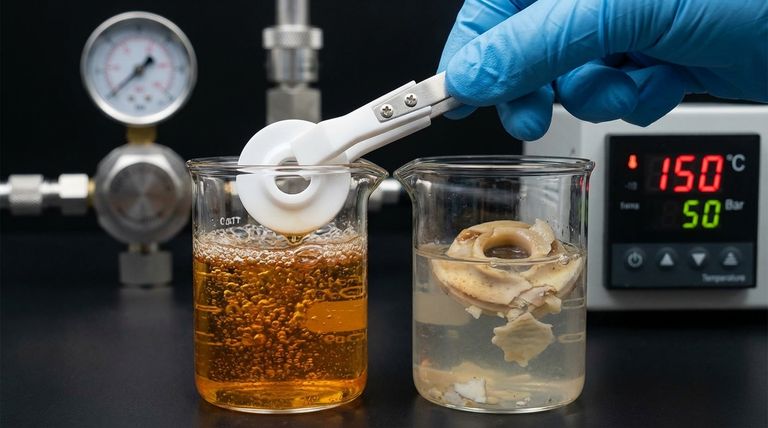
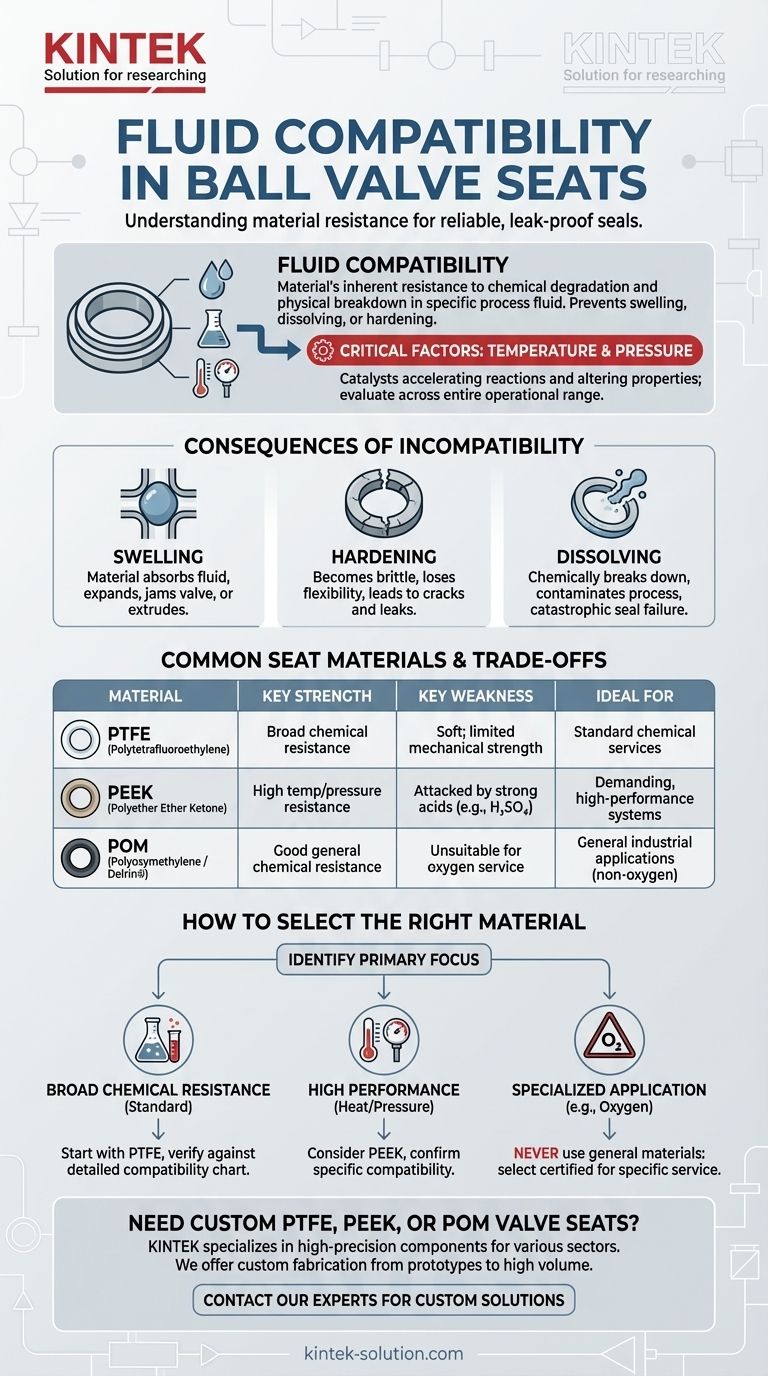
In the context of ball valve seats, fluid compatibility is a material's inherent resistance to chemical degradation or physical breakdown when exposed to a specific process fluid. This means the chosen material will not swell, dissolve, harden, or otherwise react adversely, ensuring the valve can maintain a reliable, leak-proof seal over its operational lifetime. An incorrect choice leads directly to valve failure.
Choosing the right valve seat material is not just about chemical resistance. True fluid compatibility can only be determined by considering the material's reaction to the fluid under the specific operating temperature and pressure of your system, as these factors can dramatically alter its performance.

Why Compatibility is More Than a Chemical Checklist
Understanding fluid compatibility is fundamental to ensuring the safety and reliability of any process system. A mismatch between the seat material and the fluid can have significant operational consequences.
The Primary Function of the Valve Seat
The ball valve seat is the critical component that creates the seal against the ball. Its integrity is paramount.
When the valve is closed, the seat must press firmly against the ball to prevent the process fluid from passing through.
The Consequences of Incompatibility
If the seat material is not compatible with the fluid, it will begin to degrade. This degradation can manifest in several ways:
- Swelling: The material absorbs the fluid, expands, and can jam the valve or extrude from its groove.
- Hardening: The material becomes brittle, losing its ability to flex and form a tight seal, leading to cracks and leaks.
- Dissolving: The fluid chemically breaks down the seat material, contaminating the process and causing a catastrophic seal failure.
The Critical Link to Temperature and Pressure
A material that is perfectly compatible with a chemical at room temperature may fail when that same chemical is heated or pressurized.
Temperature and pressure act as catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions and altering a material's physical properties. Therefore, you must evaluate compatibility across the entire operational range of your system, not just under ambient conditions.
A Practical Look at Common Seat Materials
The choice of material depends entirely on the specific application. Each common polymer has a distinct compatibility profile with unique strengths and weaknesses.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
PTFE is known for its extremely broad chemical compatibility, making it a common default choice for many applications.
However, it is not invincible. PTFE can be attacked by highly reactive substances like elemental fluorine and some molten alkali metals.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
PEEK offers excellent chemical resistance similar to PTFE but with superior mechanical strength, especially at high temperatures and pressures.
Despite its robustness, PEEK has known vulnerabilities. It is susceptible to attack by concentrated sulfuric acid, which can cause it to degrade rapidly.
POM (Polyoxymethylene / Delrin®)
POM is a strong, rigid thermoplastic with good resistance to a wide range of chemicals and solvents.
Its primary limitation is in specialized services. For example, it is never suitable for oxygen flow, where it can pose a significant safety hazard.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a valve seat material is never about finding a single "best" option; it's about finding the optimal balance for a specific set of conditions.
Chemical Resistance vs. Mechanical Strength
Often, the most chemically inert materials, like PTFE, are also the softest. This makes them excellent for sealing but less suitable for high-pressure applications or services with abrasive media where a harder material like PEEK would be required.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance materials that offer broad compatibility under extreme temperatures and pressures, such as PEEK, come at a significant cost premium. Over-specifying a material can lead to unnecessary project expenses.
The Danger of "Good Enough"
Never assume a material is compatible based on general information. Factors like the concentration of a chemical, the presence of trace contaminants, and the exact operating temperature can all lead to unexpected failures. Always consult detailed chemical compatibility charts.
How to Select the Right Material for Your Application
Your final decision must be a direct response to your system's specific operational demands. Use the following guidelines to frame your selection process.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical resistance in standard conditions: Start with a material like PTFE, but always verify every chemical in your process fluid against a detailed compatibility chart.
- If your primary focus is high performance under heat and pressure: Consider advanced materials like PEEK, but confirm its specific compatibility with your fluid to avoid costly failures with aggressive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is a specialized application (like oxygen service): Never use general-purpose materials; you must select a material explicitly tested and certified for that specific, high-risk service.
Ultimately, rigorous verification against manufacturer data and industry-standard compatibility charts is the only way to ensure the long-term integrity and safety of your system.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Strength | Key Weakness | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | Broad chemical resistance | Soft; limited mechanical strength | Standard chemical services |
| PEEK | High temp/pressure resistance | Attacked by strong acids (e.g., H₂SO₄) | Demanding, high-performance systems |
| POM (Delrin®) | Good general chemical resistance | Unsuitable for oxygen service | General industrial applications (non-oxygen) |
Need a Custom PTFE, PEEK, or POM Ball Valve Seat?
Selecting the right material is critical for your system's safety and performance. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals and valve seats, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your component is perfectly compatible with your fluid, temperature, and pressure requirements.
Ensure a leak-proof seal and long-term reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a custom solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















