In electrical applications, PTFE sheets are primarily used for high-performance insulation in components like printed circuit boards (PCBs), coaxial cables, wire wraps, and high-voltage connectors. Its unique combination of electrical, thermal, and chemical resistance makes it indispensable for demanding electronic environments.
The core reason PTFE is a superior electrical insulator is its stable and exceptionally low dielectric constant and dissipation factor. This means it prevents electrical breakdown under high voltage and allows high-frequency signals to pass through with minimal energy loss or signal distortion.

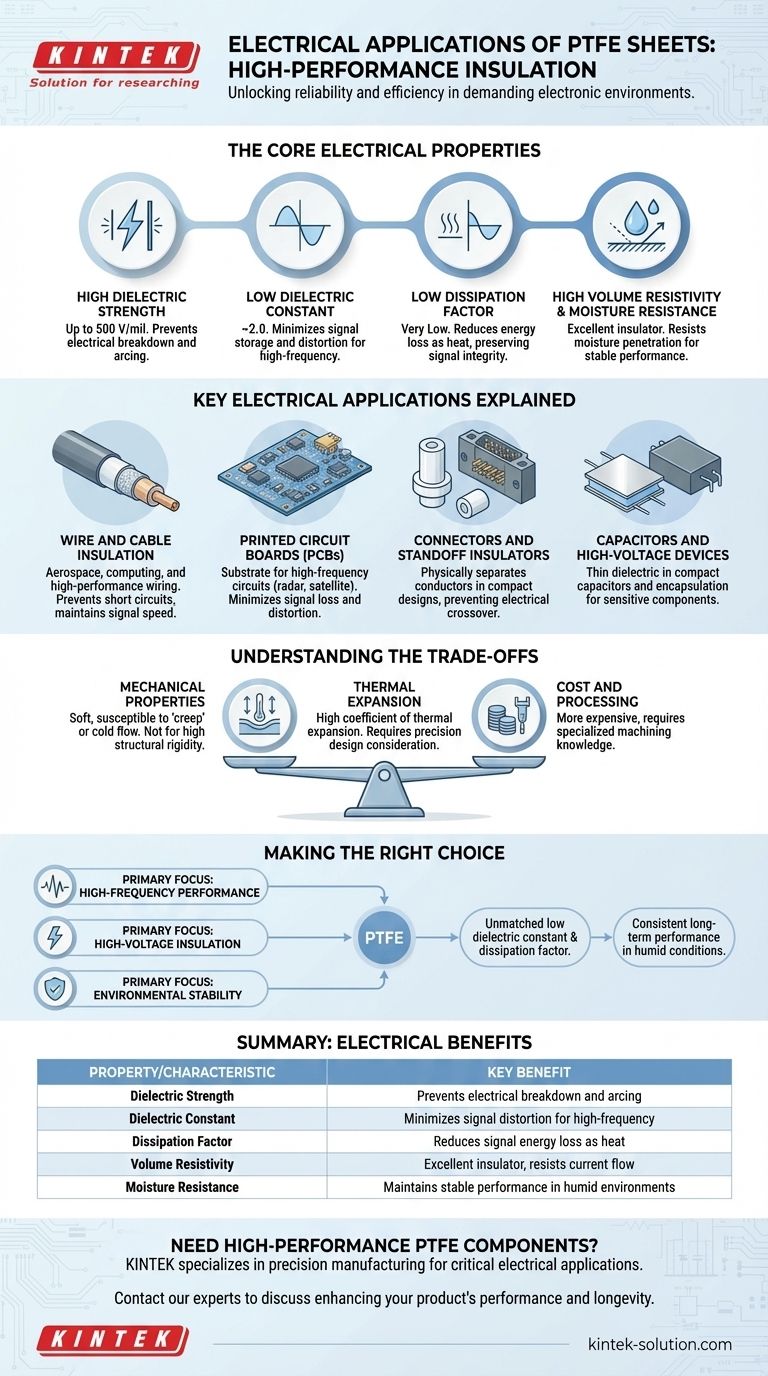
The Core Electrical Properties of PTFE
To understand why PTFE is chosen for specific applications, we must first examine its fundamental electrical characteristics. These properties work in concert to create one of the most effective insulating materials available.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down and conducting electricity.
PTFE exhibits a very high dielectric strength, capable of insulating up to 500 volts per mil in thin sections. This makes it an exceptional barrier for preventing electrical arcing between conductors.
Low Dielectric Constant
A material's dielectric constant indicates how much electrical energy it can store. For insulation in high-frequency circuits, a lower number is better.
PTFE's dielectric constant is extremely low (around 2.0) due to its symmetrical molecular structure. This ensures that signals pass through it cleanly without being stored or distorted, which is critical for high-speed data cables and PCBs.
Low Dissipation Factor
The dissipation factor measures how much energy is lost (as heat) when an AC signal passes through the material.
PTFE has a very low dissipation factor, meaning it is highly efficient. It wastes very little signal energy, preventing heat buildup and preserving signal integrity in components like high-frequency connectors and capacitors.
High Volume Resistivity & Moisture Resistance
Volume resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current.
PTFE is an excellent resistor, but more importantly, it resists moisture penetration far better than plastics like nylon or PVC. Because water degrades insulating properties, PTFE's moisture resistance ensures its high performance remains stable over time, even in humid environments.
Key Electrical Applications Explained
These fundamental properties translate directly into practical applications where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Wire and Cable Insulation
PTFE is used as a wrap or coating for high-performance wiring, especially in coaxial cables and hookup wires used in aerospace and computing. Its high dielectric strength prevents short circuits, while its low dielectric constant maintains signal speed and clarity.
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
For circuits operating at high frequencies (e.g., in radar and satellite communication), the substrate material is critical. PTFE is used as the base for PCBs to minimize signal loss and distortion, ensuring the circuit performs as designed.
Connectors and Standoff Insulators
Because it can be easily machined into precise shapes, PTFE is used to create insulating standoffs, bushings, and connector assemblies. These components physically separate conductive elements, relying on PTFE's high dielectric strength to prevent electrical crossover in compact designs.
Capacitors and High-Voltage Devices
In capacitors, thin sheets of PTFE are used to separate conductive surfaces. Its ability to insulate high voltages in a thin profile allows for the creation of compact, high-performance capacitors. It is also machined for encapsulation devices that protect sensitive high-voltage components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. While its electrical properties are elite, it's important to recognize PTFE's limitations to make an informed decision.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material. While durable, it is susceptible to "creep" or cold flow, where the material can deform over time under sustained pressure. It is not suitable for applications requiring high structural rigidity on its own.
Thermal Expansion
While PTFE operates over a very wide temperature range (-190°C to +260°C), it has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts more than metals or ceramics with temperature changes, which must be accounted for in precision designs.
Cost and Processing
PTFE is a high-performance polymer and is generally more expensive than common insulators like PVC or polyethylene. Machining and processing it also requires specialized knowledge to maintain tight tolerances without causing stress to the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine if PTFE is the optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance: PTFE is the superior choice for PCBs, antennae, and coaxial cables due to its unmatched low dielectric constant and dissipation factor.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: Its excellent dielectric strength makes it a reliable solution for wire wraps, standoff insulators, and critical connector assemblies.
- If your primary focus is environmental stability: PTFE's resistance to moisture and chemicals ensures consistent, long-term insulating performance where other materials would degrade and fail.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision to prioritize electrical performance and long-term reliability in demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Characteristic | Key Benefit for Electrical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | Up to 500 V/mil | Prevents electrical breakdown and arcing in high-voltage settings. |
| Dielectric Constant | ~2.0 | Minimizes signal distortion, ideal for high-frequency circuits. |
| Dissipation Factor | Very Low | Reduces signal energy loss as heat, preserving integrity. |
| Volume Resistivity | Very High | Excellent insulator that resists electrical current flow. |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Maintains stable performance in humid environments. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical electrical applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom sheets, seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure the superior dielectric properties and reliability your designs demand, from prototyping to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















