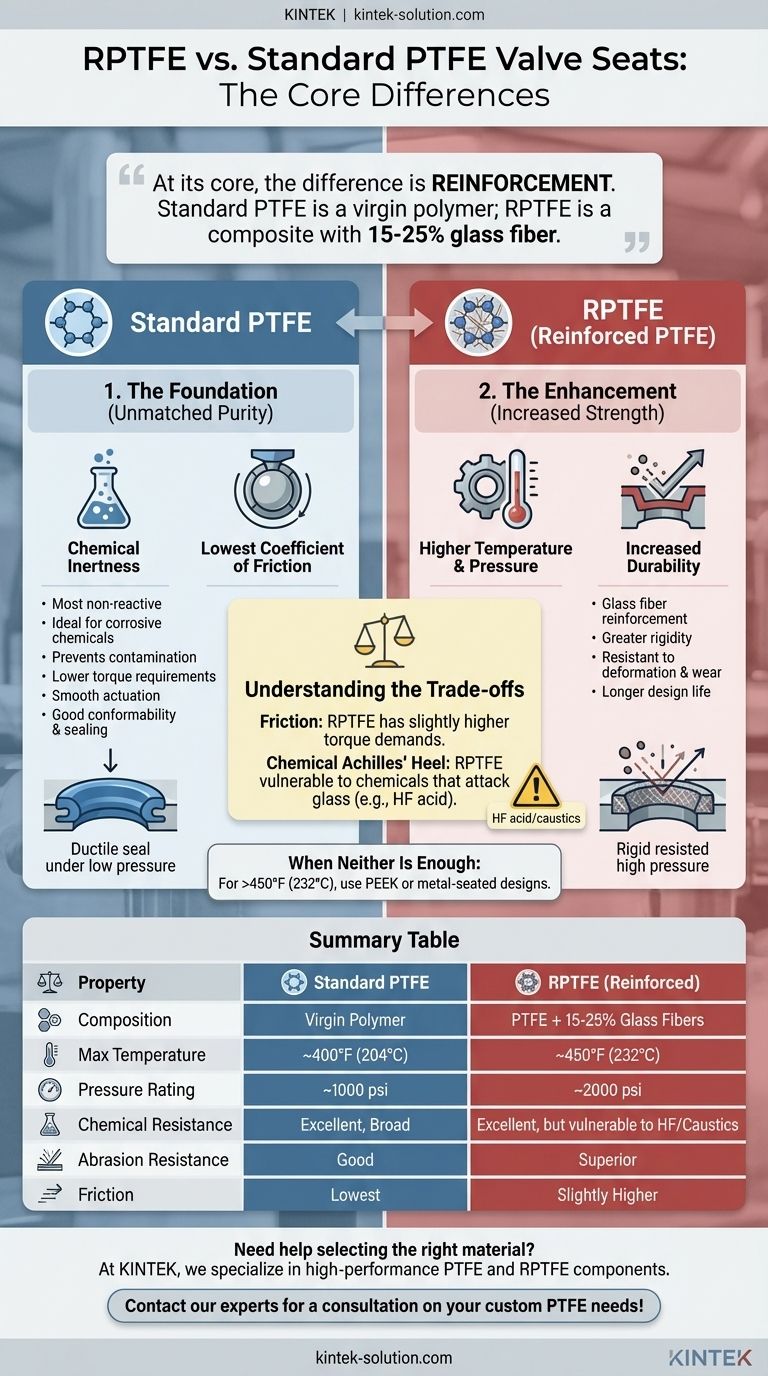
At its core, the difference between RPTFE and standard PTFE for valve seats is reinforcement. Standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a virgin polymer, while Reinforced PTFE (RPTFE) is a composite material containing 15-25% glass fiber reinforcement. This addition of glass fibers significantly enhances RPTFE's mechanical properties, giving it higher temperature and pressure ratings compared to standard PTFE.
The decision between RPTFE and PTFE is a strategic trade-off. You are choosing between the superior mechanical performance and durability of RPTFE versus the unmatched chemical purity and lower friction of standard, virgin PTFE.

The Foundation: Understanding Standard PTFE
Standard PTFE, often known by the brand name Teflon, has long been a benchmark material for valve seats due to its unique combination of properties. It excels in applications where chemical compatibility and low friction are paramount.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. Its inertness makes it the ideal choice for service with highly corrosive or aggressive chemicals where material purity is critical to prevent contamination or degradation.
Lowest Coefficient of Friction
Of any solid material, PTFE exhibits an extremely low coefficient of friction. This results in lower torque requirements to operate the valve, prevents stick-slip behavior, and ensures smooth, consistent actuation over the valve's life.
Superior Sealing Performance
The inherent ductility of standard PTFE allows it to conform well to the valve ball or disc, creating a tight, reliable seal even under lower pressures. It has good stress recovery, enabling it to maintain its shape and sealing capability after repeated cycling.
The Enhancement: Introducing RPTFE
RPTFE was developed to overcome the mechanical limitations of standard PTFE. By embedding glass fibers into the PTFE matrix, the material gains rigidity and durability for more demanding applications.
Higher Temperature and Pressure Ratings
The glass reinforcement is the key to RPTFE's improved performance. It typically increases the maximum service temperature from around 400°F (204°C) for PTFE to 450°F (232°C) for RPTFE. More importantly, it can double the pressure rating from 1000 psi to 2000 psi in many valve designs.
Increased Durability and Abrasion Resistance
The embedded fibers provide significant mechanical strength. This makes RPTFE seats more resistant to deformation under load and far more resistant to wear and abrasion from slurries or particulate matter in the process media, resulting in a longer design life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing RPTFE for its enhanced strength is not without compromises. The addition of glass fibers introduces new limitations that must be considered for your specific application.
Friction and Torque
The glass fibers, while adding strength, slightly increase the material's coefficient of friction. This can lead to higher torque demands for valve actuation, which may influence the sizing of your pneumatic or electric actuator.
The Chemical Achilles' Heel
This is the most critical trade-off. While PTFE is nearly universally chemically compatible, the glass fibers in RPTFE are not. RPTFE is vulnerable to chemicals that attack glass, such as hydrofluoric acid and strong caustic solutions. In these specific services, standard PTFE is the only viable choice.
When Neither Is Enough
It's important to recognize the limits of both materials. For service temperatures exceeding approximately 450°F (232°C), neither PTFE nor RPTFE is suitable. In these cases, you must move to higher-performance polymers like PEEK or, more commonly, to metal-seated valve designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seat material is essential for valve performance and longevity. Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility: Choose standard PTFE for its unmatched inertness, especially when dealing with media that attacks glass.
- If your primary focus is high pressure or temperature service: Select RPTFE for its significantly higher operational ratings and superior mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is longevity with an abrasive media: RPTFE is the superior choice due to its enhanced abrasion resistance from the glass reinforcement.
By understanding this fundamental trade-off between enhanced performance and chemical purity, you can confidently specify the right material for your system's demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | RPTFE (Reinforced) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Virgin polymer | PTFE + 15-25% glass fibers |
| Max Temperature | ~400°F (204°C) | ~450°F (232°C) |
| Pressure Rating | ~1000 psi | ~2000 psi |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, broad compatibility | Excellent, but vulnerable to HF acid/strong caustics |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Friction | Lowest | Slightly higher |
Need help selecting the right PTFE valve seat material for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and RPTFE components, including custom valve seats, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get a solution that balances chemical compatibility, pressure ratings, and durability for optimal valve performance and longevity.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your custom PTFE needs, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















