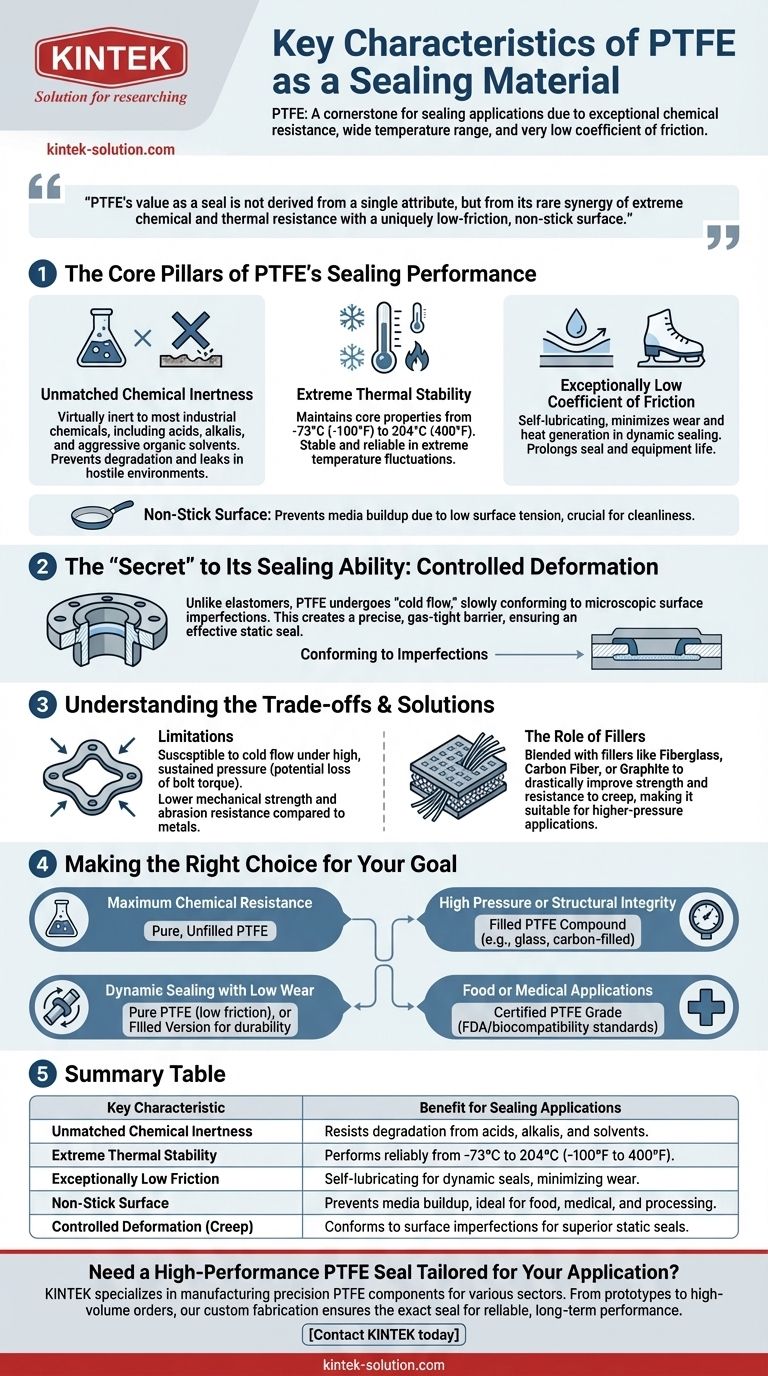
In the world of high-performance materials, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a cornerstone for sealing applications due to a unique combination of properties. Its defining characteristics are exceptional chemical resistance, an extremely wide operating temperature range, and a very low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most versatile sealing materials available.
PTFE's value as a seal is not derived from a single attribute, but from its rare synergy of extreme chemical and thermal resistance with a uniquely low-friction, non-stick surface. This combination makes it a default choice for the most demanding industrial applications.
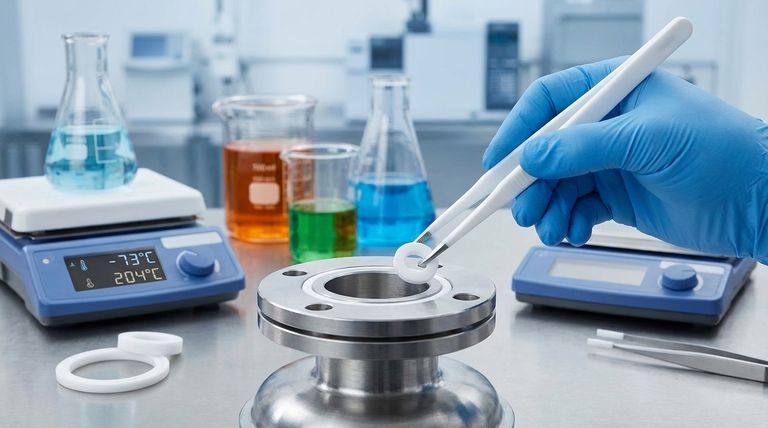

The Core Pillars of PTFE's Sealing Performance
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at how its primary characteristics contribute directly to creating and maintaining a reliable seal under challenging conditions.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, alkalis, and aggressive organic solvents. This means the seal will not degrade, swell, or weaken when exposed to corrosive fluids. This property is fundamental to ensuring long-term seal integrity and preventing leaks in chemically hostile environments.
Extreme Thermal Stability
The material maintains its core properties across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, typically from cryogenic levels around -73°C (-100°F) up to 204°C (400°F). Unlike many polymers that become brittle when cold or soften when hot, PTFE remains stable and reliable, making it suitable for processes involving extreme temperature fluctuations.
An Exceptionally Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on ice. This self-lubricating property is critical in dynamic sealing applications where parts move against each other. It minimizes wear and heat generation, prolonging the life of both the seal and the equipment.
Non-Stick Surface
Related to its low friction is PTFE's non-stick nature, a result of its low surface tension. This prevents media from sticking to the seal, which is crucial in food, medical, and processing industries where cleanliness and prevention of material buildup are paramount.
The "Secret" to Its Sealing Ability: Controlled Deformation
While its resistance properties are well-known, a less obvious characteristic is what truly makes PTFE an excellent static seal: its tendency to creep or "cold flow."
Conforming to Imperfections
When compressed between two mating surfaces (like flanges), PTFE lacks the "memory" of elastomeric materials like rubber. Instead of bouncing back to its original shape, it slowly flows into the microscopic imperfections of the surfaces. This action creates an exact mirror image of the hardware, resulting in a highly effective, gas-tight seal.
A Feature, Not a Flaw
In many materials, creep is a weakness. For PTFE in a static seal, it is the key to its effectiveness. This controlled deformation ensures that even if the surfaces are not perfectly smooth, the PTFE gasket will conform to create a comprehensive barrier against leaks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and a trusted advisor must highlight the limitations. The very properties that make PTFE a great seal can also be its weaknesses if misapplied.
Susceptibility to Cold Flow
While controlled creep is beneficial for sealing, under very high, sustained pressure, pure PTFE can continue to deform and extrude out of the seal area. This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and eventual seal failure.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to many engineering plastics and metals, pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it unsuitable for high-load structural components.
The Role of Fillers
To overcome these mechanical limitations, PTFE is often blended with fillers like fiberglass, carbon fiber, or graphite. These fillers drastically improve the material's strength and resistance to creep, making it suitable for higher-pressure applications. However, adding fillers can sometimes slightly reduce the overall chemical resistance of the compound.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct form of PTFE depends entirely on the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical resistance: Pure, unfilled PTFE provides the most robust defense against aggressive media.
- If your primary focus is high pressure or structural integrity: Select a filled PTFE compound (e.g., glass or carbon-filled) to resist creep and deformation.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing with low wear: PTFE's inherent low friction is ideal, but consider a filled version for better durability in high-cycle equipment.
- If your primary focus is food or medical applications: Ensure the specific PTFE grade is certified to meet FDA or other relevant biocompatibility standards.
By understanding these core characteristics and their trade-offs, you can confidently select the right PTFE variant for reliable, long-term sealing performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Benefit for Sealing Applications |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Chemical Inertness | Resists degradation from acids, alkalis, and solvents. |
| Extreme Thermal Stability | Performs reliably from -73°C to 204°C (-100°F to 400°F). |
| Exceptionally Low Friction | Self-lubricating for dynamic seals, minimizing wear. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents media buildup, ideal for food, medical, and processing. |
| Controlled Deformation (Creep) | Conforms to surface imperfections for superior static seals. |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal Tailored for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the ultimate chemical resistance of pure PTFE or the enhanced strength of a filled compound, our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get the exact seal for reliable, long-term performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing requirements and let our expertise provide the solution you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















