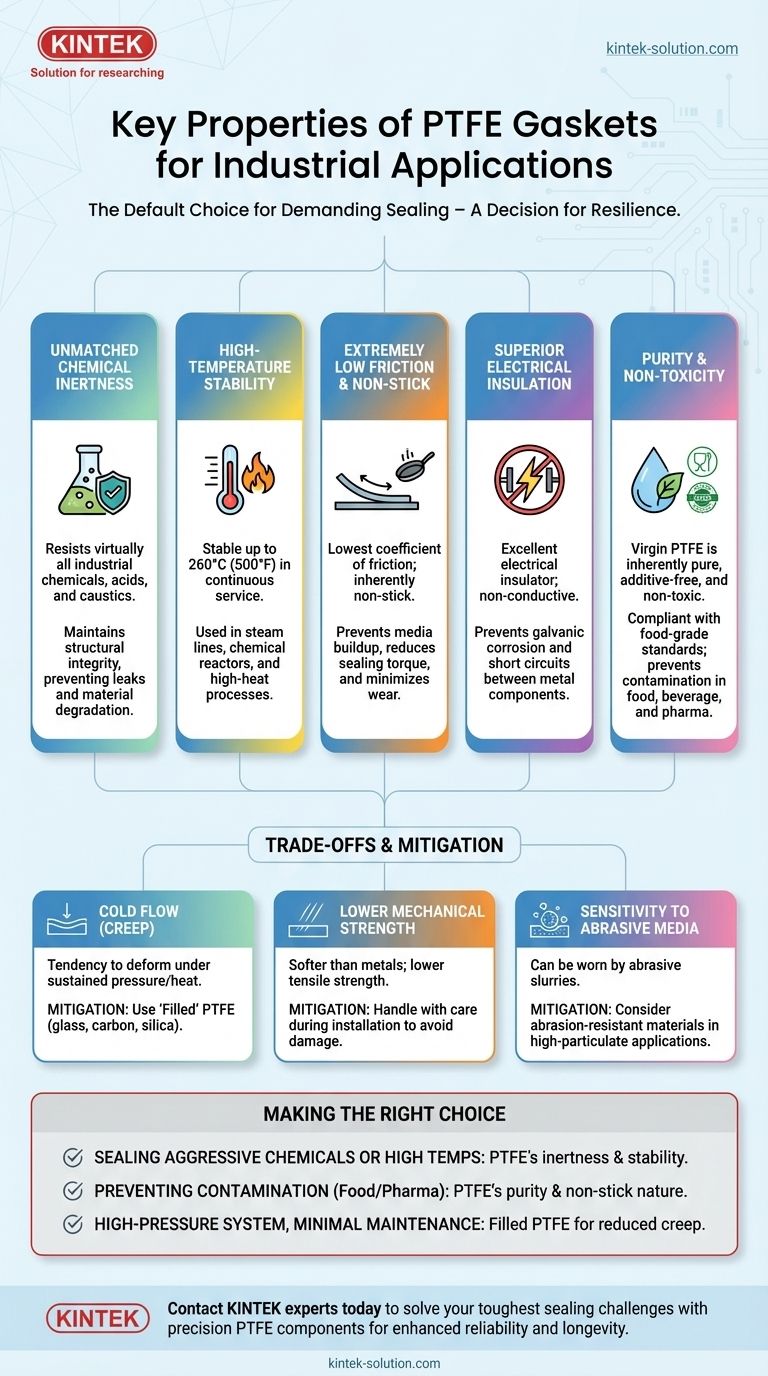
At its core, the suitability of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets for industrial use stems from a unique combination of properties that other materials cannot match. PTFE excels due to its extreme chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, low-friction surface, and inherent purity, making it a default choice for the most demanding sealing applications.
The decision to use a PTFE gasket is a decision for resilience. While other materials may excel in one area, PTFE provides a balanced portfolio of high-performance traits, ensuring operational reliability where chemical corrosion, high heat, and product purity are non-negotiable.

The Core Properties of PTFE Gaskets Explained
To understand why PTFE is so prevalent, we must look at each of its defining characteristics and the specific problems they solve in an industrial setting.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, acids, and caustics. This property is its most significant advantage.
Where other elastomers or even metals would corrode and fail, a PTFE gasket maintains its structural integrity, preventing dangerous leaks and costly material degradation.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE gaskets remain stable and functional in continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
This allows them to be used in high-temperature processes like steam lines, chemical reactors, and processing equipment where typical rubber or plastic seals would melt or become brittle.
Extremely Low Friction and Non-Stick Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. Its surface is also inherently non-stick.
This prevents media from sticking to the gasket surface, which is critical in food, pharmaceutical, and paint applications. It also reduces torque needed to seal flanges and minimizes wear in dynamic applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity.
This property makes it essential for applications where a gasket must also serve as an electrical isolator between two metal components, preventing galvanic corrosion or short circuits.
Purity and Non-Toxicity
Virgin PTFE is inherently pure, contains no additives, and is non-toxic, making it compliant with food-grade standards.
This is a mandatory requirement for equipment in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and bioprocessing industries, where preventing product contamination is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the trade-offs of PTFE is critical for correct application and avoiding gasket failure.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
The most significant limitation of pure PTFE is its tendency to exhibit creep, or "cold flow." Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform and move out of place.
This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and, eventually, a failed seal. This is often mitigated by using "filled" PTFE, which incorporates materials like glass, carbon, or silica to enhance rigidity and creep resistance.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has lower tensile strength and is more susceptible to physical damage.
Care must be taken during installation to avoid scratching or gouging the gasket surface, which could create a leak path.
Sensitivity to Abrasive Media
While its non-stick surface resists buildup, it can be worn away by highly abrasive slurries or crystalline media.
In applications with significant particulate matter, the gasket's service life may be reduced, or a more abrasion-resistant material might be necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right gasket material requires matching its properties to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals or high temperatures: PTFE's unmatched chemical inertness and thermal stability make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination in food or pharmaceutical lines: PTFE's inherent purity, non-toxic nature, and non-stick surface ensure compliance and product integrity.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure system with minimal maintenance: Consider a filled PTFE gasket to gain the benefits of PTFE while mitigating its tendency to creep under load.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is an investment in long-term reliability for your most critical and challenging environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Industrial Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all industrial chemicals, acids, and caustics. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Stable in continuous service up to 260°C (500°F). |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Prevents media buildup, reduces sealing torque. |
| Purity & Non-Toxicity | Ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and bioprocessing industries. |
| Electrical Insulation | Prevents galvanic corrosion and short circuits. |
Ready to solve your toughest sealing challenges with precision PTFE components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE gaskets, seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the perfect balance of PTFE's superior properties—like chemical resistance and thermal stability—tailored to your specific operational needs, from custom prototypes to high-volume production runs.
Contact our experts today for a consultation and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance the reliability and longevity of your equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















