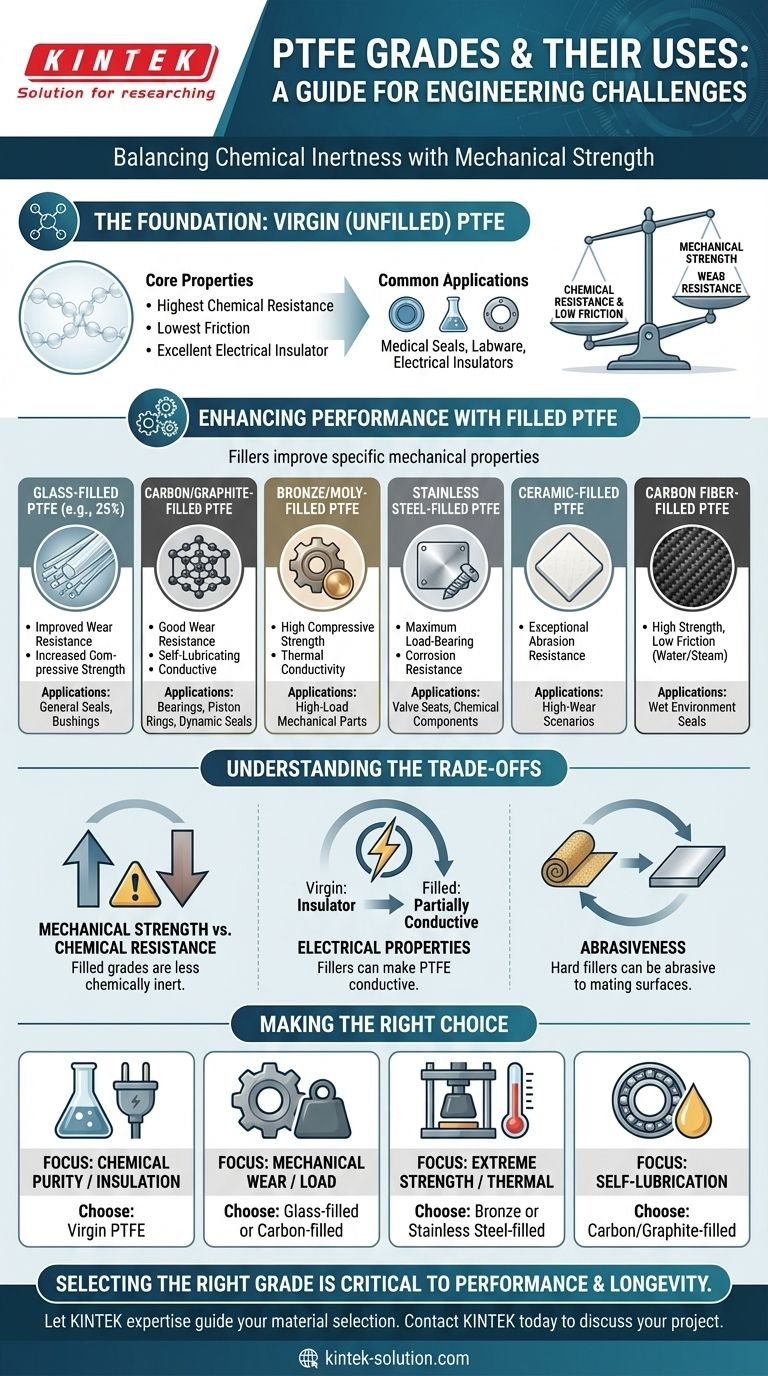
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not a single material, but a base polymer that is frequently modified to create distinct grades for specific engineering challenges. While pure, or "virgin," PTFE is known for its extreme chemical resistance and low friction, its mechanical properties are often enhanced by adding fillers such as glass, carbon, or stainless steel to improve everything from wear resistance to load-bearing strength.
The core principle to understand is that selecting a PTFE grade is an exercise in trade-offs. You are often balancing the exceptional chemical inertness and low friction of virgin PTFE against the superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity offered by filled grades.

The Foundation: Virgin (Unfilled) PTFE
Virgin PTFE is the pure, unfilled form of the polymer. It sets the baseline for the material's most well-known characteristics.
Core Properties
This grade offers the highest physical and electrical insulation properties. It is also the most chemically resistant and possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any PTFE grade.
Common Applications
Its purity and inertness make it ideal for seals, gaskets, and bushings in the medical, food and beverage, and chemical processing industries. It's also used for laboratory containers and electrical insulators where preventing contamination or electrical current is paramount.
Enhancing Performance with Filled PTFE Grades
Fillers are added to the PTFE base to improve specific mechanical properties that are weak points for the virgin material, such as deformation under load (creep) and wear resistance.
Glass-Filled PTFE
A common formulation is 25% fiberglass-filled PTFE. The addition of glass fibers significantly increases compressive strength and wear resistance compared to the virgin grade. This makes it a workhorse material for many common seals and bushings.
Carbon and Graphite-Filled PTFE
Adding carbon or a blend of carbon and graphite enhances compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance. These grades also have good chemical resistance and are known for their self-lubricating properties, making them excellent for bearings, piston rings, and dynamic seals.
Bronze and Molybdenum-Filled PTFE
Fillers like bronze and molybdenum disulfide (moly) dramatically increase compressive strength and thermal conductivity. This allows heat to dissipate from the running surface, making these grades ideal for high-load mechanical applications where strength and durability are critical.
Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE
For extreme environments, grades like 50% stainless steel-filled PTFE offer maximum load-bearing capability and high strength. This grade is often specified for applications demanding both structural integrity and corrosion resistance, such as valve seats and chemical service components.
Ceramic-Filled PTFE
Ceramic fillers provide exceptional wear and abrasion resistance, often surpassing other filled grades in high-friction scenarios. This makes them suitable for components that face aggressive wear conditions.
Carbon Fiber-Filled PTFE
The addition of carbon fiber, such as in a 35% carbon fiber-filled grade, creates a material with high compressive strength, low friction, and excellent wear performance, especially in water and steam applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers to PTFE is not a universal upgrade. Enhancing one property often comes at the expense of another, and understanding these compromises is crucial for proper material selection.
The Cost of Mechanical Strength
The primary trade-off is a reduction in chemical resistance. While still very good, filled grades are generally less chemically inert than virgin PTFE because the filler material itself can be attacked by certain chemicals.
Impact on Electrical Properties
Fillers like carbon, graphite, and metals are conductive. Their inclusion turns PTFE from an excellent electrical insulator into a material that is partially conductive, making it completely unsuitable for applications requiring high dielectric strength.
Considerations for Abrasiveness
Hard fillers like glass and ceramic can be abrasive to the mating surface, especially softer metals like aluminum or brass. For these situations, a non-abrasive filler like graphite may be a more appropriate choice to preserve the life of the entire assembly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct PTFE grade requires you to clearly define your most critical performance requirement.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the only suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is general mechanical wear and load-bearing: Glass-filled or carbon-filled grades offer a balanced and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is extreme compressive strength and thermal management: Bronze or stainless steel-filled grades are designed for high-load, high-temperature service.
- If your primary focus is self-lubrication in dynamic seals or bearings: Carbon/graphite-filled grades provide excellent performance with minimal friction.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can select a PTFE grade that delivers the precise performance characteristics your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Grade | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Highest chemical resistance, low friction, excellent insulator | Medical seals, labware, food processing, electrical insulators |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | Improved wear resistance, compressive strength | General-purpose seals, bushings |
| Carbon/Graphite-Filled PTFE | Good wear resistance, self-lubricating | Bearings, piston rings, dynamic seals |
| Bronze/Moly-Filled PTFE | High compressive strength, thermal conductivity | High-load mechanical parts |
| Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE | Maximum load-bearing, corrosion resistance | Valve seats, chemical service components |
| Ceramic-Filled PTFE | Exceptional abrasion resistance | High-wear applications |
| Carbon Fiber-Filled PTFE | High strength, low friction in steam/water | Seals and components for wet environments |
Selecting the right PTFE grade is critical to your component's performance and longevity.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production, ensuring your parts are made from the optimal material for your specific application's chemical, mechanical, and thermal challenges.
Let our expertise guide your material selection. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















