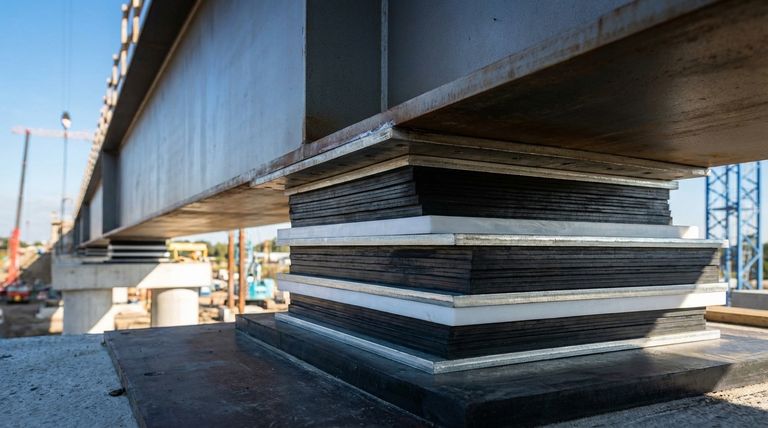
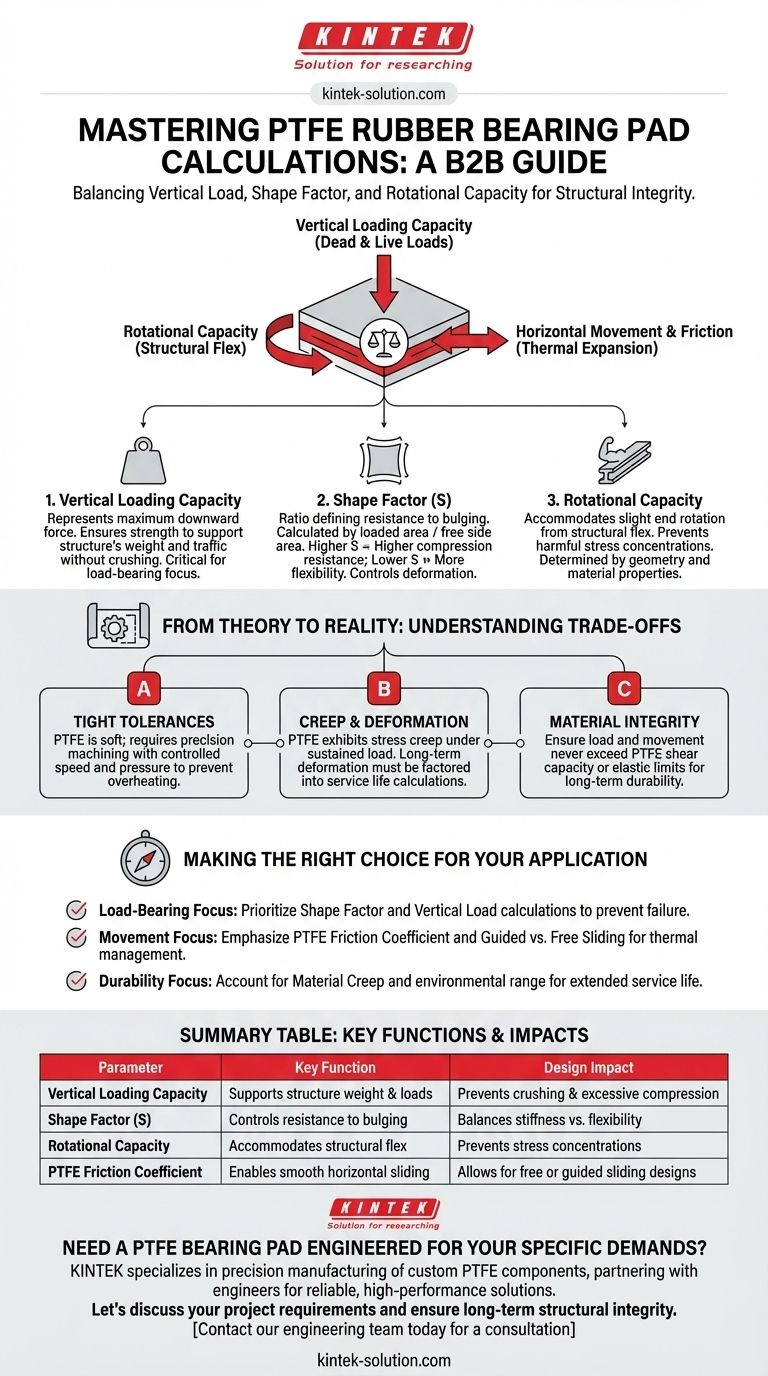
At its core, calculating a PTFE rubber bearing pad involves three primary technical parameters: the vertical loading capacity it must support, its shape factor which dictates how it resists deformation, and the rotational movement it must accommodate. These factors work together to ensure the bearing can safely manage the forces and movements of a large structure.
The challenge is not merely listing these parameters, but understanding their interplay. A successful design balances the raw strength needed to support a vertical load with the flexibility required to allow for subtle but critical structural rotations and horizontal sliding.

The Core Calculation Parameters Explained
To properly engineer a PTFE elastomeric bearing, you must analyze how it will behave under the specific stresses of your application. Each parameter addresses a different type of force or movement the structure will exert.
Vertical Loading Capacity
This is the most fundamental parameter. It represents the maximum downward force, or compressive load, the bearing is designed to withstand from the structure above, such as a bridge deck or building beam.
This calculation ensures the bearing pad has sufficient strength to support the dead load (the structure's own weight) and live loads (traffic, wind, etc.) without being crushed or excessively compressed.
Shape Factor (S)
The shape factor is a critical ratio that defines the bearing's ability to resist bulging under load. It is calculated by dividing the loaded surface area by the area of the sides that are free to bulge.
A higher shape factor (a wider, thinner pad) provides more resistance to vertical compression. A lower shape factor (a narrower, thicker pad) is more flexible but compresses more easily. This parameter is crucial for controlling deformation.
Rotational Capacity
Structures are not perfectly rigid. As a bridge beam or girder flexes under load, its ends rotate slightly. The bearing pad must be able to accommodate this angular movement without generating harmful stress concentrations.
The rotational capacity is determined by the bearing's geometry and the elastomeric material's properties, ensuring it can flex with the structure as intended.
Horizontal Movement and Friction
The defining feature of a PTFE bearing is its ability to allow for smooth horizontal movement. This is governed by the low coefficient of friction of the Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) surface.
This sliding capability is essential for accommodating thermal expansion and contraction of the structure. Depending on the design, bearings can be:
- Free Sliding: Allowing movement in any horizontal direction.
- Guided Sliding: Restricting movement to a single axis.
Understanding the Trade-offs: From Theory to Reality
While the calculations provide a theoretical model, the inherent properties of PTFE and rubber present practical challenges that must be considered. The design on paper must be achievable in fabrication and perform reliably over decades.
The Challenge of Tight Tolerances
PTFE is a relatively soft material with a high coefficient of thermal expansion. This makes precision machining more complex than with metals.
Achieving the exact dimensions specified in the calculations requires careful control of cutting speeds, tool sharpness, and clamping pressure to prevent overheating or compressing the material during fabrication.
Creep and Long-Term Deformation
Under a constant, sustained load, PTFE can exhibit stress creep—a slow, gradual deformation over time.
Engineers must account for this phenomenon in their long-term calculations. The initial deflection of the bearing is not its final state, and this slow change must be factored into the structure's overall service life and performance.
Material Integrity and Durability
While PTFE is highly resistant to chemical and environmental degradation, its physical properties are not infinite. The design must ensure that the combination of load, movement, and rotation never exceeds the material's shear capacity or elastic limits.
This ensures the bearing functions predictably and avoids premature failure, providing the intended shock isolation and buffering for the life of the structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your design priorities will determine which parameters require the most focus. A successful bearing pad is one that is precisely tuned to the specific demands of its location.
- If your primary focus is load-bearing capacity: The shape factor and vertical load calculations are your most critical starting points to prevent failure from compression.
- If your primary focus is accommodating movement: The PTFE layer's friction coefficient and the design for guided vs. free sliding are paramount to manage thermal cycles.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability: You must account for material creep and the environmental operating range in your calculations to ensure service life.
Ultimately, engineering a PTFE bearing pad is a process of balancing these theoretical calculations with the practical realities of the material itself.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Key Function | Design Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Loading Capacity | Supports the structure's weight and live loads | Prevents crushing and excessive compression |
| Shape Factor (S) | Controls resistance to bulging and deformation | Balances stiffness (high S) vs. flexibility (low S) |
| Rotational Capacity | Accommodates structural flex and end rotations | Prevents harmful stress concentrations |
| PTFE Friction Coefficient | Enables smooth horizontal sliding for thermal movement | Allows for free or guided sliding designs |
Need a PTFE Bearing Pad Engineered for Your Specific Demands?
Calculating the perfect balance of load, movement, and durability is complex. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including bearing pads for bridges and large-scale structures.
We partner with engineers to transform theoretical calculations into high-performance, reliable products, accounting for critical factors like material creep and tight tolerances.
Let's discuss your project requirements and ensure long-term structural integrity.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















