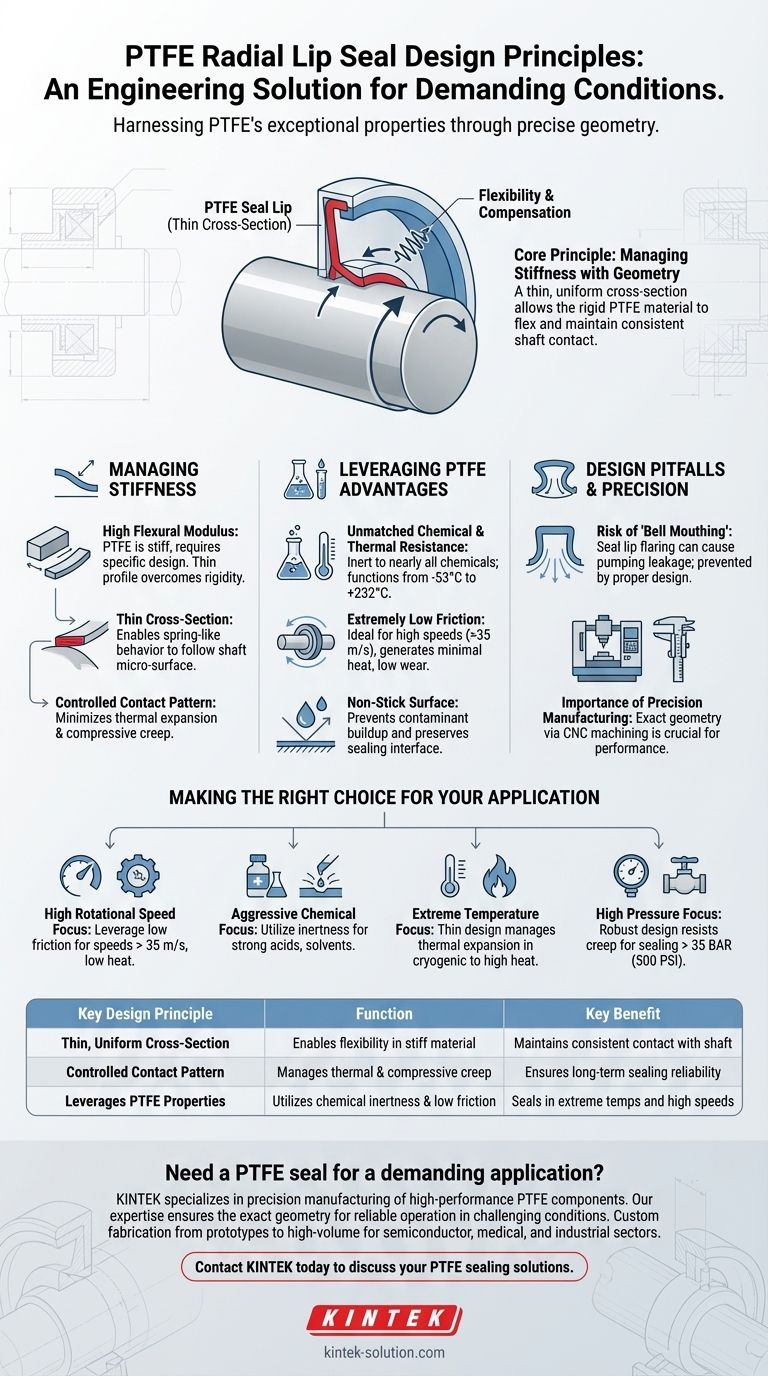
At its core, the design of a PTFE radial lip seal is a deliberate engineering solution to harness the exceptional properties of a stiff material. Unlike flexible elastomers, PTFE's rigidity requires a specific geometry—primarily a uniformly thin cross-section—to allow the seal lip to flex, maintain contact with the shaft, and provide a reliable seal under demanding conditions.
The central challenge in PTFE seal design is managing the material's high stiffness (flexural modulus). The solution is a precisely engineered, thin lip geometry that enables flexibility, compensates for shaft imperfections, and leverages PTFE's unmatched thermal, chemical, and low-friction advantages.

The Core Principle: Managing Stiffness with Geometry
The entire design philosophy revolves around making a naturally rigid material behave like an effective, dynamic seal. This is achieved primarily through the shape of the sealing element.
Compensating for High Flexural Modulus
PTFE is not a rubber; it is a relatively stiff plastic. This property, known as a high flexural modulus, means it does not deflect or bend easily.
A thick, bulky PTFE seal would be too rigid to conform to a rotating shaft, especially one with any run-out (wobble) or surface imperfections.
The Thin, Uniform Cross-Section
To overcome this stiffness, engineers design the sealing element with a uniformly thin cross-section. This geometric feature is the most critical design principle.
This thin profile allows the otherwise rigid material to act as a flexible spring, enabling it to follow the shaft's micro-surface and maintain a consistent sealing line.
Maintaining a Controlled Contact Pattern
The ultimate goal of this design is to create a stable and controlled contact pattern on the shaft.
The thin section minimizes the negative effects of thermal expansion and compressive creep (the tendency of a material to deform permanently under load), ensuring the seal's contact force remains consistent throughout its service life.
Leveraging PTFE's Inherent Material Advantages
The reason engineers go to such lengths to design around PTFE's stiffness is to capitalize on its unparalleled performance characteristics in harsh environments.
Unmatched Chemical and Thermal Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, including oils, acids, and solvents.
It also operates effectively across an extremely wide temperature range, from cryogenic conditions (-53°C or lower) up to 232°C (450°F) or more, where traditional elastomers would fail catastrophically.
Extremely Low Friction
The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. This property is critical for high-speed applications (over 35 m/s), as it generates minimal heat and reduces wear on both the seal and the shaft.
This also allows PTFE seals to function in dry-running or abrasive media conditions that would destroy other seal types.
Non-Stick Surface Properties
PTFE's non-stick nature prevents contaminants, sludge, or other media from building up on the seal lip, which could otherwise compromise the sealing interface.
Understanding the Design Pitfalls
While highly effective, the unique design of PTFE seals introduces specific failure modes that must be understood and mitigated through careful engineering and application.
The Risk of "Bell Mouthing"
A primary concern, especially in spring-activated designs with a wide contact area, is a failure mode called bell mouthing.
This occurs when the seal lip flares away from the shaft, creating a wedge that can actively pump the sealed fluid out, resulting in a high leakage rate. Proper design prevents this by carefully controlling the contact pressures and lip geometry.
Importance of Precision Manufacturing
The performance of a PTFE seal is highly dependent on precision. The process involves molding or extruding high-quality PTFE resins, heat treating the material to enhance its properties, and then CNC machining the final profile to exact dimensions.
Any deviation from the intended geometry can compromise the seal's ability to maintain a controlled contact pattern, leading to premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE seal design requires matching its inherent properties to the specific demands of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is high rotational speed: The low-friction characteristic of the PTFE material is the key advantage, preventing heat buildup and enabling speeds over 35 m/s.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical exposure: PTFE's chemical inertness makes it the only viable choice for sealing strong acids, solvents, or other corrosive media.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature range: The thin design's ability to manage thermal expansion ensures a consistent seal in environments where other materials would become brittle or degrade.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing: The robust, creep-resistant nature of the PTFE design provides a tight, reliable seal in systems operating above 35 BAR (500 PSI).
Understanding that PTFE seal design is a balance of material science and mechanical geometry empowers you to select a highly reliable solution for your most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Design Principle | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thin, Uniform Cross-Section | Enables flexibility in a stiff material | Maintains consistent contact with the shaft |
| Controlled Contact Pattern | Manages thermal expansion and compressive creep | Ensures long-term sealing reliability |
| Leverages PTFE Properties | Utilizes chemical inertness and low friction | Seals in extreme temperatures and high speeds |
Need a PTFE seal for a demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including custom radial lip seals. Our expertise in CNC machining ensures the exact geometry required for reliable operation in the most challenging conditions—from high-speed rotation and extreme temperatures to aggressive chemical exposure.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE sealing solutions can enhance your equipment's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















