoric acid, and certain strong fluorinating agents.
The core principle behind a Teflon encapsulated O-ring is combining two materials: a flexible, resilient elastomer core for physical sealing properties and a chemically inert Teflon (FEP or PFA) jacket for exceptional chemical resistance. Understanding the limits of the outer jacket is the key to ensuring system integrity.

What Makes Encapsulated O-Rings So Resistant?
The unique design of these seals is what gives them their powerful combination of physical and chemical properties. This construction solves a problem where a single material cannot provide both elasticity and broad chemical inertness.
The Two-Part Construction
An encapsulated O-ring consists of a seamless Teflon jacket that completely encloses a solid elastomer core. This design leverages the strengths of both materials.
The Role of the Teflon Sheath
The outer jacket, made of FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) or PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy), is the component that contacts the process media. Teflon is one of the most chemically inert substances known, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of chemicals.
The Purpose of the Elastomer Core
The inner core, typically made of Silicone or Viton®, provides the elasticity and memory required for an effective seal. This gives the O-ring its ability to compress and rebound, maintaining sealing integrity even under pressure fluctuations. This also grants it excellent compression set resistance.
Chemical Compatibility: Strengths and Weaknesses
While its resistance is broad, it is not absolute. Knowing the specific exceptions is critical for safe and effective application.
Excellent Resistance
Teflon encapsulated O-rings show excellent resistance (often rated 10 out of 10) to a wide array of common and aggressive chemicals.
This includes most acids and bases. It also covers a vast list of solvents such as water, ethanol, acetone, methanol, chloroform, hexane, toluene, and DMSO.
Known Vulnerabilities
You must avoid using these O-rings in applications involving a few specific substances that are known to attack the Teflon jacket.
These critical exceptions include:
- Molten alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium.
- Hydrofluoric acid (HF).
- Extremely strong fluorinating agents, like elemental fluorine, especially at high temperatures and pressures.
- Certain ketones and amines may also degrade performance under specific conditions.
Understanding the Operational Limits
Beyond chemical compatibility, the physical environment plays a crucial role in the O-ring's performance and longevity.
Temperature Constraints
The Teflon jacket has strict temperature limits. FEP is generally rated for service up to 200°C (400°F), while PFA can handle higher temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). Exceeding these temperatures will cause the material to fail.
The Difference Between FEP and PFA
While both provide similar chemical resistance, the choice between them depends on the physical demands of the application. PFA offers higher mechanical strength and superior temperature resistance compared to FEP, making it the preferred choice for more extreme thermal or mechanical environments.
Mechanical Stress
While robust, the Teflon jacket is a relatively thin layer. Abrasive media, sharp edges on hardware, or excessive mechanical stress can physically damage the encapsulation. A breach in the jacket exposes the less-resistant inner core, leading to rapid seal failure.
How to Select the Right O-Ring for Your Application
Choosing the correct seal requires matching the material's capabilities to your specific operational environment.
- If your primary focus is sealing against common acids, bases, and solvents: Teflon encapsulated O-rings are an excellent and highly reliable choice.
- If your application involves high temperatures (above 200°C) or demands greater durability: Specify the PFA-encapsulated version for its superior thermal and mechanical properties.
- If your system uses hydrofluoric acid, molten alkali metals, or potent fluorinating agents: These O-rings are unsuitable, and a different sealing material must be selected to prevent catastrophic failure.
Ultimately, verifying your specific process chemicals against a detailed compatibility chart is the most reliable way to ensure a safe and effective seal.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against most acids, bases, and solvents. |
| Key Weaknesses | Molten alkali metals, Hydrofluoric Acid (HF), strong fluorinating agents. |
| Temperature Range (FEP) | Up to 200°C (400°F) |
| Temperature Range (PFA) | Up to 260°C (500°F) |
| Core Function | Teflon jacket provides chemical inertness; elastomer core provides sealing force. |
Need a Seal That Withstands Your Toughest Chemicals?
For semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications, a compromised seal is not an option. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom Teflon encapsulated O-rings.
We ensure your seals are fabricated to the highest standards, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders.
Let's engineer the perfect seal for your specific chemical environment. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















