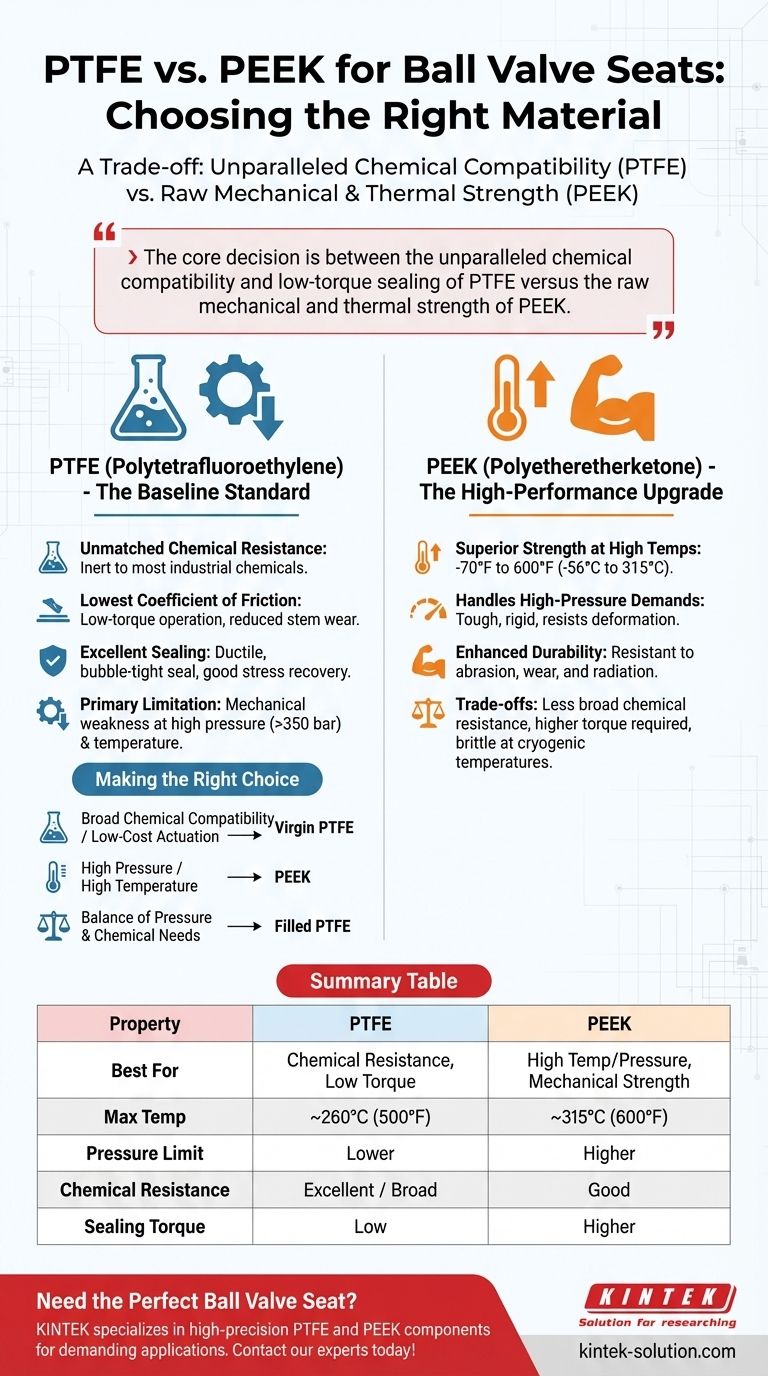
For ball valve seats, PTFE is the versatile default choice, prized for its exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, while PEEK is the high-performance specialist, selected for its superior mechanical strength in high-temperature and high-pressure applications where PTFE would mechanically fail. Both are excellent materials, but they solve fundamentally different operational challenges.
The core decision between PTFE and PEEK is a trade-off: you are choosing between the unparalleled chemical compatibility and low-torque sealing of PTFE versus the raw mechanical and thermal strength of PEEK.

The Baseline Standard: Understanding PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), often known by the brand name Teflon, serves as the foundation for a vast range of ball valve seat applications. Its unique properties make it an ideal starting point for system design.
### Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Low Friction
PTFE is virtually inert to most industrial chemicals, making it the safest choice for services with corrosive or varied media.
It also possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material. This results in low-torque valve operation, reducing the need for large actuators and minimizing stem wear over the valve's life.
### Excellent Sealing Capabilities
The material's natural ductility allows it to conform easily to the ball's surface, creating a reliable, bubble-tight seal with minimal force.
PTFE also exhibits good stress recovery and low thermal expansion, meaning it maintains its shape and sealing integrity across a range of temperatures.
### The Primary Limitation: Mechanical Weakness
The key drawback of virgin PTFE is its relative softness and lower strength, which limits its operational envelope.
For smaller bore valves, PTFE seats are often not recommended for pressures exceeding 350 bar (approx. 5,000 psi). This pressure limit drops significantly as valve sizes increase. Similarly, its strength degrades at elevated temperatures, making it unsuitable for high-heat services.
The High-Performance Upgrade: Understanding PEEK
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is an advanced polymer used when the mechanical or thermal demands of an application exceed the capabilities of PTFE.
### Superior Strength at High Temperatures
PEEK maintains its structural integrity and hardness across a very wide temperature range, typically cited from -70°F to 600°F (-56°C to 315°C).
This makes it the clear choice for applications involving steam, hot oil, or other high-temperature industrial processes where PTFE would soften and fail.
### Handling High-Pressure Demands
PEEK is a significantly tougher and more rigid material than PTFE. This inherent strength allows it to resist deformation and extrusion under extreme pressure, making it suitable for high-pressure gas and liquid systems.
### Enhanced Durability
Beyond temperature and pressure, PEEK offers greater resistance to abrasion and wear. It also has excellent resistance to radiation, a critical property in nuclear and specialized medical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is never about finding a "perfect" option, but rather the one with the right compromises for your specific environment.
### Chemical Compatibility
While PEEK has good chemical resistance, it is not as broad as PTFE's. It is notably susceptible to attack from concentrated sulfuric acid and other highly corrosive media where PTFE would remain unaffected.
### Sealing and Torque
PEEK's rigidity is a double-edged sword. While it provides strength, it also means higher torque is required to achieve a positive seal compared to the more pliable PTFE. This can necessitate larger, more expensive actuators.
### Low-Temperature Performance
Despite its wide operating range, PEEK can become brittle at the lower end of its temperature spectrum. This is a critical consideration for cryogenic or extreme cold-weather applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your operational parameters are the ultimate guide to material selection. Consider your primary system demands to make a definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility or low-cost actuation: Virgin PTFE is the definitive and most cost-effective choice for general-purpose applications.
- If your primary focus is high pressure or high temperature: PEEK is the necessary upgrade required for mechanical strength and operational safety in extreme conditions.
- If your primary focus is a balance of pressure and chemical needs: Filled PTFE, which incorporates materials like glass or carbon, can offer a middle ground with improved rigidity over virgin PTFE without the cost and torque implications of PEEK.
Ultimately, choosing the correct seat material is about precisely matching its engineering properties to the demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | PEEK |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Chemical Resistance, Low Torque | High Temp/Pressure, Mechanical Strength |
| Max Temp (Continuous) | ~260°C (500°F) | ~315°C (600°F) |
| Pressure Limit | Lower (e.g., <350 bar for small valves) | Higher |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent / Broad | Good (but not as broad as PTFE) |
| Sealing Torque | Low | Higher |
| Key Trade-off | Mechanical Weakness at High P/T | Higher Cost & Torque |
Need the Perfect Ball Valve Seat for Your Demanding Application?
Choosing between PTFE and PEEK is critical for your system's performance, safety, and cost. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE and PEEK components, including custom ball valve seats, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver the right material solution for your specific needs, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications



















