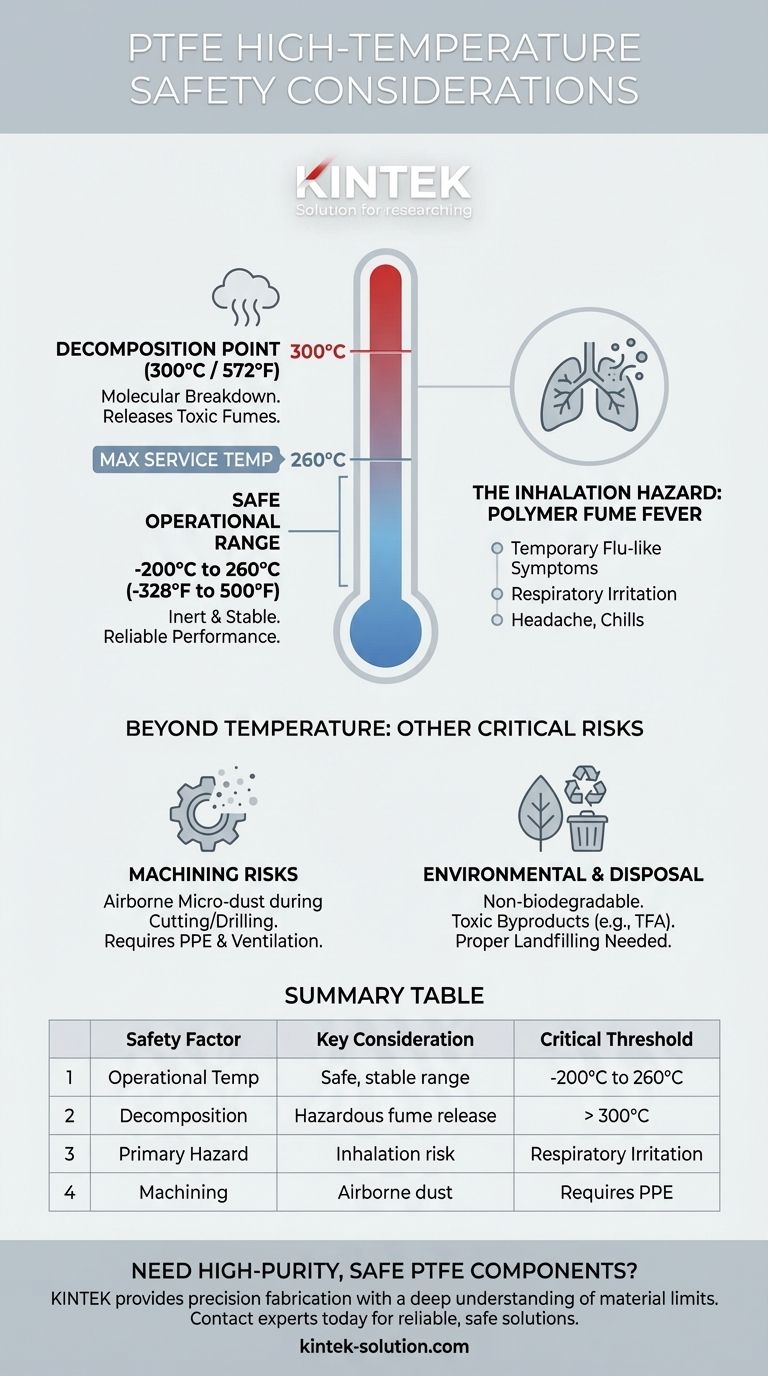
The primary safety consideration for using Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) at high temperatures is its decomposition point. While exceptionally stable within its designed operational range, PTFE begins to break down when heated above 300°C (572°F), releasing fumes that can cause respiratory irritation and other health concerns.
The core principle for PTFE safety is strict temperature management. The material is inert and safe within its vast operating window of -200°C to 260°C, but exceeding this range introduces significant respiratory hazards that must be controlled with proper engineering and ventilation.

The Critical Temperature Threshold
Understanding PTFE's thermal behavior is essential for its safe application. Its properties change dramatically at specific temperatures, creating a clear line between safe use and potential hazard.
Recommended Operational Range
PTFE is valued for its remarkable thermal stability. It performs reliably across an extremely wide operational temperature range, from cryogenic conditions at -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F).
Within this range, the material remains inert, stable, and safe for its intended applications.
The Point of Decomposition
The safety risk emerges when temperatures exceed the recommended maximum. Above 300°C (572°F), the molecular bonds in PTFE begin to break down.
This process, known as pyrolysis, releases various toxic fluorocarbon particles and gases into the atmosphere.
The Inhalation Hazard
The fumes released during decomposition are a serious health hazard. Inhaling these microscopic particles can lead to a temporary, flu-like condition known as polymer fume fever, with symptoms including chills, headache, and respiratory irritation.
Beyond Temperature: Other Safety Factors
While temperature is the most cited concern, a complete safety assessment includes handling during fabrication and its end-of-life disposal.
Risks During Machining
Heating from friction during machining can also produce hazardous airborne particles. Even without significant heat, the fine micro-dust created can be harmful if inhaled.
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as a mask, and the use of coolants are critical safety measures during any cutting, drilling, or sanding operations.
Environmental and Disposal Concerns
The lifecycle of PTFE presents environmental challenges. Its manufacturing can produce toxic byproducts like hydrofluoric acid, and the material can degrade into trifluoroacetate (TFA), a persistent substance toxic to plants.
Because it does not readily biodegrade, proper disposal is necessary to prevent the release of harmful substances into the environment over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using PTFE effectively requires balancing its unique benefits against its specific, well-defined limitations.
Exceptional Stability vs. High-Heat Hazard
The material's incredible resistance to chemicals, weather, and a wide temperature range makes it invaluable. This stability is an asset, but it creates a stark contrast with the distinct hazard that arises only when it is overheated.
The key is to treat its maximum service temperature of 260°C as a firm operational limit, not a guideline.
Lifecycle Impact
The benefits of PTFE's durability during its service life must be weighed against the environmental concerns related to its manufacturing and disposal. The material's persistence means that choosing it for an application is a long-term commitment.
Responsible use includes planning for its entire lifecycle, concluding with proper disposal methods like landfilling to contain it securely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To ensure safety, align your operational conditions with the material's known properties.
- If your primary focus is operating in a controlled environment below 260°C: PTFE is an exceptionally safe and stable material choice.
- If your application involves machining or has the potential for uncontrolled overheating: You must implement strict engineering controls, including robust ventilation, temperature monitoring, and appropriate PPE.
- If your priority is minimizing long-term environmental impact: You must factor in the challenges of PTFE disposal and consider its entire lifecycle from production to end-of-life.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE safely and responsibly comes down to respecting its documented operational limits.
Summary Table:
| Safety Factor | Key Consideration | Critical Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Temperature | Safe and stable performance range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Decomposition Point | Onset of hazardous fume release | Above 300°C (572°F) |
| Primary Hazard | Risk of polymer fume fever from inhalation | Respiratory irritation, flu-like symptoms |
| Machining Hazard | Airborne micro-dust from fabrication | Requires PPE and ventilation |
Need High-Purity, Safe PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
At KINTEK, we manufacture precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware with a deep understanding of material safety and performance limits. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, or industrial sector, our custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your components operate reliably within safe thermal parameters.
Let us provide the precision and expertise your application requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















