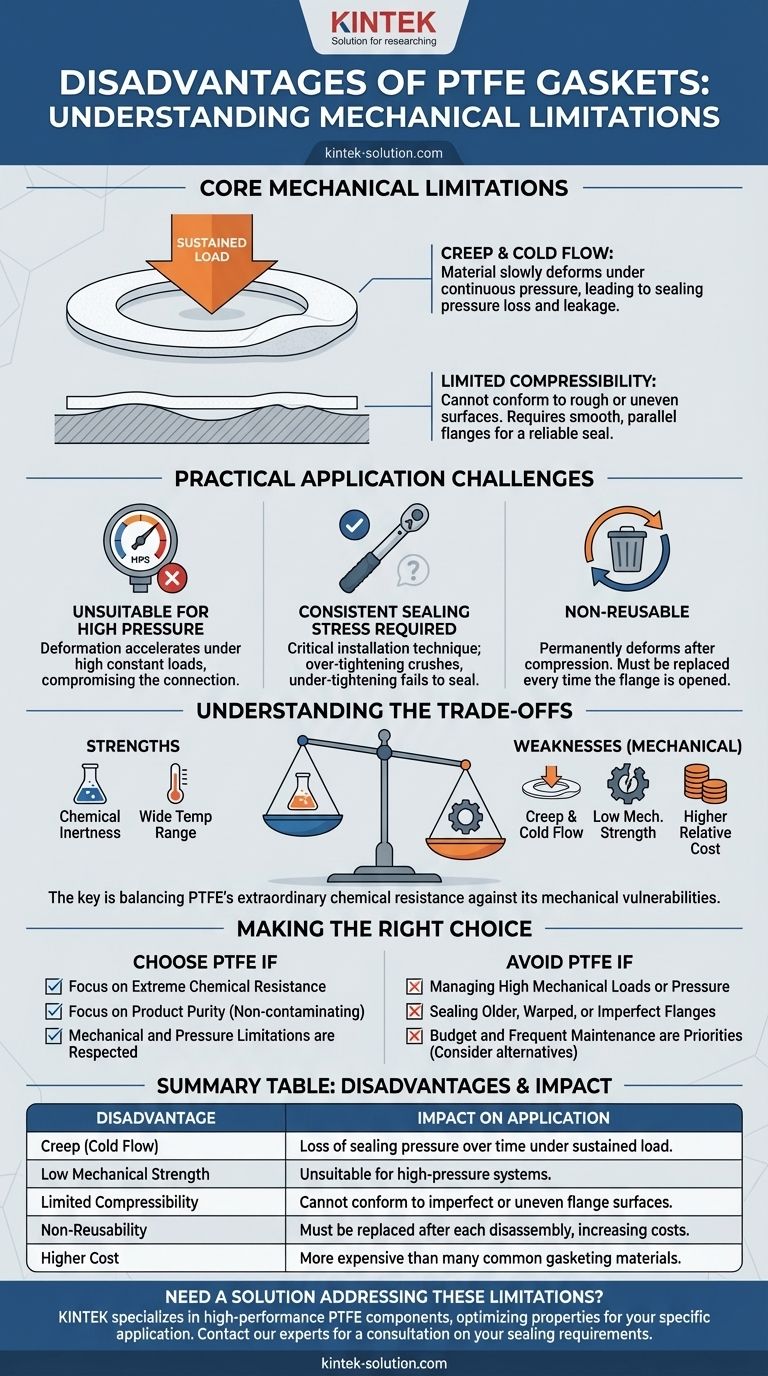
The primary disadvantages of PTFE gaskets stem from their mechanical properties. While renowned for chemical and thermal resistance, their key limitations are a tendency to deform under sustained load (creep), low mechanical strength, limited compressibility, and a higher relative cost. These factors make them unsuitable for high-pressure applications or for sealing imperfect or uneven flange surfaces.
While PTFE offers best-in-class chemical inertness and temperature range, its core weaknesses are entirely mechanical. The material's tendency to slowly deform under pressure—known as creep or cold flow—is the critical factor to consider in any engineering application.

The Core Mechanical Limitations
To understand when not to use a PTFE gasket, you must first understand its fundamental physical behaviors under stress. These are not flaws, but inherent properties of the material itself.
Creep: The Problem of Sustained Pressure
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress.
PTFE is particularly susceptible to creep. This means that even under a constant, acceptable load, the gasket will gradually deform over time, potentially leading to a loss of sealing pressure and eventual leakage.
Cold Flow: Deformation Without High Stress
Cold flow is a related phenomenon where the material deforms under relatively low stress, especially as temperatures increase.
This makes PTFE a poor choice for applications where bolt torque might relax over time due to thermal cycling, as the gasket material will flow away from the high-pressure points.
Limited Compressibility and Conformity
Unlike elastomeric (rubber) gaskets, PTFE is a relatively rigid material with very limited compressibility.
This means it cannot easily conform to surface imperfections like scratches, pits, or waviness in a flange face. It requires a smooth, flat, and parallel surface to achieve a reliable seal.
Practical Application and Installation Challenges
These core mechanical properties translate directly into specific challenges during installation and operation.
Unsuitability for High-Pressure Systems
The combination of creep and cold flow makes standard PTFE gaskets a risk in very high-pressure applications. The high, constant load required for the seal will accelerate material deformation, compromising the connection.
Requirement for Consistent Sealing Stress
Because PTFE doesn't compress and conform like rubber, achieving a proper seal depends entirely on maintaining a consistent and correct amount of pressure across the entire gasket surface.
Over-tightening can crush the material, while under-tightening will fail to create a seal, making proper installation technique critical.
Non-Reusability
Once a PTFE gasket is compressed, it deforms permanently. It takes a "set" and will not spring back to its original shape.
This means PTFE gaskets are strictly for single use. If a flange is opened for maintenance, the gasket must be replaced every time, adding to operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of PTFE do not exist in a vacuum. They are the direct trade-off for its extraordinary strengths, and understanding this balance is key to proper material selection.
Cost vs. Chemical Inertness
PTFE is more expensive than many common gasketing materials. However, it is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals across the entire 0-14 pH range. In an aggressive chemical environment, the higher initial cost prevents costly failures from chemical attack.
Mechanical Weakness vs. Purity and Low Friction
The same polymer structure that makes PTFE susceptible to creep also gives it an extremely low coefficient of friction and non-stick properties. This makes it non-contaminating and ideal for food, pharmaceutical, or high-purity applications where other materials might leach or shed particles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if a standard PTFE gasket's disadvantages outweigh its benefits for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance or product purity: PTFE is likely the correct choice, provided the mechanical and pressure limitations are respected.
- If your primary focus is managing high mechanical loads or high pressure: Avoid standard PTFE and consider a filled-PTFE variant or a completely different material like spiral-wound gaskets.
- If your primary focus is sealing older, warped, or imperfect flanges: Do not use virgin PTFE; its rigidity will prevent a proper seal. Consider expanded PTFE (ePTFE) or an elastomer instead.
- If your primary focus is budget and frequent maintenance cycles: The higher cost and non-reusability of PTFE make it a less economical choice compared to other single-use gaskets.
Ultimately, understanding these mechanical trade-offs is the key to leveraging PTFE's unparalleled chemical resilience effectively.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Application |
|---|---|
| Creep (Cold Flow) | Loss of sealing pressure over time under sustained load |
| Low Mechanical Strength | Unsuitable for high-pressure systems |
| Limited Compressibility | Cannot conform to imperfect or uneven flange surfaces |
| Non-Reusability | Must be replaced after each disassembly, increasing costs |
| Higher Cost | More expensive than many common gasketing materials |
Need a PTFE gasket solution that addresses these limitations?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication allows us to optimize PTFE properties for your specific application, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders.
We understand the mechanical trade-offs of PTFE and can help you select or engineer the right solution to balance chemical resistance with mechanical performance.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your sealing requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















