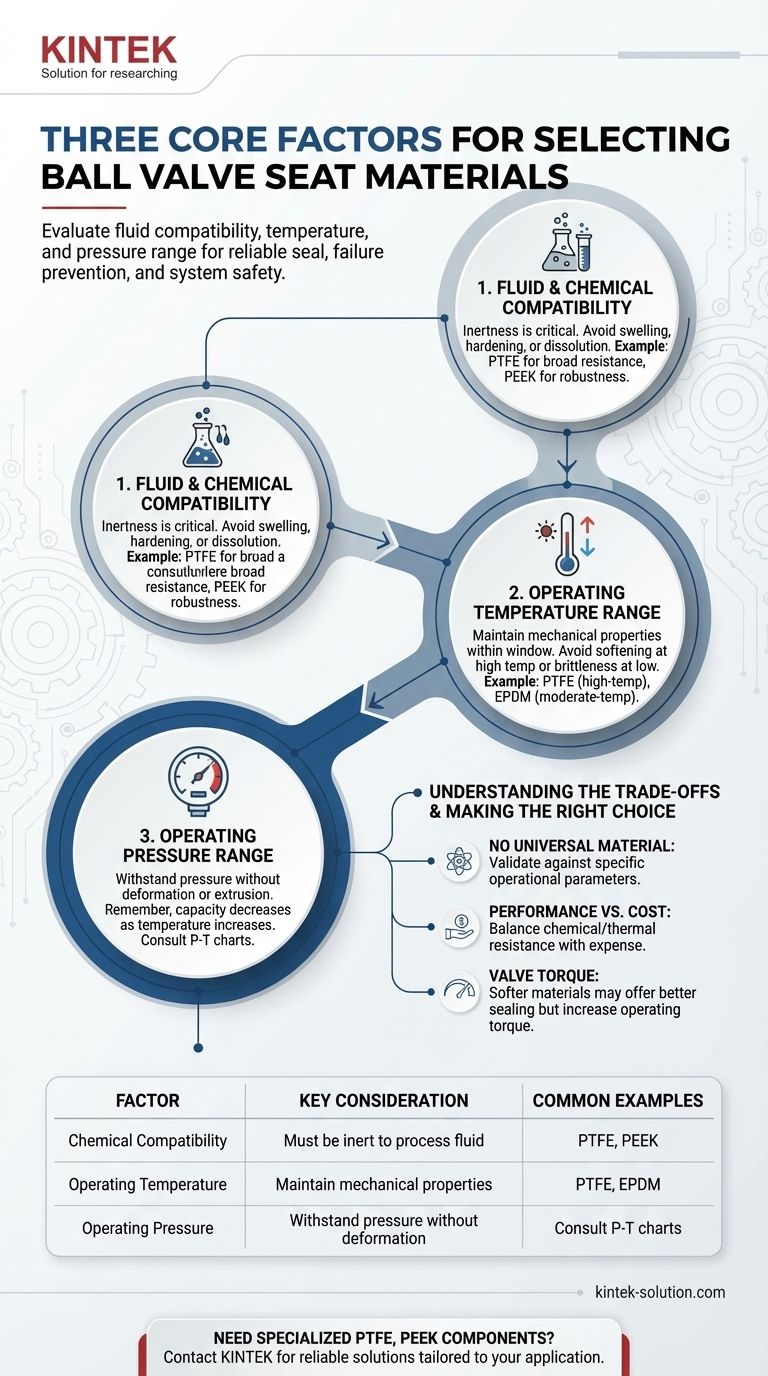
To select the right ball valve seat material, you must evaluate three core operational factors: the chemical compatibility of the fluid, the operating temperature range, and the operating pressure range. These three pillars dictate whether a valve will provide a reliable seal, prevent failure, and ensure the safety of the entire system.
The goal is not to find the single "best" material, but to identify the optimal material for a specific combination of chemical, thermal, and pressure demands. A mismatch in any one of these three factors will inevitably lead to compromised performance and potential valve failure.

Deconstructing the Core Factors
The performance of a ball valve is directly tied to the integrity of its seat. The seat is responsible for creating the seal and distributing stress across the valve. Choosing an unsuitable material compromises this fundamental function.
Factor 1: Fluid & Chemical Compatibility
This is the most critical initial consideration. The seat material must remain inert and not degrade when in constant contact with the process fluid.
An adverse chemical reaction can cause the seat to swell, harden, or dissolve, leading to immediate leakage and potential system contamination.
For example, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) offers excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals but can be attacked by molten alkali metals or fluorine. Similarly, PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) is highly robust but can fail when exposed to concentrated sulfuric acid.
Factor 2: Operating Temperature Range
Every seat material has a specific temperature window in which it maintains its ideal mechanical properties.
Operating above the maximum temperature can cause the material to soften and extrude from its position, destroying the seal. Operating below the minimum temperature can cause it to become brittle and crack under stress.
The choice between materials often comes down to temperature. PTFE is well-suited for many high-temperature environments, while a material like EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a common choice for moderate-temperature water and steam applications.
Factor 3: Operating Pressure Range
The valve seat must be strong enough to withstand the system's operating pressure without deforming.
High pressure exerts significant force on the seat. If the material is too soft for the pressure rating, it can be forced into the valve's bore, a failure known as "extrusion," which creates a leak path.
It is crucial to remember that a material's pressure-holding capability often decreases as temperature increases. Always consult a manufacturer's Pressure-Temperature (P-T) chart for the specific material grade.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a valve seat requires a clear-eyed view of the compromises involved. There is no single material that excels in every possible condition.
The Myth of a "Universal" Material
While materials like PTFE are extremely versatile, they are not a universal solution. Their limitations with specific chemicals or extreme temperatures highlight the need for careful validation against your unique operational parameters. Assuming one material fits all applications is a common and costly mistake.
Performance vs. Cost
High-performance materials that offer superior chemical and thermal resistance, such as PEEK, typically come at a significantly higher cost. The goal is to specify a material that reliably meets the demands of the application without over-engineering and incurring unnecessary expense.
The Impact on Valve Torque
The seat material also influences the force, or torque, required to operate the valve. Softer materials generally provide a tighter seal at lower pressures but can result in higher operating torque. This factor can be important when selecting an actuator for automated valves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your specific operational goal as the starting point for your material selection process.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: Your analysis must begin with fluid compatibility. Start by cross-referencing materials like PTFE or PEEK against the specific chemical datasheet to ensure inertness.
- If your primary focus is a general utility like water or steam: Temperature and pressure are your primary guides. Cost-effective materials like EPDM or standard PTFE are often sufficient and reliable choices.
- If your primary focus is maximizing safety and reliability: You must evaluate all three factors—fluid, temperature, and pressure—in unison, paying close attention to the material's P-T curve.
A methodical evaluation of these three factors is the foundation for a reliable and safe fluid control system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Common Material Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Compatibility | Must be inert to the process fluid to prevent swelling, hardening, or dissolution. | PTFE, PEEK |
| Operating Temperature | Material must maintain mechanical properties (not soften or become brittle). | PTFE (high-temp), EPDM (moderate-temp) |
| Operating Pressure | Material must withstand pressure without deforming or extruding; capacity decreases with temperature. | Consult P-T charts for specific grades |
Need a custom PTFE, PEEK, or other specialized component for your ball valve or fluid system?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your components are chemically compatible and rated for your specific temperature and pressure requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today for a reliable solution tailored to your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















