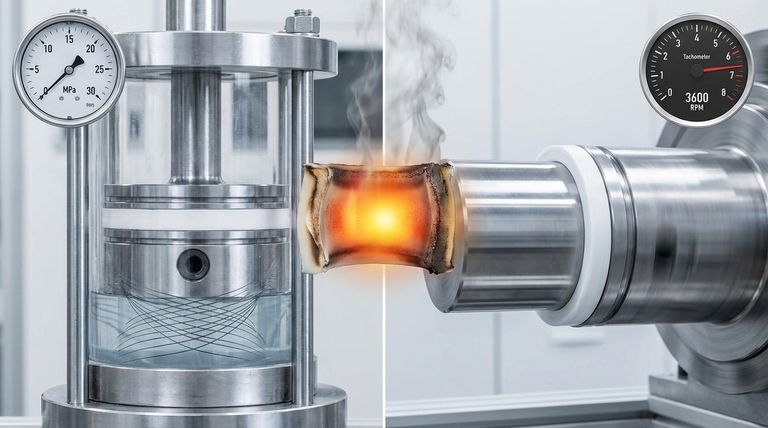
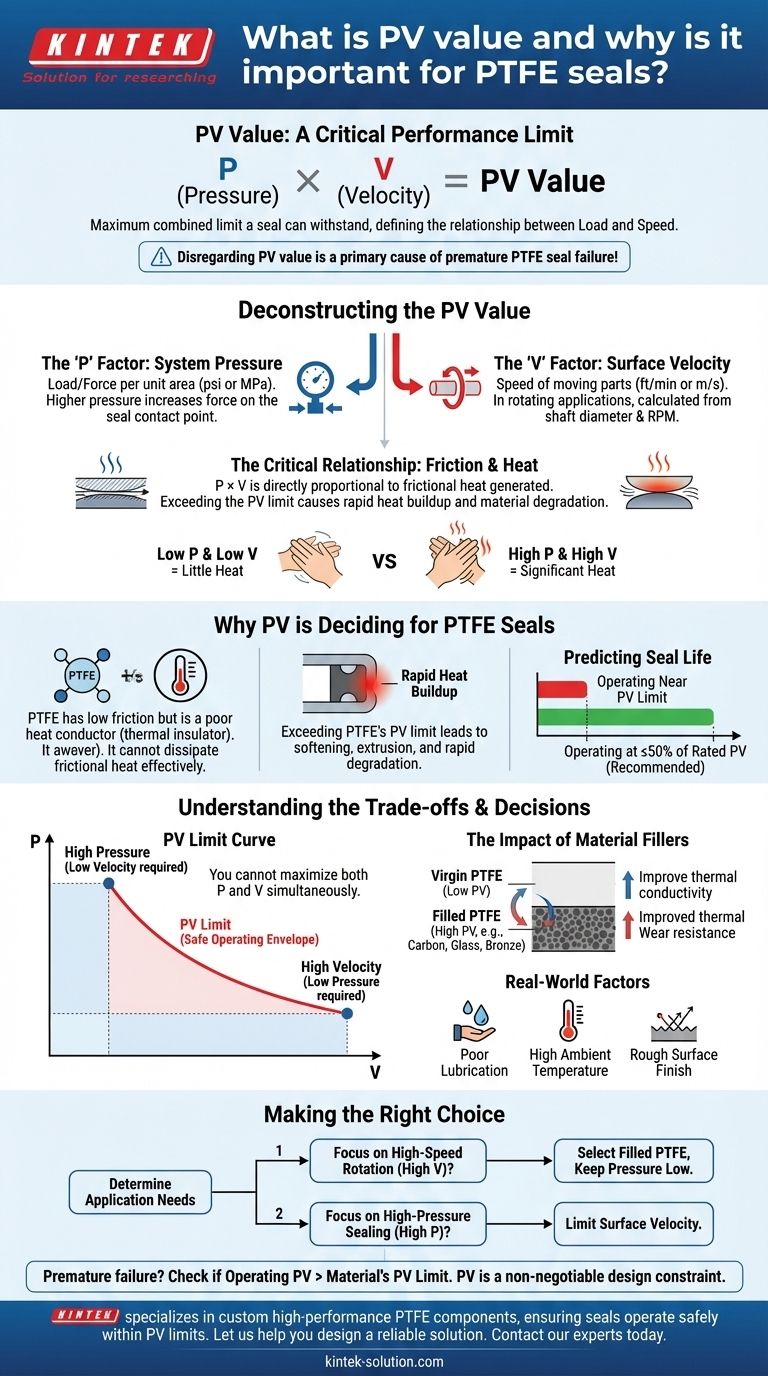
PV value is a critical performance limit for a material, representing the maximum combined pressure (P) and velocity (V) a seal can withstand before failing. It quantifies the fundamental relationship between the load on a seal and the speed of its moving parts. Disregarding this value is a primary cause of premature seal failure, particularly in dynamic applications involving materials like PTFE.
The PV value isn't just a material specification; it's a proxy for the frictional heat generated at the sealing interface. Exceeding a material's PV limit causes a rapid temperature rise, leading to material degradation, increased wear, and ultimately, catastrophic seal failure.

Deconstructing the PV Value
To properly apply the PV value, you must first understand its constituent parts and the physical principle it represents. It is a direct measure of the energy being put into the seal system.
The 'P' Factor: System Pressure
The 'P' in PV stands for Pressure. This is the load, or force per unit area, that the seal must contain.
In practical terms, this is the system pressure (in psi or MPa) acting on the effective area of the seal. Higher pressure means more force is being pushed against the seal's contact point.
The 'V' Factor: Surface Velocity
The 'V' in PV stands for Velocity. This is the speed at which the two dynamic surfaces are moving relative to one another.
This is typically expressed in feet per minute (ft/min) or meters per second (m/s). In rotating applications, velocity is calculated based on the shaft diameter and its rotational speed (RPM).
The Critical Relationship: Friction and Heat
The reason P and V are multiplied together is that their product is directly proportional to the frictional heat generated. Think of rubbing your hands together: rubbing them lightly (low P) and slowly (low V) generates little heat.
However, pressing them together hard (high P) and rubbing them quickly (high V) generates significant heat almost instantly. The PV value defines the point at which this generated heat overwhelms the seal material's ability to dissipate it.
Why PV is the Deciding Factor for PTFE Seals
While PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is known for its extremely low coefficient of friction, it is not immune to the laws of physics. Understanding the PV limit is especially crucial when using this material.
PTFE's Thermal Limitations
PTFE is a polymer, and like most plastics, it is a poor conductor of heat. It cannot dissipate the heat generated by friction as effectively as a metal component can.
When the operational PV of an application exceeds the PTFE grade's PV limit, heat builds up rapidly at the sealing interface. This leads to softening, extrusion, and rapid degradation of the material.
Predicting Seal Life and Wear Rate
A material's PV rating is its absolute maximum limit for short-term survival. For reliable, long-term performance, a system should operate at a PV value significantly below the material's stated limit.
Operating close to the PV limit will drastically shorten the seal's operational life. Operating at 50% or less of the rated PV value is a common engineering practice for ensuring durability.
A Concrete Example: Piston Seals
The stated maximum velocity for some PTFE piston seals is 3.2 ft/sec. This specification is not arbitrary; it is derived from the material's PV rating.
This velocity limit assumes a typical range of operating pressures. If your application requires a higher pressure, you would need to decrease the velocity to stay within the same overall PV limit to prevent failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The PV value is not a single number but a curve that defines a safe operating envelope. This forces critical design decisions and trade-offs.
The Pressure vs. Velocity Balance
The core trade-off is in the name itself. You cannot maximize both pressure and velocity simultaneously.
If an application requires very high pressure (high P), you are forced to use a much lower velocity (low V). Conversely, a high-velocity application (like a high-RPM shaft) will only tolerate low pressures to stay within the material's PV limit.
The Impact of Material Fillers
Not all PTFE is created equal. The PV rating of virgin PTFE is relatively low.
To improve performance, fillers like carbon, glass fiber, or bronze are added. These fillers dramatically increase the PV rating by improving thermal conductivity and wear resistance, allowing the seal to be used in more demanding applications.
Beyond the Numbers: Environmental Factors
The datasheet PV value is determined under specific lab conditions. Real-world factors can significantly alter a seal's effective PV limit.
Factors like poor lubrication, high ambient temperatures, and rough surface finishes on mating parts will all increase friction and heat, effectively lowering the PV limit the seal can tolerate in practice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use the PV value as your primary guide when selecting a seal material for any dynamic application. This single metric will help you avoid the most common cause of failure.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotation (high V): You must select a filled PTFE grade with a very high PV rating and ensure system pressure (P) is low enough to stay within the material's operating envelope.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing (high P): You will be limited to lower surface velocities (V) to prevent the system from exceeding the material's thermal limit.
- If you are experiencing premature seal failure: Calculate the operational PV of your application (Pressure x Velocity) and compare it against the datasheet limit for your seal material; it is highly likely you are operating beyond its capability.
Ultimately, treating the PV value as a non-negotiable design constraint is the key to creating reliable and long-lasting sealing systems.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| P (Pressure) | Load or force per unit area on the seal. | Higher pressure increases force on the seal contact point. |
| V (Velocity) | Speed of moving surfaces relative to each other. | Higher velocity increases the rate of friction and heat generation. |
| PV Limit | Maximum combined P x V value a material can withstand. | Exceeding this limit causes rapid heat buildup and seal failure. |
| PTFE Consideration | PTFE is a poor heat conductor. | Filled PTFE grades (carbon, glass) have higher PV ratings for demanding uses. |
Struggling with premature PTFE seal failure? Your application's PV value is likely the culprit.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals are precision-engineered to operate safely within their PV limits, guaranteeing longevity and reliability.
Let us help you design a sealing solution that lasts. Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific pressure and velocity requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does the low coefficient of friction in PTFE bushes benefit industrial applications? Reduce Wear & Maintenance
- Why are PTFE energized seals a preferred choice for aerospace engineers? Ensure Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What makes PTFE an ideal sealing material overall? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the primary applications of PTFE expansion bellows? Protect Piping Systems from Stress & Corrosion
- What are the main differences between RPTFE and standard PTFE for valve seats? Choose the Right Material for Your System
- What is the smallest size PTFE seal that can be manufactured? Achieve Micro-Scale Sealing for Your Precision Designs
- What are the main technical features of PTFE rotary shaft seals? Unlock Extreme Performance & Reliability
- How does the PTFE sliding pad function smoothly? An Inside Look at Low-Friction Engineering



















