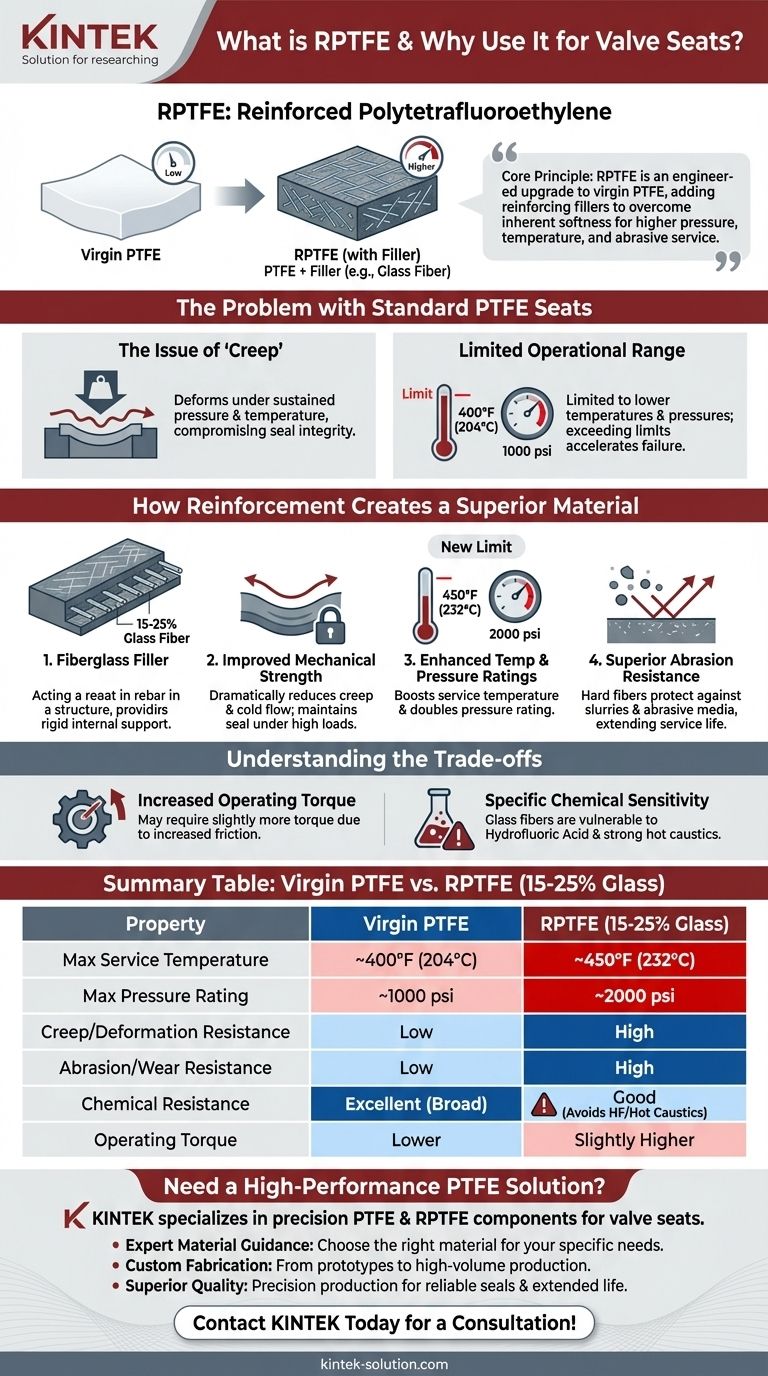
RPTFE, or Reinforced Polytetrafluoroethylene, is a composite material created by adding a filler, most commonly glass fiber, to a standard PTFE base. It is a popular choice for valve seats because it significantly enhances the performance of standard PTFE, offering greater strength, wider operating ranges, and a longer service life in demanding applications.
The core principle to understand is that RPTFE is not a fundamentally different material, but rather an engineered upgrade to virgin PTFE. By adding reinforcing fillers, RPTFE overcomes the inherent softness of PTFE, making it a more robust material for higher pressure, temperature, and abrasive service conditions.

The Problem with Standard PTFE Seats
To understand the value of RPTFE, one must first recognize the limitations of its base material, virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). While known for its excellent chemical resistance and low friction, it has key weaknesses.
The Issue of "Creep"
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, it can deform or "creep." This deformation can compromise the integrity of a valve seat, leading to leaks over time.
Limited Operational Range
Standard PTFE has clear operational boundaries. It is generally limited to temperatures around 400°F (204°C) and pressures up to 1000 psi. Exceeding these limits accelerates material creep and potential failure.
How Reinforcement Creates a Superior Material
Adding a filler material directly addresses the mechanical weaknesses of virgin PTFE, creating a far more durable composite.
The Role of Fiberglass Filler
RPTFE typically contains 15-25% glass fiber filler. These fibers act like rebar in concrete, creating a rigid internal structure within the flexible PTFE matrix. This structure provides the necessary support to resist deformation.
Improved Mechanical Strength
The internal fiber structure dramatically reduces creep and cold flow. This allows an RPTFE seat to maintain its shape and provide a reliable seal under high mechanical loads for a much longer period.
Enhanced Temperature and Pressure Ratings
The added reinforcement allows RPTFE to perform reliably in more demanding conditions. It typically boosts the maximum service temperature to 450°F (232°C) and doubles the pressure rating to 2000 psi.
Superior Abrasion Resistance
The hard glass fibers embedded in the surface provide excellent protection against wear from slurries or media containing abrasive particles. This significantly extends the valve's service life in challenging environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs of RPTFE
While RPTFE offers significant advantages, it is not a universal upgrade. The addition of glass fibers introduces specific limitations that must be considered.
Increased Operating Torque
The glass fibers increase the material's coefficient of friction compared to virgin PTFE. This means a valve fitted with RPTFE seats may require slightly more torque to actuate.
Specific Chemical Sensitivity
This is the most critical trade-off. The glass fiber filler can be attacked by certain chemicals that would not harm pure PTFE. These include hydrofluoric acid and strong hot caustics, which will degrade the filler and cause the seat to fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between RPTFE and virgin PTFE requires a clear understanding of your specific operational needs and media.
- If your primary focus is low friction and broad chemical compatibility: Virgin PTFE is the better choice, provided the temperature and pressure are well within its limits.
- If you need durability in high-pressure or high-temperature service: RPTFE is the superior option due to its enhanced mechanical strength and wider operational range.
- If your media contains abrasive particles: RPTFE's excellent wear resistance makes it the definitive choice to ensure a longer service life.
- If you are handling chemicals known to attack glass: You must avoid RPTFE and opt for virgin PTFE or another specialized seat material to prevent chemical degradation.
Ultimately, selecting the correct seat material is an engineering decision that balances the need for mechanical robustness against specific chemical and operational constraints.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | RPTFE (15-25% Glass) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Service Temperature | ~400°F (204°C) | ~450°F (232°C) |
| Max Pressure Rating | ~1000 psi | ~2000 psi |
| Creep/Deformation Resistance | Low | High |
| Abrasion/Wear Resistance | Low | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Broad) | Good (Avoids HF/Hot Caustics) |
| Operating Torque | Lower | Slightly Higher |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Solution for Your Valves?
Selecting the right seat material is critical for valve performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE and RPTFE components, including custom valve seats, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Guidance: Help you choose between virgin PTFE, RPTFE, and other formulations based on your specific pressure, temperature, chemical, and abrasion requirements.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production, we engineer components to your exact specifications.
- Superior Quality: Precision production ensures reliable seals and extended service life in demanding applications.
Let our experts help you optimize your valve performance. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















