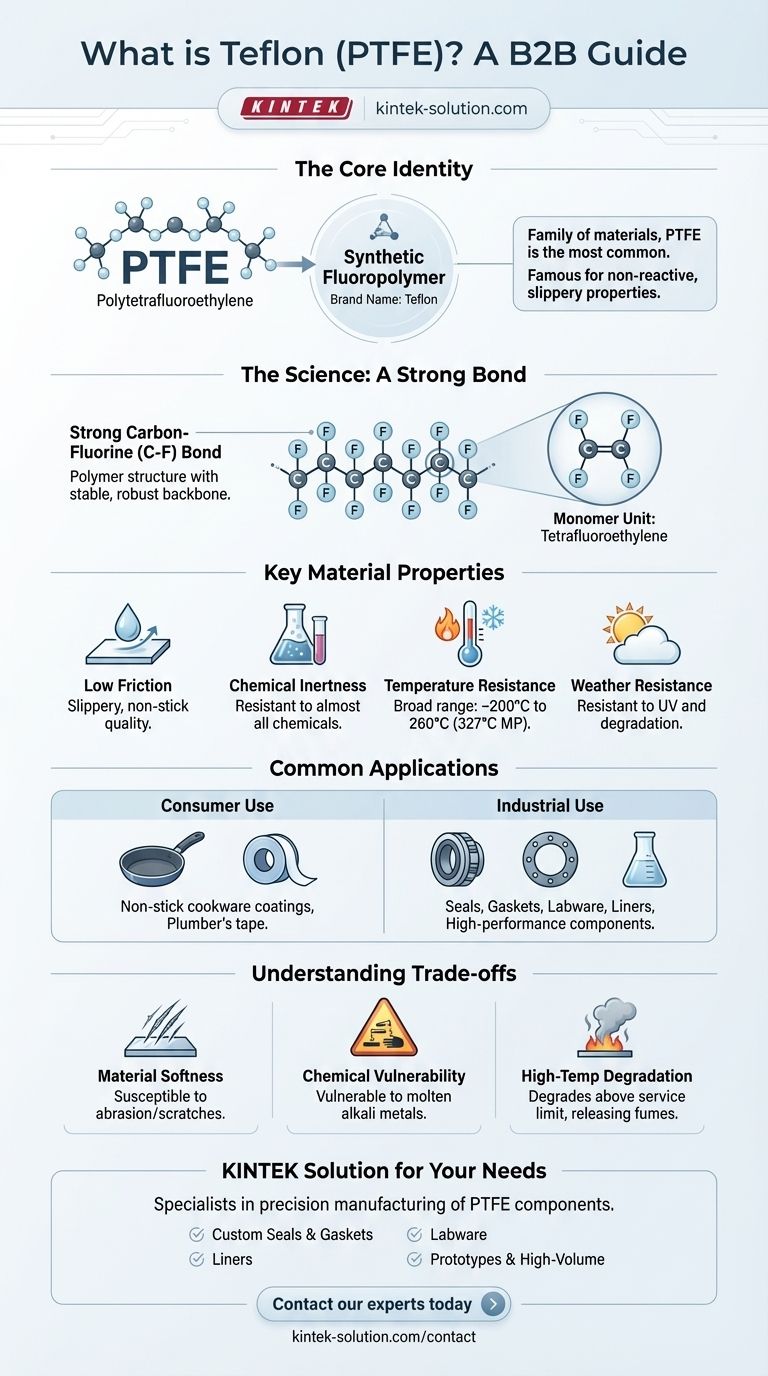
At its core, Teflon is the well-known brand name for a synthetic material called PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a high-performance fluoropolymer, a type of plastic characterized by a strong bond between carbon and fluorine atoms, which is the source of its unique and valuable properties.
Teflon is not a single substance but a family of materials, with PTFE being the most famous. Its value comes from a unique chemical structure that makes it exceptionally non-reactive and slippery, solving problems from industrial sealing to non-stick cooking.

Deconstructing PTFE: The Science Behind the Material
To truly understand Teflon, we must look at its chemical identity and the properties that arise from it. It's more than just a coating on a pan; it's a distinct class of polymer.
The Chemical Foundation
The scientific name, polytetrafluoroethylene, describes its structure perfectly. It is a polymer, which means it's a long chain of repeating molecular units. The unit in this case is tetrafluoroethylene, which consists of two carbon atoms bonded together and surrounded by four fluorine atoms.
A Synthetic Fluoropolymer
PTFE belongs to a class of materials called fluoropolymers. These are plastics where strong carbon-fluorine bonds form the backbone of the material. This specific bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry, making the material incredibly stable and resistant to being broken down.
Key Material Properties
This robust chemical structure gives Teflon its famous characteristics:
- Low Friction: It is one of the most slippery materials known, resulting in its "non-stick" quality.
- Chemical Inertness: It is highly resistant to almost all chemicals and solvents.
- Temperature Resistance: It can withstand a wide range of temperatures, from very low to a high melting point of around 600 K (327°C / 620°F).
- Weather Resistance: It is highly resistant to degradation from UV rays and weathering.
Common Forms and Applications
Teflon's versatility allows it to be manufactured in various forms, far beyond just a coating for cookware.
Consumer and Household Use
The most recognized application is as a non-stick coating on pots and pans. Another common form is plumber's tape, used to seal pipe threads.
Industrial and Mechanical Use
In industrial settings, PTFE is crucial for performance-critical applications. It is formed into sheets, films, pipes, and coated fabrics. It is also used to create high-performance mechanical seals and gaskets that must resist aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and its strengths often create corresponding limitations. Understanding these is key to using it effectively.
Material Softness
PTFE is a relatively soft fluoropolymer. This can make it susceptible to scratches and abrasion in certain applications, which is why metal utensils are discouraged on Teflon-coated cookware.
Chemical Vulnerability
While famously inert, it is not completely invincible. Extremely reactive chemicals, specifically molten alkali metals, are capable of breaking down the material's strong chemical bonds.
High-Temperature Degradation
Although it has a high melting point, PTFE can begin to degrade at temperatures above its service limit, releasing fumes. This is a critical safety consideration in both industrial and consumer applications.
How to Think About Teflon for Your Needs
The right way to view this material depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is household use: Think of it as a surface technology defined by its low friction, which prevents food from sticking.
- If your primary focus is industrial performance: See it as a problem-solver for harsh environments, valued for its extreme chemical resistance and temperature stability.
- If your primary focus is material science: Understand it as the prime example of how the unique strength of the carbon-fluorine bond creates a polymer with exceptionally stable and non-reactive properties.
Ultimately, Teflon's identity as polytetrafluoroethylene is the key to its role as a uniquely versatile and high-performance material.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Material Class | Synthetic Fluoropolymer |
| Key Characteristics | Non-stick, chemically inert, high temperature resistance |
| Common Forms | Coatings, tapes, sheets, seals, gaskets, labware |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures material integrity and performance in the most demanding environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















